|
Qiong
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly larger, is claimed but not controlled by the PRC. It is instead controlled by the Republic of China, a ''de facto'' separate country. makes up the vast majority (97%) of the province. The name means "south of the sea", reflecting the island's position south of the Qiongzhou Strait, which separates it from Leizhou Peninsula. The province has a land area of , of which Hainan the island is and the rest is over 200 islands scattered across three archipelagos: Zhongsha, Xisha and Nansha. It was part of Guangdong from 1950–88, after which it resumed as a top-tier entity and almost immediately made the largest Special Economic Zone by Deng Xiaoping as part of the then-ongoing Chinese economic reform program. Indigenous peoples like the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
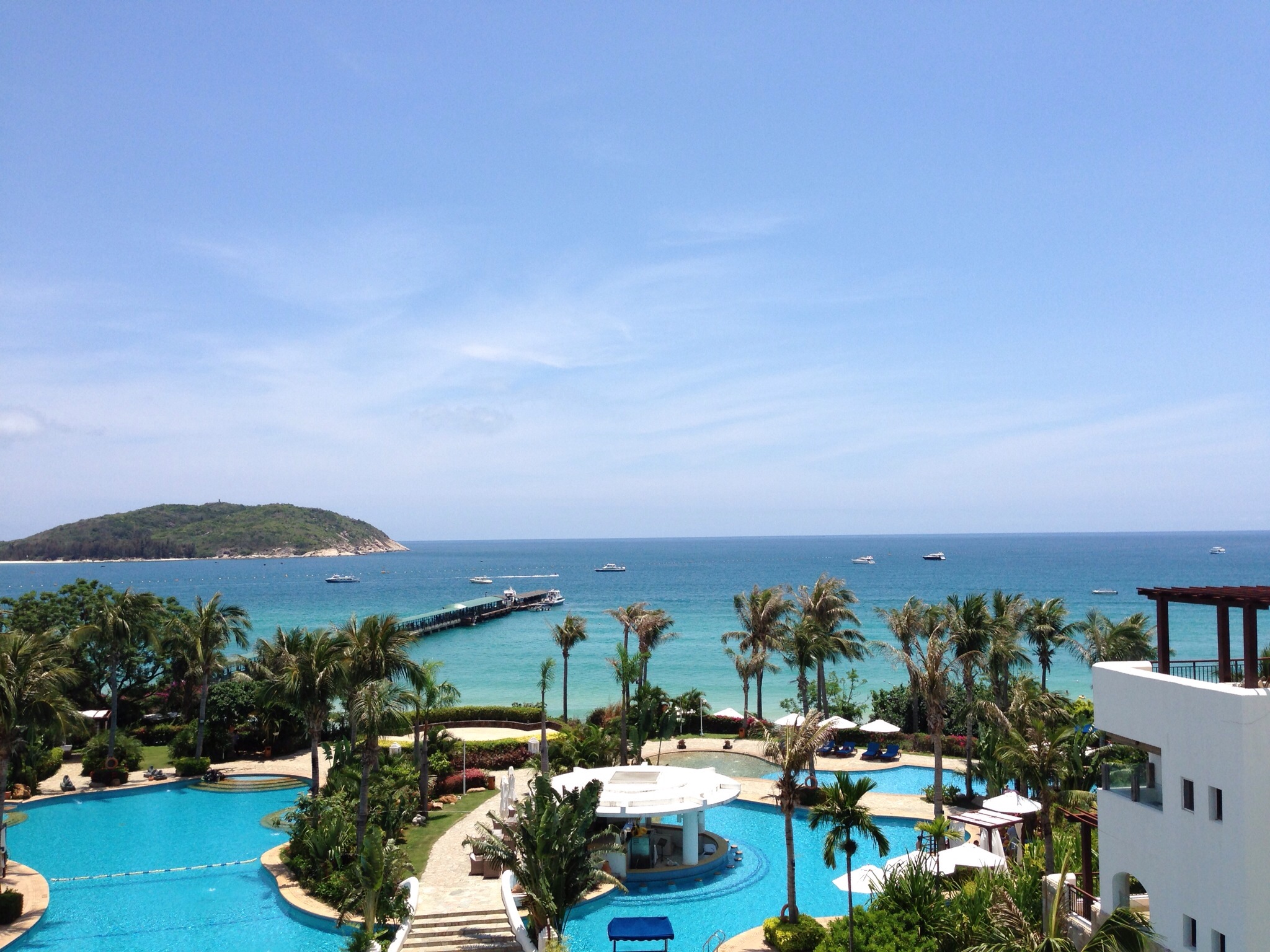
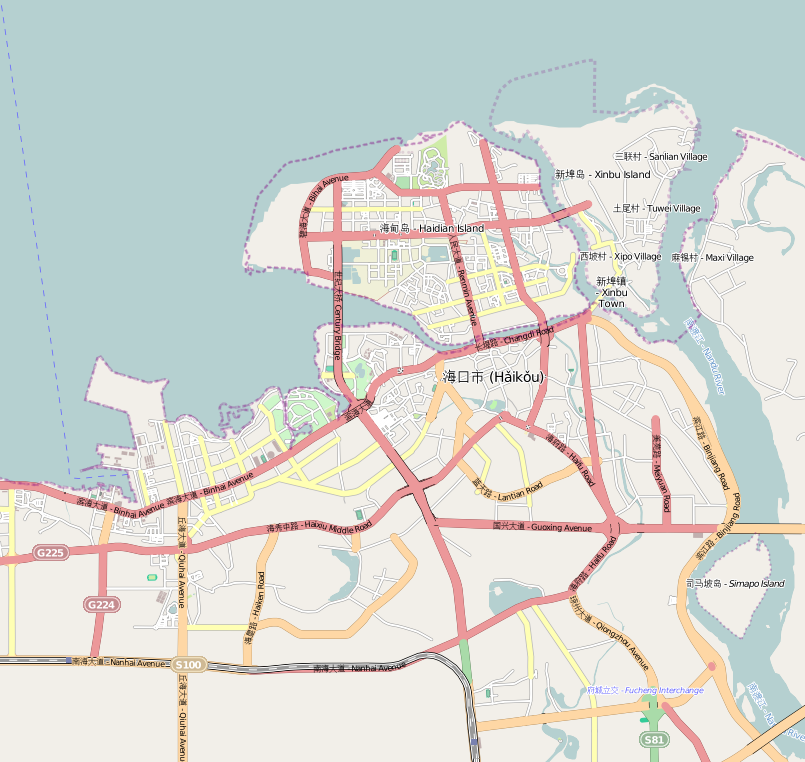
Haikou
Haikou (; ), also spelled as Hoikow is the capital and most populous city of the Chinese province of Hainan. Haikou city is situated on the northern coast of Hainan, by the mouth of the Nandu River. The northern part of the city is on the Haidian Island, which is separated from the main part of Haikou by the Haidian River, a branch of the Nandu. Administratively, Haikou is a prefecture-level city, comprising four districts, and covering . There are 2,046,189 inhabitants in the built-up area, all living within the four urban districts of the city. Haikou was originally a port city, serving as the port for Qiongshan. During the Chinese Civil War, Haikou was one of the last Nationalist strongholds to be taken by the Communists — with the Battle of Hainan Island in 1950. Currently, more than half of the island's total trade still goes through Haikou's ports. The Temple of the Five Lords is located to the southeast of the city. The city is home to Hainan University, a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Be Language
Be (), also known as Ong Be, Bê, or ''Vo Limgao'' (Mandarin 臨高 ''Lín'gāo''), is a pair of languages spoken by 600,000 people, 100,000 of them monolingual, on the north-central coast of Hainan Island, including the suburbs of the provincial capital Haikou. The speakers are counted as part of the Han Chinese nationality in census. According to '' Ethnologue'', it is taught in primary schools. Names Be speakers refer to themselves as ', with ' being the prefix for persons and ' meaning 'village' (Liang 1997:1). Liang (1997) notes that it is similar to the autonym ' (from ' 'person' and ' 'village'), by which Gelong 仡隆 ( Cun language) speakers refer to themselves. Classification Be is a Kra–Dai language, but its precise relationship to other branches within the Kra-Dai family has yet not been conclusively determined. Hansell (1988) considers Be to be a sister of the Tai branch based on shared vocabulary, and proposes a ''Be–Tai'' grouping. Based on toponymic evide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hainanese
Hainanese ( Hainan Romanised: ', Hainanese Pinyin: ',), also known as Qióngwén, Heng2 vun2 () or Qióngyǔ, Heng2 yi2 (), is a group of Min Chinese varieties spoken in the southern Chinese island province of Hainan and Overseas Chinese such as Malaysia. In the classification of Yuan Jiahua, it was included in the Southern Min group, being mutually unintelligible with other Southern Min varieties such as Hokkien– Taiwanese and Teochew. In the classification of Li Rong, used by the '' Language Atlas of China'', it was treated as a separate Min subgroup. Hou Jingyi combined it with Leizhou Min, spoken on the neighboring mainland Leizhou Peninsula, in a Qiong–Lei group. "Hainanese" is also used for the language of the Li people living in Hainan, but generally refers to Min varieties spoken in Hainan. Phonology Hainanese has seven phonemic vowels . Hainanese notably has a series of implosive consonants, which it acquired through contact with surrounding langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hainan Island
The Battle of Hainan Island occurred in 1950 during the final phase of the Chinese Civil War. The People's Republic of China (PRC) conducted an amphibious assault on the island in mid-April, assisted by the independent Hainan Communist movement, which controlled much of the island's interior, while the Republic of China (ROC) controlled the coast; their forces were concentrated in the north near Haikou and were forced to retreat south after the landings. The Communists secured the southern cities by the end of the month and declared victory on May 1. Background Hainan Communist movement The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) established a branch on Hainan in 1926. Lines of communication between the branch and the CCP leadership were tenuous from the beginning, resulting in the Hainan Communist movement developing as an independent entity and operating with minimal outside support. The Hainan Communists were hard hit by ROC repression that followed the end of the First United Front. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) across a total area of about , Guangdong is the most populous province of China and the 15th-largest by area as well as the second-most populous country subdivision in the world (after Uttar Pradesh in India). Its economy is larger than that of any other province in the nation and the fifth largest sub-national economy in the world with a GDP (nominal) of 1.95 trillion USD (12.4 trillion CNY) in 2021. The Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, a Chinese megalopolis, is a core for high technology, manufacturing and International trade, foreign trade. Located in this zone are two of the Chinese city tier system, four top Chinese cities and the List of Chinese prefecture-level cities by GDP, top two Chinese prefecture-level cities by GDP; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuzhi Mountain
Wuzhi Mountain () is the highest mountain in Hainan, China, towering above the center of Hainan Island. The surrounding areas of Wuzhi Mountain are inhabited mainly by the Li ethnic group. It is located adjacent to Wuzhishan City Wuzhishan (literally five point mountain) is a county-level city in the highlands of Hainan island, China. Although called a "city", Wuzhishan refers to a large land area in Hainan - an area which was once a county. Within this area is the main ... but is not part of that city's administrative area. Various Li myths concern the name for the mountain (Five Finger Mountain) and its formation. One legend has it that the five mountain peaks are the fossilized fingers of a dead Li clan chief. Another tale is that the five peaks are dedicated to the five most powerful Li gods. Numerous historical poems have also been written about the mountain, the most famous of all by the Hainan writer, Qiujun. See also * List of Ultras of Tibet and East Asia Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of China
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan". Every province on Mainland China (including the island province of Hainan) has a Chinese Communist Party (CCP) provincial committee (), headed by a secretary (). The Committee Secretary is effectively in charge of the province, rather than the governor of the provincial government. The same arrangement exists for the autonomous regions and municipalities. Types of provincial level divisions Province The government of each standard province () is nominally led by a provincial co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
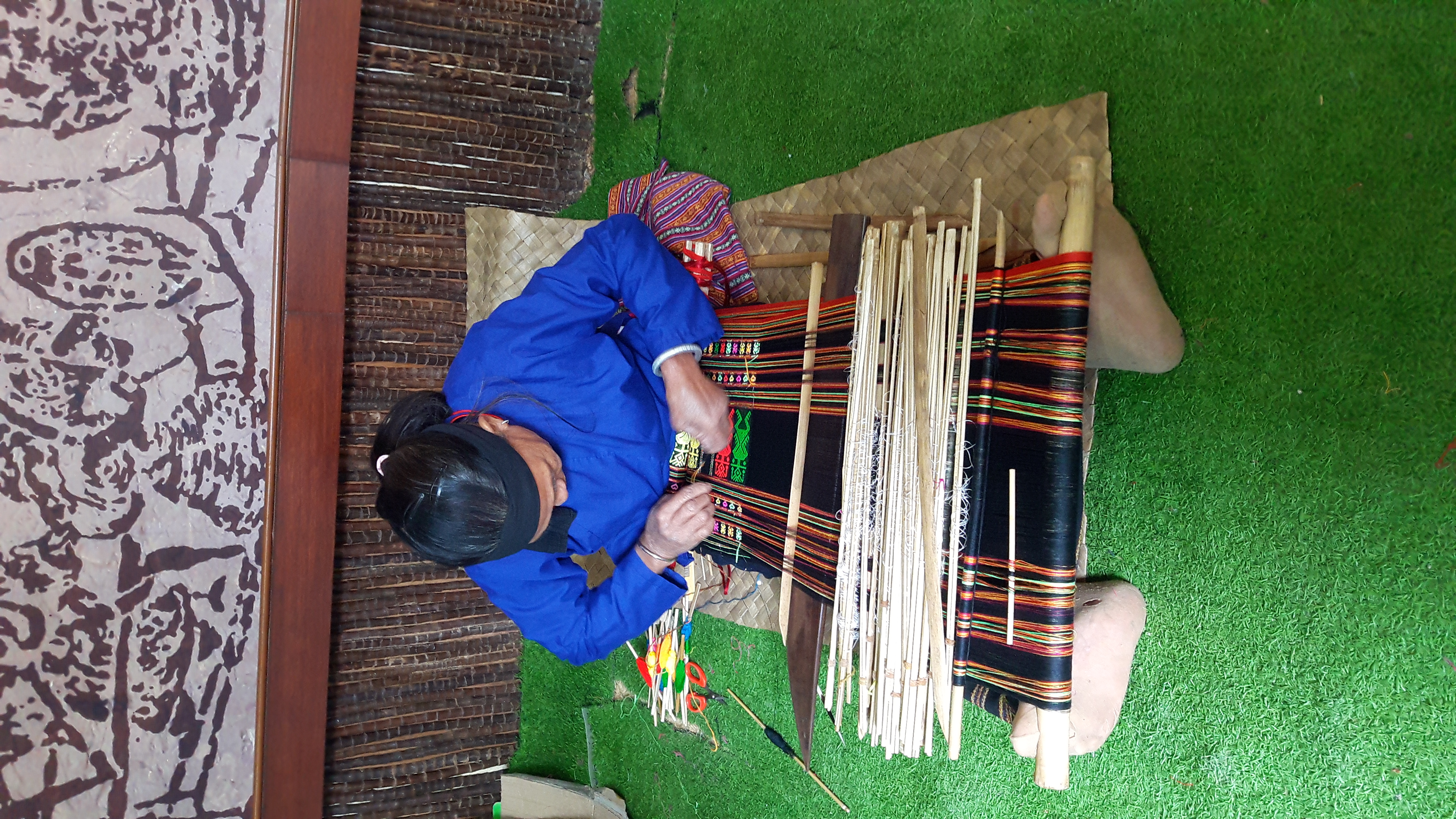
Li People
The Hlai, also known as Li or Lizu, are a Kra–Dai-speaking ethnic group, one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. The vast majority live off the southern coast of China on Hainan Island, where they are the largest minority ethnic group. Divided into the five branches of the Qi (Gei), Ha, Run (Zwn), Sai (Tai, Jiamao) and Meifu (Moifau), the Hlai have their own distinctive culture and customs. Names 黎 (Lí), which was pronounced /lei/ in Middle Chinese is the Chinese transcription of their native name, which is Hlai. They are sometimes also known as the "Sai" or "Say". During China's Sui Dynasty, their ancestors were known by various names, including ''Lǐliáo'' (), a general term encompassing several non-Han ethnic groups in Southern China. The name Li first is recorded during the Later Tang period (923–937 CE). History Liang & Zhang (1996:18-21) believe that the original homeland of the Hlai languages was the Leizh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Administrative Divisions By Population
This is a list of Chinese administrative divisions in order of their total resident populations. It includes all provinces of China, provinces, autonomous administrative divisions of China, autonomous regions, direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-controlled municipalities and special administrative regions of China, special administrative regions controlled by the Republic of China (1912–1949) or the China, People's Republic of China (1949–present). For the Taiwan, Republic of China after 1949, see List of administrative divisions of Taiwan. Census data Current population References Footnotes Sources {{DEFAULTSORT:Chinese Administrative Divisions By Population Ranked lists of Chinese administrative divisions, Population Demographics of China, Population Demographic lists Ranked lists of country subdivisions, China, population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Administrative Divisions By Population Density
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan". Every province on Mainland China (including the island province of Hainan) has a Chinese Communist Party (CCP) provincial committee (), headed by a secretary (). The Committee Secretary is effectively in charge of the province, rather than the governor of the provincial government. The same arrangement exists for the autonomous regions and municipalities. Types of provincial level divisions Province The government of each standard province () is nominally led by a provincial co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Chinese
The Han Chinese () or Han people (), are an East Asian ethnic group native to China. They constitute the world's largest ethnic group, making up about 18% of the global population and consisting of various subgroups speaking distinctive varieties of the Chinese language. The estimated 1.4 billion Han Chinese people, worldwide, are primarily concentrated in the People's Republic of China (including Mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau) where they make up about 92% of the total population. In the Republic of China (Taiwan), they make up about 97% of the population. People of Han Chinese descent also make up around 75% of the total population of Singapore. Originating from Northern China, the Han Chinese trace their cultural ancestry to the Huaxia, the confederation of agricultural tribes living along the Yellow River. This collective Neolithic confederation included agricultural tribes Hua and Xia, hence the name. They settled along the Central Plains around the middle a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standardized form of Mandarin Chinese that was first developed during the Republican Era (1912‒1949). It is designated as the official language of mainland China and a major language in the United Nations, Singapore, and Taiwan. It is largely based on the Beijing dialect. Standard Chinese is a pluricentric language with local standards in mainland China, Taiwan and Singapore that mainly differ in their lexicon. Hong Kong written Chinese, used for formal written communication in Hong Kong and Macau, is a form of Standard Chinese that is read aloud with the Cantonese reading of characters. Like other Sinitic languages, Standard Chinese is a tonal language with topic-prominent organization and subject–verb–object (SVO) word order. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |