|
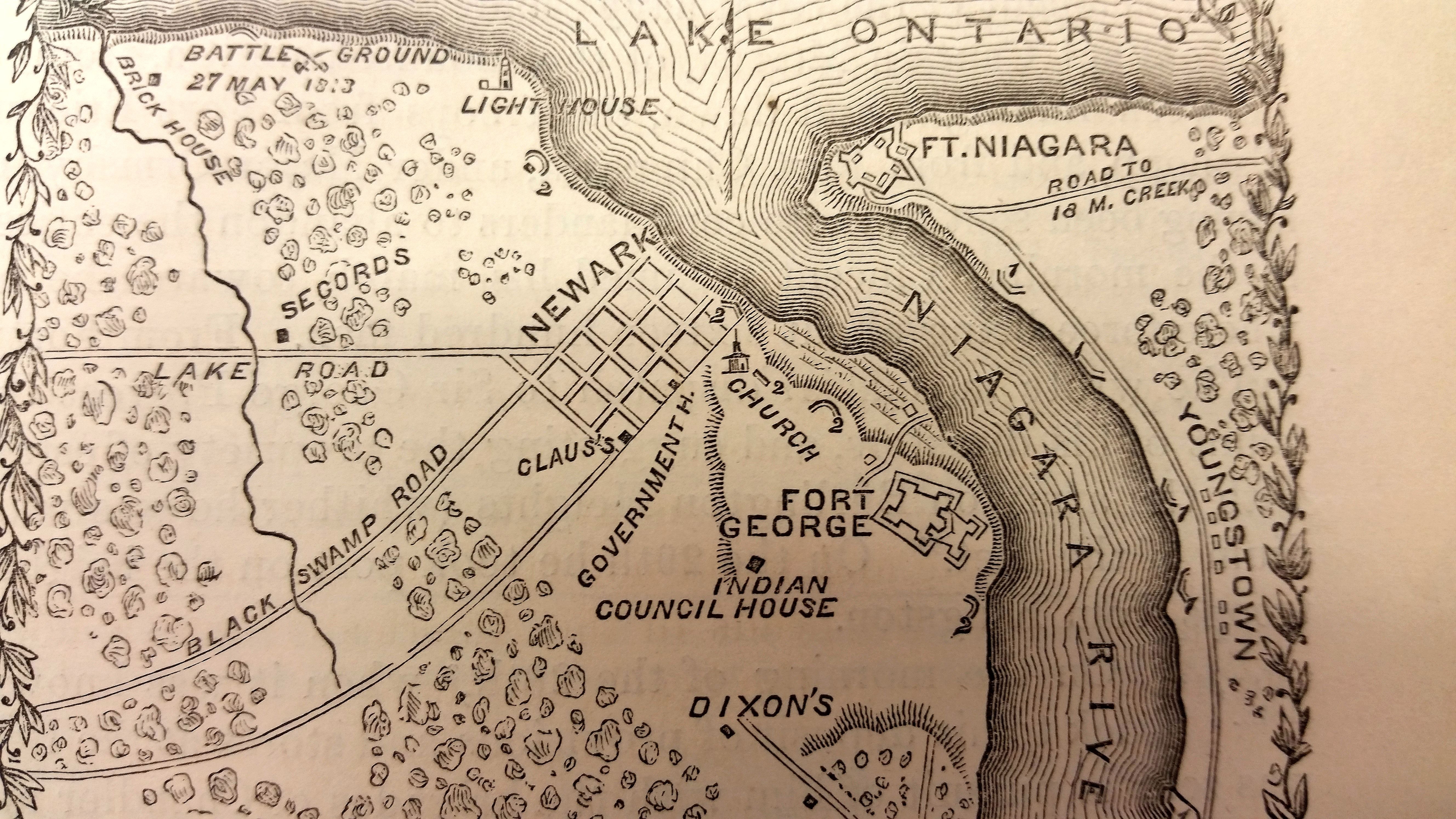
Queenston Bridge
Queenston is a compact rural community and unincorporated place north of Niagara Falls in the Town of Niagara-on-the-Lake, Ontario, Canada. It is bordered by Highway 405 to the south and the Niagara River to the east; its location at the eponymous Queenston Heights (heights) on the Niagara Escarpment led to the establishment of the Queenston Quarry in the area. Across the river and the Canada–US border is the village of Lewiston, New York. The Lewiston-Queenston Bridge links the two communities. This village is at the point where the Niagara River began eroding the Niagara Escarpment. During the ensuing 12,000 years the Falls cut an long gorge in the Escarpment southward to its present-day position. In the early 19th century, the community's name was spelled as Queenstown. Queenston marks the southern terminus of the Bruce Trail. The cairn marking the trail's terminus is in a parking lot, about 160 metres (520 ft) from General Brock's Monument on the easterly side of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, second-largest country by total area, with the List of countries by length of coastline, world's longest coastline. Its Canada–United States border, border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both Temperature in Canada, meteorologic and Geography of Canada, geological regions. With Population of Canada, a population of over 41million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in List of the largest population centres in Canada, urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewiston (village), New York
Lewiston is a village in Niagara County, New York, United States. The population was 2,701 at the 2010 census. The village is named after Morgan Lewis, an early 19th-century governor of New York. It is part of the Buffalo–Niagara Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area. The Village of Lewiston, NY (also known as Yehęwakwáʼthaʼ in Tuscarora) is within the Town of Lewiston. The Earl W. Brydges Artpark State Park lies at its southern border. Lewiston was selected by Rand McNally as one of the "Top Ten Best Small Towns in America" in November 2012. Lewiston is situated on the Niagara River, just across the river from Canada. The Niagara River intersects the Niagara Escarpment between Lewiston and Queenston, Ontario, identifying the escarpment's Lewiston-Queenston section as the geologic origin of Niagara Falls. Over a roughly 12,500 year span, the falls have eroded nearly seven miles south from Lewiston to their present location in Niagara Falls, creating the seven-mile long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohawk Nation
The Mohawk, also known by their own name, (), are an Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous people of North America and the easternmost nation of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy (also known as the Five Nations or later the Six Nations). Mohawk are an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian-speaking people with communities in southeastern Canada and northern New York (state), New York State, primarily around Lake Ontario and the St. Lawrence River. As one of the five original members of the Iroquois Confederacy, the Mohawk are known as the Keepers of the Eastern Door who are the guardians of the confederation against invasions from the east. Today, Mohawk people belong to the Mohawk Council of Akwesasne, Mohawks of the Bay of Quinte First Nation, Mohawks of Kahnawà:ke, Mohawks of Kanesatake, Six Nations of the Grand River, and Saint Regis Mohawk Tribe, a federally recognized tribe in the United States. At the time of European contact, Mohawk people were based in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort George, Ontario
Fort George was a military fortification in Niagara-on-the-Lake, Ontario, Canada. The fort was used by the British Army, the Canadian militia, and the Jeffersonian democracy, Jeffersonian American Republic United States Army, Army for a brief period. The fort was mostly destroyed during the War of 1812. The site of the fort has been a National Historic Sites of Canada, National Historic Site of Canada since 1921, and features a reconstruction of Fort George. The British established Fort George in the 1790s to replace Fort Niagara. Many of its structures were demolished in May 1813, during the Battle of Fort George. After the battle, American forces occupied the fort for seven months before withdrawing in December 1813. Although the British regained the fort shortly afterwards, little effort was put into its reconstruction after they capture of Fort Niagara, captured Fort Niagara the following week. The poor wartime design of Fort George led to its replacement by Fort Mississauga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Brock
Major-General Sir Isaac Brock KB (6 October 1769 – 13 October 1812) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator from Guernsey. He is best remembered for his victory at the Siege of Detroit and his death at the Battle of Queenston Heights during the War of 1812. Brock joined the army as a ensign in 1785. By 1797, he was a lieutenant colonel with the 49th Regiment of Foot. The regiment participated in the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland in 1799 and in the 1801 naval expedition against Copenhagen. In 1802, the 49th Regiment was assigned to garrison duty in British North America. Despite facing desertions and near-mutinies, Brock successfully commanded his regiment in Upper Canada (part of present-day Ontario) for several years. He was promoted to colonel in 1805 and appointed brigadier general in 1808. In 1811 he was promoted to major general and given responsibility for defending Upper Canada against the threat of an American invasion. While many in Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Queenston Heights
The Battle of Queenston Heights was the first major engagement of the War of 1812. The battle took place on 13 October 1812 at Queenston in Upper Canada (now Ontario) and was a decisive British victory. United States regulars and New York (state), New York militia led by Major General Stephen Van Rensselaer crossed the Niagara River from Lewiston, New York, Lewiston and engaged British regulars and Canadian militia led by Major General Isaac Brock. Major General Roger Hale Sheaffe took command of British forces after Brock was killed. Mohawk people, Mohawk warriors led by John Norton (Mohawk chief), John Norton supported the British during the battle. The battle was an American attempt to establish a foothold on the Canadian side of the Niagara River before campaigning ended with the onset of winter. The British victory was mainly due to the poorly managed American offensive. Despite their numerical advantage and the widely dispersed British forces defending the Niagara frontier, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Lyon MacKenzie
William Lyon Mackenzie (March12, 1795 August28, 1861) was a Scottish-born Canadian-American journalist and politician. He founded newspapers critical of the Family Compact, a term used to identify the establishment of Upper Canada. He represented York County, Ontario, York County in the Legislative Assembly of Upper Canada and aligned with Reform movement (Upper Canada), Reformers. He led the rebels in the Upper Canada Rebellion; after its defeat, he unsuccessfully rallied American support for an invasion of Upper Canada as part of the Patriot War. Although popular for criticising government officials, he failed to implement most of his policy objectives. He is one of the most recognizable Reformers of the early 19th century. Raised in Dundee, Scotland, Mackenzie emigrated to York, Upper Canada, in 1820. He published his first newspaper, the ''Colonial Advocate'' in 1824, and was elected a York County representative to the Legislative Assembly in 1827. York became the city of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laura Secord
Laura Secord (; 13 September 1775 – 17 October 1868) was a Canadian woman involved in the War of 1812. She is known for having walked out of American-occupied territory in 1813 to warn British forces of an impending American attack. Her contribution to the war was little known during her lifetime, but since her death she has been frequently honoured in Canada. Though Laura Secord had no relation to it, most Canadians associate her with the Laura Secord Chocolates company, named after her on the centennial of her walk. Laura Secord's father, Thomas Ingersoll, lived in Massachusetts and fought on the side of the Patriots during the Revolutionary War (1775–1783). In 1795 he moved his family to the Niagara region of Upper Canada after he had applied for and received a land grant. Shortly after, Laura married Loyalist James Secord, who was later seriously wounded at the Battle of Queenston Heights early in the War of 1812. While he was still recovering in 1813, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the United Kingdom, declared war on Britain on 18 June 1812. Although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, the war did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by the 13th United States Congress, United States Congress on 17 February 1815. AngloAmerican tensions stemmed from long-standing differences over territorial expansion in North America and British support for Tecumseh's confederacy, which resisted U.S. colonial settlement in the Old Northwest. In 1807, these tensions escalated after the Royal Navy began enforcing Orders in Council (1807), tighter restrictions on American trade with First French Empire, France and Impressment, impressed sailors who were originally British subjects, even those who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Graves Simcoe
Lieutenant-General (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-General John Graves Simcoe (25 February 1752 – 26 October 1806) was a British army officer, politician and colonial administrator who served as the lieutenant governor of Upper Canada from 1791 until 1796. He founded York, Upper Canada, York, which is now known as Toronto, and was instrumental in introducing institutions such as courts of law, Jury trial, trial by jury, English law, English common law, Fee simple, freehold land tenure, and also in the abolition of Slavery in Canada, slavery in Upper Canada. His long-term goal was the development of Upper Canada (Ontario) as a model community built on aristocratic and conservative principles, designed to demonstrate the superiority of those principles to the republicanism of the United States. His energetic efforts were only partially successful in establishing a local gentry, a thriving Church of England, and an anti-American coalition with select indigenous nations. He is seen by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Against Slavery
The ''Act Against Slavery'' was an anti-slavery law passed on July 9, 1793, in the second legislative session of Upper Canada, the colonial division of British North America that would eventually become Ontario. It banned the importation of slaves and mandated that children born henceforth to female slaves would be freed upon reaching the age of 25. Synopsis John Graves Simcoe, Lieutenant Governor of the colony, had been a supporter of abolition before coming to Upper Canada; as a British Member of Parliament, he had described slavery as an offence against Christianity. By 1792 the slave population in Upper Canada was not large. However, when compared with the number of free settlers, the number was not insignificant. In York (the present-day city of Toronto) there were 15 African-Canadians living, while in Quebec some 1,000 slaves could be found. Furthermore, by the time the Act Against Slavery would be ratified, the number of slaves residing in Upper Canada had been signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloe Cooley
Chloe Cooley was a young black woman held as a slave in Fort Erie and Queenston, Upper Canada in the late 1700s, as the area was being settled by Loyalists from the United States. Her owner forced her into a boat to sell her in 1793 across the Niagara River in the United States. This incident was observed by several witnesses, who petitioned the Executive Council of Upper Canada. Although charges were dropped against Cooley's owner, the incident is believed to have led to passage of the Act Against Slavery, 1793, in Upper Canada. It prevented slaves from being imported into the province and provided for gradual abolition of slavery within a generation among those held there. History In 1793, Cooley was held by Loyalist Adam Vrooman, a white farmer and former sergeant with Butler's Rangers who fled to Canada from New York after the American Revolution. He had purchased her several months before from Benjamin Hardison, another Loyalist who lived nearby at what is now Fort Erie, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |