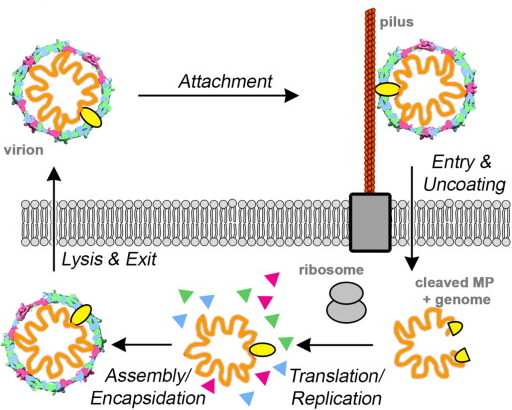
|
Qubevirus
''Qubevirus'' is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses, in the family '' Fiersviridae''. Enterobacteria serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. In 2020, the genus was renamed from ''Allolevivirus'' to its current name. Structure Viruses in ''Qubevirus'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and spherical geometries, and T=3 symmetry. The diameter is around 26 nm. Genome Qubeviruses have a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. The genome is linear and non-segmented and around 4kb in length. The genome codes for four proteins, which are the coat, replicase, maturation, and lysis protein. Life cycle Entry into the host cell is achieved by adsorption into the host cell. Replication follows the positive-strand RNA virus replication model. Positive-strand RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Translation Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage Qβ
Bacteriophage Qbeta (''Qubevirus durum''), commonly referred to as Qbeta or Qβ, is a species consisting of several strains of positive-strand RNA virus which infects bacteria that have F-pili, most commonly ''Escherichia coli''. Its linear genome is packaged into an icosahedral capsid with a diameter of 28 nm. Bacteriophage Qβ enters its host cell after binding to the side of the F-pilus. Genetics The genome of Qβ is approximately 4,217 nucleotides, depending on the source which sequenced the virus. Qβ has been isolated all over the world, multiple times, with various subspecies that code for nearly identical proteins but can have very different nucleotide sequences. The genome has three open reading frames that encode four proteins: the maturation/lysis protein A2; the coat protein; a readthrough of a leaky stop codon in the coat protein, called A1; and the β-subunit of an RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp) termed the replicase. The genome is highly structured, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiersviridae
''Fiersviridae'' is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect prokaryotes. Bacteria serve as the natural host. They are small viruses with linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes that encode four proteins. All phages of this family require bacterial pili to attach to and infect cells. The family has 308 genera, most discovered by metagenomics. In 2020, the family was renamed from ''Leviviridae'' to its current name. Structure Viruses in ''Fiersviridae'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and spherical geometries, and T=3 symmetry. Their virion diameter is around 26 nm. Genome Fiersviruses have a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. It is linear and non-segmented and around 4kb in length. The genome encodes four proteins, which are the coat, replicase, maturation, and lysis protein. Life cycle Entry into the host cell is achieved by adsorption into the host cell. Replication follows the positive-strand RNA virus replication model. Positive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus Genera
:''This is a list of genera of biological viruses. See also Comparison of computer viruses.'' This is an alphabetical list of genera of biological viruses. It includes all genus, genera and subgenera of viruses listed by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) 2022 release. *For a list of virus families and subfamilies, see List of virus families and subfamilies. *For a list of virus realms, subrealms, kingdoms, subkingdoms, phyla, subphyla, classes, subclasses, orders, and suborders, see List of higher virus taxa. A * ''Aalivirus'' * ''Aarhusvirus'' * ''Abaiavirus'' * ''Abakapovirus'' * ''Abbeymikolonvirus'' * ''Aberdnavirus'' * ''Abidjanvirus'' * ''Abouovirus'' * ''Acadevirus'' * ''Acadianvirus'' * ''Acajnonavirus'' * ''Acanvirus'' * ''Achlievirus'' * ''Acionnavirus'' * ''Acridvirus'' * ''Actinovirus'' * ''Adahivirus'' * ''Adahmuvirus'' * ''Adaiavirus'' * ''Aegirvirus'' * ''Aerosvirus'' * ''Affertcholeramvirus'' * ''Afonbuvirus'' * ''Agatevirus'' * ''Agey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Electron Micrograph
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and Focus (optics), focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a Detectors for transmission electron microscopy, detector such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device or a direct electron detector. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher Optical resolution, resolution than Optical microscope, light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilus
A pilus (Latin for 'hair'; : pili) is a hair-like cell-surface appendage found on many bacteria and archaea. The terms ''pilus'' and '' fimbria'' (Latin for 'fringe'; plural: ''fimbriae'') can be used interchangeably, although some researchers reserve the term ''pilus'' for the appendage required for bacterial conjugation. All conjugative pili are primarily composed of pilin – fibrous proteins, which are oligomeric. Dozens of these structures can exist on the bacterial and archaeal surface. Some bacteria, viruses or bacteriophages attach to receptors on pili at the start of their reproductive cycle. Pili are antigenic. They are also fragile and constantly replaced, sometimes with pili of different composition, resulting in altered antigenicity. Specific host responses to old pili structures are not effective on the new structure. Recombination between genes of some (but not all) pili code for variable (V) and constant (C) regions of the pili (similar to immunoglobulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive-strand RNA Virus
Positive-strand RNA viruses (+ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have Sense (molecular biology), positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translation (biology), translated into viral proteins by the host cell, host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome. Positive-strand RNA viruses are divided between the phyla ''Kitrinoviricota'', ''Lenarviricota'', and ''Pisuviricota'' (specifically classes ''Pisoniviricetes'' and ''Stelpaviricetes, Stelpavirictes'') all of which are in the kingdom ''Orthornavirae'' and Realm (virology), realm ''Riboviria''. They are Monophyly, monophyletic and descended from a common RNA virus ancestor. In the Baltimore classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family (biology), family of Gram-negative bacteria. It includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of Family (taxonomy), family is still a subject of debate, but one classification places it in the order Enterobacterales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota. In 2016, the description and members of this family were emended based on comparative genomic analyses by Adeolu et al. Enterobacteriaceae includes, along with many harmless Symbiosis, symbionts, many of the more familiar pathogenic bacteria, pathogens, such as ''Salmonella'', ''Escherichia coli'', ''Klebsiella'', and ''Shigella''. Other disease-causing bacteria in this family include ''Enterobacter'' and ''Citrobacter''. Members of the Enterobacteriaceae can be Bacterial taxonomy#Nomenclature, trivially referred to as enterobacteria or "enteric bacteria", as several members live in the intestines of animals. In fact, the etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sense (molecular Biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. For example, the negative-sense strand of DNA is equivalent to the template strand, whereas the positive-sense strand is the non-template strand whose nucleotide sequence is equivalent to the sequence of the mRNA transcript. DNA sense Because of the complementary nature of base-pairing between nucleic acid polymers, a double-stranded DNA molecule will be composed of two strands with sequences that are reverse complements of each other. To help molecular biologists specifically identify each strand individually, the two strands are usually differentiated as the "sense" strand and the "antisense" strand. An individual strand of DNA is referred to as positive-sense (also positive (+) or simply se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the self-replication, replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to typical DNA-dependent RNA polymerases, which all organisms use to catalyze the transcription (genetics), transcription of RNA from a DNA template. RdRp is an essential protein encoded in the genomes of most RNA-containing viruses that lack a DNA stage, including SARS-CoV-2. Some eukaryotes also contain RdRps, which are involved in RNA interference and differ structurally from viral RdRps. History Viral RdRps were discovered in the early 1960s from studies on mengovirus and polio virus when it was observed that these viruses were not sensitive to actinomycin D, a drug that inhibits cellular DNA-directed RNA synthesis. This lack of sensitivity suggested the action of a virus-specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysis
Lysis ( ; from Greek 'loosening') is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic (that is, "lytic" ) mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a ''lysate''. In molecular biology, biochemistry, and cell biology laboratories, cell cultures may be subjected to lysis in the process of purifying their components, as in protein purification, DNA extraction, RNA extraction, or in purifying organelles. Many species of bacteria are subject to lysis by the enzyme lysozyme, found in animal saliva, egg white, and other secretions. Phage lytic enzymes (lysins) produced during bacteriophage infection are responsible for the ability of these viruses to lyse bacterial cells. Penicillin and related β-lactam antibiotics cause the death of bacteria through enzyme-mediated lysis that occurs after the drug causes the bacterium to form a defective cell wall. If the cell wall is completely lost and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |