|
Quantity Adjustment
In economics, quantity adjustment is the process by which a market surplus leads to a cut-back in the quantity supplied or a market shortage causes an increase in supplied quantity. It is one possible result of supply and demand disequilibrium in a market. Quantity adjustment is complementary to pricing. In the textbook story, favored by the followers of Léon Walras, if the quantity demanded does not equal the quantity supplied in a market, "price adjustment" is the rule: if there is a market ''surplus'' or glut (excess supply), prices fall, ending the glut, while a ''shortage'' (excess demand) causes price to rise. A simple model for price adjustment is the ''Evans price adjustment model'', which proposes the differential equation: : \frac = k (QD-QS), This says that the rate of change of the price (P) is proportional to the difference between the quantity demanded (QD) and the quantity supplied (QS). However, instead of price adjustment — or, more likely, ''simultaneously' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of Agent (economics), economic agents and how economy, economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economy, economies, including individual agents and market (economics), markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and Expenditure, investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: Labour (human activity), labour, Capital (economics), capital, Land (economics), land, and Entrepreneurship, enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact gloss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
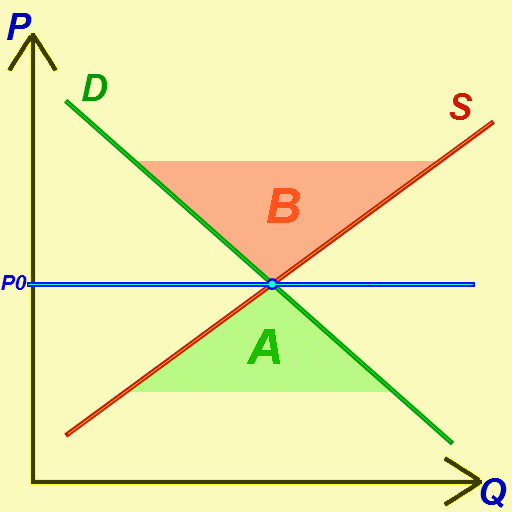
Supply And Demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a Market (economics), market. It postulates that, Ceteris_paribus#Applications, holding all else equal, the unit price for a particular Good (economics), good or other traded item in a perfect competition, perfectly competitive market, will vary until it settles at the market clearing, market-clearing price, where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied such that an economic equilibrium is achieved for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics. In situations where a firm has market power, its decision on how much output to bring to market influences the market price, in violation of perfect competition. There, a more complicated model should be used; for example, an oligopoly or product differentiation, differentiated-product model. Likewise, where a buyer has market power, models such as monopsony will be more a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which the economic forces of supply and demand are balanced, meaning that economic variables will no longer change. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. Understanding economic equilibrium An economic equilibrium is a situation when the economic agent cannot change the situation by adopting any strategy. The concept has been borrowed from the physical sciences. Take a system where physical forces are balanced for instance.This economically interpreted means no further change ensues. Properties of equilibrium Three basic prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market (economics)
In economics, a market is a composition of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations or infrastructures whereby parties engage in Exchange (economics), exchange. While parties may exchange goods and services by barter, most markets rely on sellers offering their goods or services (including labour power) to buyers in exchange for money. It can be said that a market is the process by which the value of goods and services are established. Markets facilitate trade and enable the distribution and allocation of resources in a society. Markets allow any tradeable item to be evaluated and priced. A market emergence, emerges more or less spontaneous order, spontaneously or may be constructed deliberately by human interaction in order to enable the exchange of rights (cf. ownership) of services and goods. Markets generally supplant Gift economy, gift economies and are often held in place through rules and customs, such as a booth fee, competitive pricing, and source of goods for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pricing
Pricing is the Business process, process whereby a business sets and displays the price at which it will sell its products and services and may be part of the business's marketing plan. In setting prices, the business will take into account the price at which it could acquire the goods, the manufacturing cost, the marketplace, competition, market condition, brand, and quality of the product. Pricing is a fundamental aspect of product management and is one of the four Ps of the marketing mix, the other three aspects being product, promotion, and Distribution (business), place. Price is the only revenue generating element among the four Ps, the rest being cost center (business), cost centers. However, the other Ps of marketing will contribute to decreasing price elasticity and so enable price increases to drive greater revenue and profits. Pricing can be a manual or automatic process of applying prices to purchase and sales orders, based on factors such as a fixed amount, quantit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léon Walras
Marie-Esprit-Léon Walras (; 16 December 1834 – 5 January 1910) was a French mathematical economics, mathematical economist and Georgist. He formulated the Marginalism, marginal theory of value (independently of William Stanley Jevons and Carl Menger) and pioneered the development of general equilibrium theory. Walras is best known for his book ''Éléments d'économie politique pure'', a work that has contributed greatly to the mathematization of economics through the concept of general equilibrium. For Walras, exchanges only take place after a Walrasian ''tâtonnement'' (French for "trial and error"), guided by the auctioneer, has made it possible to reach market equilibrium. It was the general equilibrium obtained from a single hypothesis, rarity, that led Joseph Schumpeter to consider him "the greatest of all economists". The notion of general equilibrium was very quickly adopted by major economists such as Vilfredo Pareto, Knut Wicksell and Gustav Cassel. John Hicks and Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Marshall
Alfred Marshall (26 July 1842 – 13 July 1924) was an English economist and one of the most influential economists of his time. His book ''Principles of Economics (Marshall), Principles of Economics'' (1890) was the dominant economic textbook in England for many years, and brought the ideas of supply and demand, marginal utility, and costs of production into a coherent whole, popularizing the modern Neoclassical economics, neoclassical approach which dominates microeconomics to this day. As a result, he is known as the father of scientific economics. Life and career Marshall was born at Bermondsey in London, the second son of William Marshall (1812–1901), a clerk and cashier at the Bank of England, and Rebecca (1817–1878), daughter of butcher Thomas Oliver, from whom, on her mother's death, she inherited property. Marshall had two brothers and two sisters; a cousin was the economist Ralph George Hawtrey, Ralph Hawtrey. The Marshalls were a West Country clergy, clerical f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Equilibrium
In economics, general equilibrium theory attempts to explain the behavior of supply, demand, and prices in a whole economy with several or many interacting markets, by seeking to prove that the interaction of demand and supply will result in an overall general equilibrium. General equilibrium theory contrasts with the theory of ''partial'' equilibrium, which analyzes a specific part of an economy while its other factors are held constant. General equilibrium theory both studies economies using the model of equilibrium pricing and seeks to determine in which circumstances the assumptions of general equilibrium will hold. The theory dates to the 1870s, particularly the work of French economist Léon Walras in his pioneering 1874 work ''Elements of Pure Economics''. The theory reached its modern form with the work of Lionel W. McKenzie (Walrasian theory), Kenneth Arrow and Gérard Debreu (Hicksian theory) in the 1950s. Overview Broadly speaking, general equilibrium tries to give a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |