|
Quasipetalichthys
''Quasipetalichthys haikouensis'' is the type and only known species of the extinct petalichthid placoderm, ''Quasipetalichthys''. Fossil remains of ''Quasipetalichthys'' have been found in the Middle Devonian, Givetian faunal stage of China. Fossils ''Quasipetalichthys'' is known primarily from two poorly preserved skulls from the Givetian-aged Haikou Formation of Haikou, Kunming, China, where they were found in association with remains of antiarch placoderms such as ''Bothriolepis sinensis'', and ''Hunanolepis''. The larger of the two skulls may have been around in length. Phylogeny ''Q. haikouensis'' is considered a basal petalichthyid (though in 1978 Denison referred to it as being "aberrant"). In Zhu's 1991 redescription of ''Diandongpetalichthys'',Zhu, M. "New information on ''Diandongpetalichthys'' (Placodermi: Petalichthyida)." Early vertebrates and related problems of evolutionary biology. Science Press, Beijing (1991): 179-192. ''Quasipetalichthys'' was place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasipetalichthyidae
Quasipetalichthyidae is a family of primitive petalichthyid placoderms from Givetian-aged marine strata of Yunnan, China, and possibly Vietnam Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it .... The family contains two confirmed genera, '' Quasipetalichthys'', and '' Eurycaraspis'', which differ from the more advanced macropetalichthyids by having more squared skulls that have the eye sockets placed on the side of their skulls, rather than nearer to the center. More basal petalichthyids, such as '' Diandongpetalichthys'' and '' Neopetalichthys'', differ from the quasipetalichthyids by having comparatively elongated skulls. References Placoderms of Asia Placoderm families Petalichthyida Middle Devonian extinctions Middle Devonian first appearances {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petalichthyida
Petalichthyida is an extinct order of small, flattened placoderm fish. They are typified by their splayed pectoral fins, exaggerated lateral spines, flattened bodies, and numerous tubercles that decorated all of the plates and scales of their armor. They reached a peak in diversity during the Early Devonian and were found throughout the world, particularly in Europe (especially in Germany), North America, Asia, South America, and Australia. The petalichthids ''Lunaspis'' and '' Wijdeaspis'' are among the best known. The earliest and most primitive known petalichthyid is ''Diandongpetalichthys'', which is from earliest Devonian-aged strata of Yunnan. The presence of ''Diandongpetalichthys'', along with other primitive petalichthyids including ''Neopetalichthys'' and ''Quasipetalichthys'', and more advanced petalichthyids, suggest that the order may have arisen in China, possibly during the late Silurian. Because they had compressed body forms, it is speculated they were bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurycaraspis
''Eurycaraspis incilis'' is an extinct petalichthid placoderm from the Middle Devonian of China. It is closely related to ''Quasipetalichthys''. Anatomy ''Eurycaraspis incilis'' differs from ''Quasipetalichthys'' by having a more circular-shaped skull. Phylogeny ''Eurycaraspis incilis'' is considered a basal petalichthyid, and is placed in Quasipetalichthyidae as ''Quasipetalichthys sister taxon. Quasipetalichthyidae Quasipetalichthyidae is a family of primitive petalichthyid placoderms from Givetian-aged marine strata of Yunnan, China, and possibly Vietnam Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group ..., in turn, is considered the sister group of Macropetalichthyidae. References Fossil taxa described in 1991 Placoderms of Asia Petalichthyida Placoderm genera {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderms Of Asia
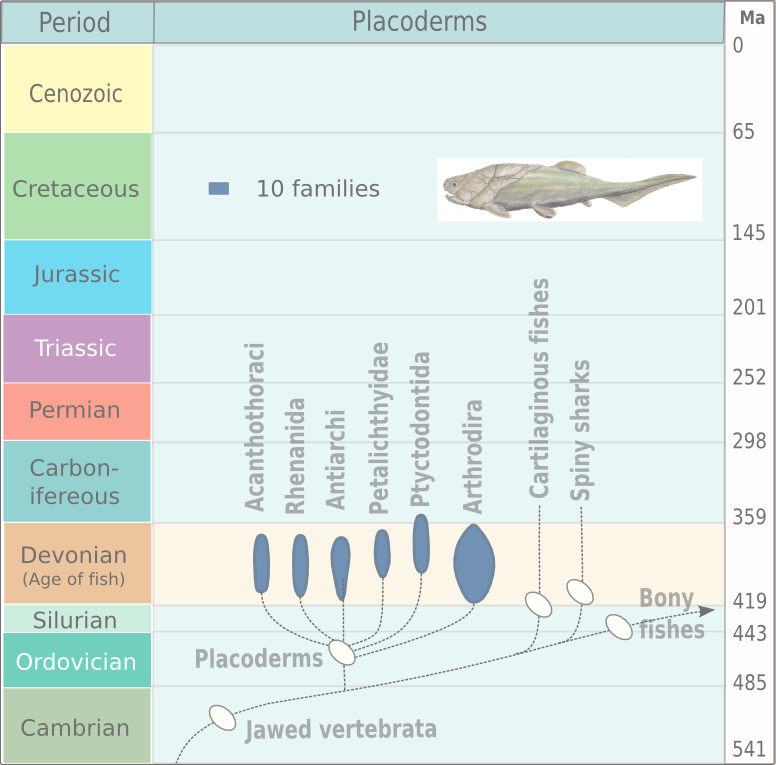
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally 'plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well as true t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placodermi
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally ' plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neopetalichthys
''Neopetalichthys yenmenpaensis'' is an extinct petalichthid placoderm from the Early Devonian of China. Fossils The holotype and only known specimen is a poorly preserved partial, and elongated skull from Emsian-aged strata in Sichuan. The skull may be around in length. Phylogeny Denison 1978 questions ''Neopetalichthys''' placement within Petalichthyida, regarding it as Placodermi ''incertae sedis'', though he does acknowledge that the skull has anatomical features in common with petalichthyids.). According to Zhu's 1991 redescription of '' Diandongpetalichthys'',Zhu, M. "New information on ''Diandongpetalichthys'' (Placodermi: Petalichthyida)." Early vertebrates and related problems of evolutionary biology. Science Press, Beijing (1991): 179-192. ''Neopetalichthys''' status as a petalichthyid is confirmed, though, in that study, it is regarded as a basal ''incertae sedis''. ''Quasipetalichthys'' is possibly closely related to ''Neopetalichthys'', and may or may not be pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Givetian
The Givetian is one of two faunal stages in the Middle Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Eifelian Stage and followed by the Frasnian Stage. It is named after the town of Givet in France. The oldest forests occurred during the late Givetian. The lower GSSP is located at Jebel Mech Irdane Jabal, Jabel, Jebel or Jibal may refer to: People * Jabal (name), a male Arabic given name * Jabal (Bible), mentioned in the Hebrew Bible Places In Arabic, ''jabal'' or ''jebel'' (spelling variants of the same word) means 'mountain'. * Dzhebel, ..., Tafilalt, Morocco. Name and definition The Givetian Stage was proposed in 1879 by French geologist Jules Gosselet and was accepted for the higher stage of the Middle Devonian by the Subcommission on Devonian Stratigraphy in 1981. References Further reading * {{Geological history, p, p Givetian, Middle Devonian Devonian geochronology Devonian Europe, . Devonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothriolepis
''Bothriolepis'' (from el, βόθρος , 'trench' and el, λεπίς 'scale') was a widespread, abundant and diverse genus of antiarch placoderms that lived during the Middle to Late Devonian period of the Paleozoic Era. Historically, ''Bothriolepis'' resided in an array of paleo-environments spread across every paleocontinent, including near shore marine and freshwater settings. Most species of ''Bothriolepis'' were characterized as relatively small, benthic, freshwater detritivores (organisms that obtain nutrients by consuming decomposing plant/animal material), averaging around in length. However, the largest species, ''B. rex'', had an estimated bodylength of . Although expansive with over 60 species found worldwide, comparatively ''Bothriolepis'' is not unusually more diverse than most modern bottom dwelling species around today. Classification ''Bothriolepis'' is a genus placed within the placoderm order Antiarchi. The earliest antiarch placoderms first appeared in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1973
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleobiology Database
The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Paleofaunal Database initiative, which operated from August 1998 through August 2000. From 2000 to 2015, PBDB received funding from the National Science Foundation. PBDB also received support form the Australian Research Council. From 2000 to 2010 it was housed at the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis, a cross-disciplinary research center within the University of California, Santa Barbara. It is currently housed at University of Wisconsin-Madison and overseen by an international committee of major data contributors. The Paleobiology Database works closely with the Neotoma Paleoecology Database, which has a similar intellectual history, but has focused on the Quaternary (with an emphasis on the late Pleistocene and Holoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycopods
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching stems bearing simple leaves called microphylls and reproduce by means of spores borne in sporangia on the sides of the stems at the bases of the leaves. Although living species are small, during the Carboniferous, extinct tree-like forms formed huge forests that dominated the landscape and contributed to coal deposits. The nomenclature and classification of plants with microphylls varies substantially among authors. A consensus classification for extant (living) species was produced in 2016 by the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group (PPG I), which places them all in the class Lycopodiopsida, which includes the classes Isoetopsida and Selaginellopsida used in other systems. (See Table 2.) Alternative classification systems have used ranks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |