|
Quad DH
QUaD, an acronym for QUEST at DASI, was a ground-based cosmic microwave background (CMB) polarization experiment at the South Pole. QUEST (Q and U Extragalactic Sub-mm Telescope) was the original name attributed to the bolometer detector instrument, while DASI is a famous CMB interferometry experiment credited with the first detection of CMB polarization. QUaD used the existing DASI mechanical infrastructure but replaced the DASI interferometric array with a bolometer detector at the end of a cassegrain optical system. The mount has housed the Keck Array since 2011. See also * Cosmic microwave background radiation * Cosmic microwave background experiments This list is a compilation of experiments measuring the cosmic microwave background radiation, cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation anisotropies and polarization since the first detection of the CMB by Arno Allan Penzias, Penzias and Rob ... References External links * http://www.stanford.edu/~schurch/quad.ht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope detects a faint background glow that is almost isotropic, uniform and is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other astronomical object, object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The accidental Discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation, discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Allan Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s. The CMB is landmark evidence of the Big Bang scientific theory, theory for the origin of the universe. In the Big Bang cosmological models, during the earliest periods, the universe was filled with an Opacity (optics), opaque fog of dense, hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is the point in the Southern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True South Pole to distinguish from the south magnetic pole. The South Pole is by definition the southernmost point on the Earth, lying antipode (geography), antipodally to the North Pole. It defines geodetic latitude 90° South, as well as the direction of true south. At the South Pole all directions point North; all lines of longitude converge there, so its longitude can be defined as any degree value. No time zone has been assigned to the South Pole, so any time can be used as the local time. Along tight latitude circles, clockwise is east and counterclockwise is west. The South Pole is at the center of the Southern Hemisphere. Situated on the continent of Antarctica, it is the site of the United States Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station, which was established in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolometer
A bolometer is a device for measuring radiant heat by means of a material having a temperature-dependent electrical resistance. It was invented in 1878 by the American astronomer Samuel Pierpont Langley. Principle of operation A bolometer consists of an absorptive element, such as a thin layer of metal, connected to a thermal reservoir (a body of constant temperature) through a thermal link. The result is that any radiation impinging on the absorptive element raises its temperature above that of the reservoir – the greater the absorbed power, the higher the temperature. The intrinsic thermal time constant, which sets the speed of the detector, is equal to the ratio of the heat capacity of the absorptive element to the thermal conductance between the absorptive element and the reservoir. The temperature change can be measured directly with an attached resistive thermometer, or the resistance of the absorptive element itself can be used as a thermometer. Metal bolometers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree Angular Scale Interferometer
The Degree Angular Scale Interferometer (DASI) was a telescope installed at the U.S. National Science Foundation's Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica. It was a 13-element interferometer operating between 26 and 36 GHz ( Ka band) in ten bands. The instrument is similar in design to the Cosmic Background Imager (CBI) and the Very Small Array (VSA). In 2001 The DASI team announced the most detailed measurements of the temperature, or power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background (CMB). These results contained the first detection of the 2nd and 3rd acoustic peaks in the CMB, which were important evidence for inflation theory. This announcement was done in conjunction with the BOOMERanG and MAXIMA experiment. In 2002 the team reported the first detection of polarization anisotropies in the CMB. In 2005, the vacant DASI mount was used for the QUaD experiment, which was another CMB imager focussed on the E-mode spectrum. In 2010, the DASI mount was agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference (wave propagation), interference'' of Superposition principle, superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, Optical fiber, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, Nuclear physics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, interactome, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
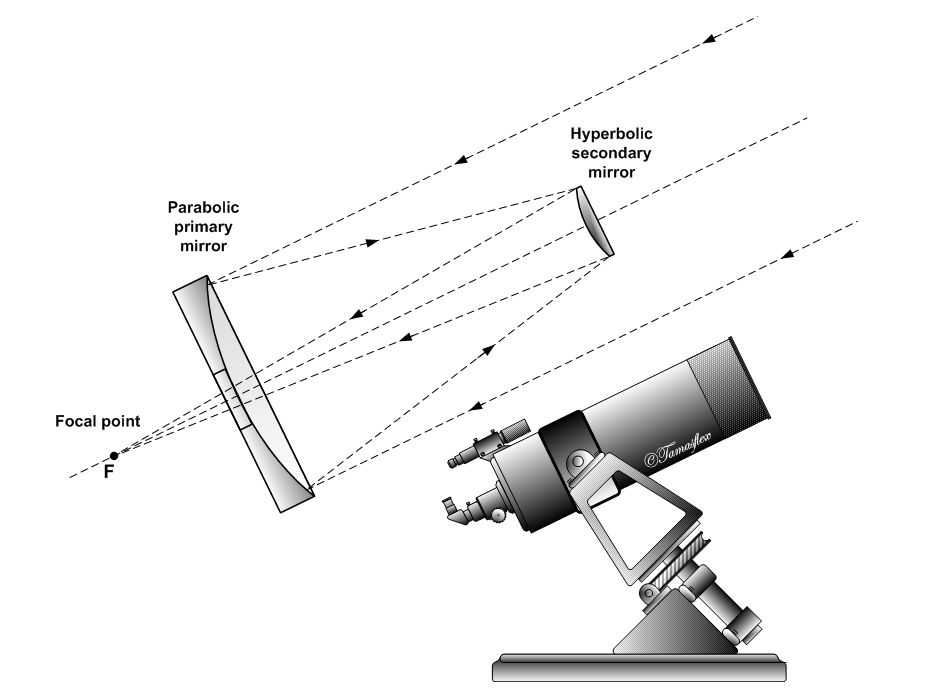
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and Antenna (radio), radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the Focus (optics), focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a Telephoto lens, telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keck Array
BICEP (Background Imaging of Cosmic Extragalactic Polarization) and the Keck Array are a series of cosmic microwave background (CMB) experiments. They aim to measure the polarization of the CMB; in particular, measuring the ''B''-mode of the CMB. The experiments have had five generations of instrumentation, consisting of BICEP1 (or just BICEP), BICEP2, the Keck Array, BICEP3, and the BICEP Array. The Keck Array started observations in 2012 and BICEP3 has been fully operational since May 2016, with the BICEP Array beginning installation in 2017/18. Purpose and collaboration The purpose of the BICEP experiment is to measure the polarization of the cosmic microwave background. Specifically, it aims to measure the ''B''-modes ( curl component) of the polarization of the CMB. BICEP operates from Antarctica, at the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station. All three instruments have mapped the same part of the sky, around the south celestial pole. The institutions involved in the vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope detects a faint background glow that is almost isotropic, uniform and is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other astronomical object, object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The accidental Discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation, discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Allan Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s. The CMB is landmark evidence of the Big Bang scientific theory, theory for the origin of the universe. In the Big Bang cosmological models, during the earliest periods, the universe was filled with an Opacity (optics), opaque fog of dense, hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background Experiments
This list is a compilation of experiments measuring the cosmic microwave background radiation, cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation anisotropies and polarization since the first detection of the CMB by Arno Allan Penzias, Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson, Wilson in 1964. There have been a variety of experiments to measure the cosmic microwave background radiation, CMB anisotropies and polarization since its first observation in 1964 by Arno Allan Penzias, Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson, Wilson. These include a mix of ground-, balloon- and space-based receivers. Some notable experiments in the list are Cosmic Background Explorer, COBE, which first detected the temperature anisotropies of the CMB, and showed that it had a black body spectrum; Degree Angular Scale Interferometer, DASI, which first detected the polarization signal from the CMB; Cosmic Background Imager, CBI, which made high-resolution observations and obtained the first E-mode polarization spectrum; WMAP; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submillimetre Telescopes
Submillimetre astronomy or submillimeter astronomy (see spelling differences) is the branch of observational astronomy that is conducted at submillimetre wavelengths (i.e., terahertz radiation) of the electromagnetic spectrum. Astronomers place the submillimetre waveband between the far-infrared and microwave wavebands, typically taken to be between a few hundred micrometres and a millimetre. It is still common in submillimetre astronomy to quote wavelengths in 'microns', the old name for micrometre. Submillimetre observations can be used to trace emission from gas and dust, including the CI, CO, and CII lines. Sources behind this emission include molecular clouds and dark cloud cores, which can be used to clarify the process of star formation from earliest collapse to stellar birth, by determining chemical abundances in dark clouds and the cooling mechanisms for the molecules which comprise them. Other sources include protoplanetary discs, dusty starburst galaxies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Telescopes
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna (radio), antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, just as optical telescopes are used to make observations in the visible light, visible portion of the spectrum in traditional optical astronomy. Unlike optical telescopes, radio telescopes can be used in the daytime as well as at night. Since astronomical radio sources such as planets, stars, nebulas and galaxy, galaxies are very far away, the radio waves coming from them are extremely weak, so radio telescopes require very large antennas to collect enough radio energy to study them, and extremely sensitive receiving equipment. Radio telescopes are typically large Parabolic antenna, parabolic ("dish") antennas similar to those employed in tracking and communicating with satellites an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |