|
Qiu Fu
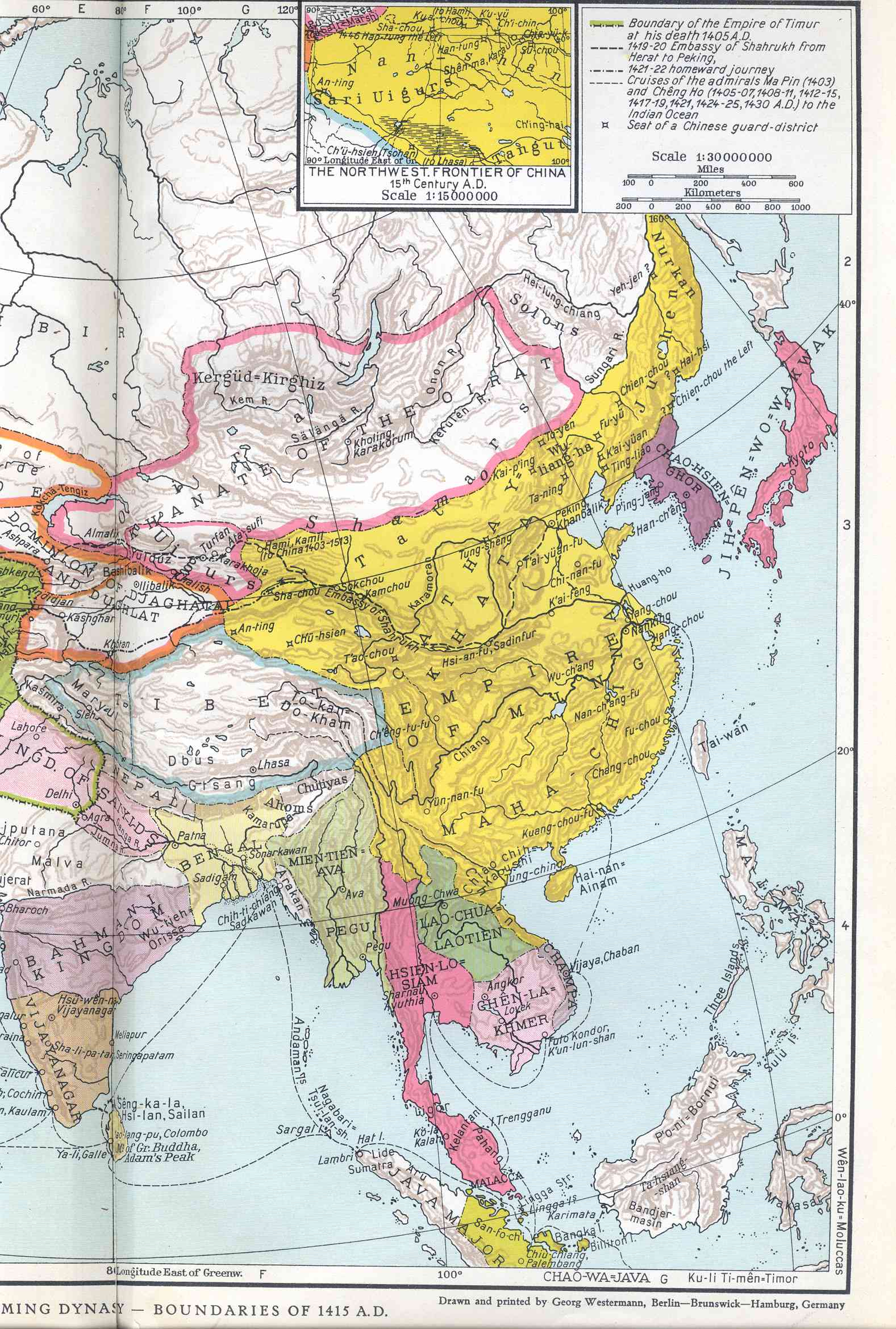
Qiu Fu (1343–1409) was a Chinese military general of the Ming dynasty, who achieved high rank during the reign of the Yongle Emperor, but fell in battle against the Mongols. Qiu Fu was from the Fengyang region and was a member of the household of Zhu Di, Prince of Yan, during his youth. He quickly rose through the ranks and, during the civil war of 1399–1402, became one of the leading generals in Zhu Di's army alongside Zhu Neng. In 1402, Zhu Di ascended to the throne as the Yongle Emperor and bestowed upon Qiu Fu the title of Duke of Qi () in October of that same year. This elevated Qiu Fu to one of the highest-ranking generals in Ming China. During discussions about the succession to the throne, Qiu Fu advocated for the appointment of the emperor's second son, Zhu Gaoxu, but in 1404, the emperor chose his eldest son Zhu Gaochi as his successor and Qiu Fu became his tutor. In 1409, the emperor entrusted Qiu Fu with leading a punitive expedition against the Eastern Mongols, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fengyang County
Fengyang County () is a county in north-central Anhui Province, China. It is under the administration of Chuzhou, a prefecture-level city. The county was home to 765,600 people as of 2013. Administrative divisions Fengyang County is divided into 14 towns and 1 township. The county seat is in Fucheng Town. 14 Towns The county is home to the following 14 towns: 1 Township The county's sole township is: * Huangwan (). Geography The county's northern border is formed by the Huai River and neighboring Wuhe County. The county is also home to the Huayuan Lake, which totals about 30 square kilometers in size. Climate The average annual temperature for Fengyang County is 14.9 °C, and the average annual precipitation is 904.4 mm. History Pre-Ming Dynasty During the Xia, Shang and early Zhou dynasties, the Dongyi peoples inhabited this area and were collectively known as the Huaiyi after the Huai River. During the late Western Zhou Period and the early Spring a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Öljei Temür Khan
Öljei Temür Khan ( ; ), born Bunyashiri (, ), (1379–1412) was a khagan of the Northern Yuan dynasty, reigning from 1408 to 1412. He was a son of Elbeg Nigülesügchi Khan and successor of Gün Temür Khan. He was one of the Borjigin princes, such as Tokhtamysh and Temür Qutlugh, backed by Timur to seize the throne. Early life Tsagaan Sechen tells that Bunyashiri (Buyanshir) was born in 1379. Twenty years after his birth, his father, Elbeg, was murdered by the Oirats led by Bahamu and Ugetchi Khashikha. Later, Öljei Temür came to Central Asia after 1399. In 1402, Gün Temür Khan was killed by Örüg Temür Khan or Guilichi in the struggle for the crown. Conversion to Islam Due to internal struggles of the Mongols, the infant prince, Bunyashiri, fled to Beshbalik where Timur's governor stationed. Timur ordered his governor to receive him kindly. Bunyashiri converted to Islam while he stayed at the court of Timur in Samarkand, thus making Öljei Temür Khan one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Generals
Chinese may refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China. **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese characters in traditional and simplified forms) *** Standard Chines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1409 Deaths
Year 1409 ( MCDIX) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. Events January–March * January 1 – The Welsh surrender Harlech Castle to the English. * January 18 – The Decree of Kutná Hora strengthens the Bohemian nation at the cost of foreign, mostly German speaking students at the University of Prague. Over a thousand students leave Prague as a consequence, choosing instead the universities of Heidelberg and the new University of Leipzig established later in the year. * February 15 – The Galle Trilingual Inscription, with inscriptions in three languages ( Chinese, Tamil and Persian) is installed by the Chinese admiral Zheng He at Galle in Sri Lanka, where he has stopped while on his way home during the second of his treasure voyages. * February 24 – Traveling in Valencia in Aragon, Father Joan Gilabert Jofré, known as "Padre Jofré", witnesses a mentally ill man being beaten by two young attackers. After rescuin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1343 Births
Year 1343 ( MCCCXLIII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * January 14 – Arnošt of Pardubice becomes the last bishop of Prague and, subsequently, the first Archbishop of Prague. * January 27 – Pope Clement VI issues his bull ''Unigenitus'', defining the doctrine of "The Treasury of Merits" or "The Treasury of the Church" as the basis for the issuance of indulgences by the Catholic Church. * April 23 – The St. George's Night Uprising begins in Estonia. * May 4 – St. George's Night Uprising: The "Four Estonian kings" are murdered, at the negotiations with the Livonian Order. * August 15 – Magnus IV of Sweden abdicates from the throne of Norway, in favor of his son Haakon VI of Norway. However, Haakon is still a minor, allowing Magnus to remain de facto ruler. * August 31 – A naval league is formed between the Pope, the Republic of Venice, the Knights Hospitaller and the Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hainan
Hainan is an island provinces of China, province and the southernmost province of China. It consists of the eponymous Hainan Island and various smaller islands in the South China Sea under the province's administration. The name literally means "South of the Sea". The province has a land area of , of which Hainan Island is and the rest is over 200 islands scattered across three archipelagos: Zhongsha Islands, Zhongsha, Xisha Islands, Xisha and Nansha Islands, Nansha. It was part of Guangdong from 1950 to 1988, after which it was made a province of its own and was designated as a special economic zones of China, special economic zone by Deng Xiaoping, as part of the Chinese economic reform program. The Han Han Chinese, Chinese population, who compose a majority of the population at 82%, speak a wide variety of languages including Standard Chinese, Hainanese, Hainam Min, Yue Chinese, Cantonese, Hakka Chinese, etc. Indigenous peoples such as the Hlai people, Hlai, a Kra–Dai l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kherlen
The Battle of Kherlen () was fought between the Eastern Mongols and the Ming dynasty at the banks of Kherlen River (Kerülen River) on the Mongolian Plateau on 23 September 1409.Tsai, Shih-Shan Henry (2001). ''Perpetual Happiness: The Ming Emperor Yongle''. University of Washington Press. p. 167. Background A conflict erupted between two Eastern Mongol leaders, the khan Guilichi and his principal retainer Arughtai, which culminated in the killing of Guilichi in 1408. Arughtai, the victor of the conflict, installed Bunyashiri as the new khan. Afterwards, the Ming court sent the envoy Guo Ji to demand the dispatch of a tribute embassy, but they killed the envoy instead. In contrast, the Mongol leader Mahmud of the Oyirad Mongols (Western Mongols) sent a tribute mission to the Yongle Emperor of Ming China in 1408. The Ming court, who were appalled that the Eastern Mongols refused to establish tributary relations and murdered their envoy, would use the Oyirad Mongols to off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arughtai
Arughtai, also known as Alutai (; d. 1434), was a chingsang of the Northern Yuan dynasty who fought against the Yongle Emperor of the Ming dynasty and the Four Oirats. According to the Mongolian and Chinese chronicles, there are similar named figures among the Western and Eastern Mongols. One of them named Asud Arugtai was a war prisoner of the Oirats, who was released by the Borjigin princess Samur while another person, Alutai, raided the Ming districts. Whatever his origin, the Oirad leaders, Gulichi and Mahamud, overthrew Elbeg Khan in 1399; and the former had himself enthroned as Khagan who appointed Arugtai or Alutai chingsang (councillor). However, Mahamud and Arughtai defeated Ugetchi or Gulichi; and Mahamud himself died soon after that. In 1409 Alutai (Arughtai) set up the heir, Öljei Temür Khan Bunyashiri, of the Northern Yuan dynasty at Beshbalik, and ignored Ming demands for satisfaction regarding the murder of an envoy in the previous year. War followed, in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolian Campaigns Yongle Emperor
Mongolian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Mongolia, a country in Asia * Mongolian people, or Mongols * Bogd Khanate of Mongolia, the government of Mongolia, 1911–1919 and 1921–1924 * Mongolian language * Mongolian alphabet * Mongolian (Unicode block) * Mongolian cuisine * Mongolian culture Other uses * Mongolian idiocy, now more commonly referred to as Down syndrome See also * * Languages of Mongolia * List of Mongolians * Mongolian nationalism (other) * Mongolian race (other) * Mongoloid (other) Mongoloid refers to an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to East Asia, Central Asia, Southeast Asia, North Asia, Polynesia, and the Americas. Mongoloid may also refer to: * Mongoloid idiot, previously used to refer to a p ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hongguang Emperor
The Hongguang Emperor (1607–1646), personal name Zhu Yousong, childhood nickname Fuba, was the first emperor of the Chinese Southern Ming dynasty. He reigned briefly in southern China from 1644 to 1645. His era name, "Hongguang", means "great light". In 1646, Zhu Yousong was captured and executed by the Qing dynasty at the Caishikou Execution Grounds. Early life Zhu Yousong was a member of Ming imperial family. He was eldest son of Zhu Changxun, and a grandson of the Wanli Emperor and Noble Consort Zheng. He followed his father to his fief at Luoyang in 1614 and later was granted the title "Commandery Prince of Dechang" (德昌郡王). He was later designated as Hereditary Prince of Fu. In 1641, Li Zicheng's forces invaded Luoyang, and Zhu managed to escape but his father was killed. He held his father's princely title in two years later. In 1644, he escaped again to Weihui to seek asylum from his distant uncle, Zhu Changfang, Prince of Lu (grandson of the Longqing Emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Gaochi
The Hongxi Emperor (16 August 1378 – 29 May 1425), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Renzong of Ming, personal name Zhu Gaochi, was the fourth emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1424 to 1425. He was the eldest son of the Yongle Emperor and Empress Renxiaowen and the grandson of both the Hongwu Emperor and Xu Da, Prince of Zhongshan. He ascended the throne after the death of his father, but his reign lasted less than a year. Zhu Gaochi's father, Zhu Di, was the fourth son of the Hongwu Emperor. After the death of the Hongwu Emperor, Zhu Di emerged victorious in a civil war against the Jianwen Emperor and became the Yongle Emperor in 1402. He prioritized providing his eldest son with a comprehensive education based on Confucian principles. During his father's military campaigns, Zhu Gaochi served as a regent in either Nanjing or Beijing. As soon as the Hongxi Emperor ascended to the throne, he discontinued Zheng He's overseas expeditions, halted the trade of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Gaoxu
Zhu Gaoxu (30 December 1380 – 6 October 1426) was the second son of the Yongle Emperor and Empress Renxiaowen. During the Jingnan campaign, which brought his father to the throne, he proved himself to be a capable military leader. In 1426, he revolted against his nephew, the Xuande Emperor, but was quickly defeated and executed. Biography Zhu Gaoxu was born in 1380 as the second son of Zhu Di, who was then the Prince of Yan. Zhu Di was the fourth son of the Hongwu Emperor, the founder of the Ming dynasty. In 1395, he was made the Prince of Gaoyang (). In 1399, Zhu Di rebelled against his nephew, the Jianwen Emperor, and the subsequent civil war ended in 1402 with Zhu Di's victory, after which he ascended the throne. Physically fit and energetic, but also arrogant, Zhu Gaoxu proved himself to be a capable military leader in battle. In 1404, he was created as the Prince of Han () and given control of Yunnan. However, he refused to go to the distant province, so the emperor all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |