|
Qielan
Guan Yu (; ), courtesy name Yunchang, was a Chinese military general serving under the warlord Liu Bei during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Along with Zhang Fei, he shared a brotherly relationship with Liu Bei and accompanied him on most of his early exploits. Guan Yu played a significant role in the events leading up to the end of the Han dynasty and the establishment of Liu Bei's state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. While he is remembered for his loyalty towards Liu Bei, he is also known for repaying Cao Cao's kindness by slaying Yan Liang, a general under Cao Cao's rival Yuan Shao, at the Battle of Boma. After Liu Bei gained control of Yi Province in 214, Guan Yu remained in Jing Province to govern and defend the area for about seven years. In 219, while he was away fighting Cao Cao's forces at the Battle of Fancheng, Liu Bei's ally Sun Quan broke the Sun–Liu alliance and sent his general Lü Meng to conquer Liu Bei's territories in Jing Province. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu ( zh, t=蜀, p=Shǔ; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Su'' < Middle Chinese: *''źjowk'' < Eastern Han Chinese: *''dźok''), was a Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic state of China and one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the Three Kingdoms period. The state was based in the area around present-day Hanzhong, Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, Guizhou, and north Guangxi, an area historically referred to as "Shu" based on the name of the past Shu (kingdom), ancient kingdom of Shu, which also occupied this approximate geographical area. Its core territory also coincided with Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang's Emperor Gaozu of Han#King of Han, Kingdom of Han, the precursor of the Han dynasty. Shu Han's founder, Liu Bei (Emperor Zhaolie), had named his dynasty "Han", as he considered it a rump state of the Han dynasty and thus the legitimate successor to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guān (surname)
Guan () is a Chinese surname. Guan is 394th in the Hundred Family Surnames. In Hong Kong, the surname is Hong Kong Government Cantonese Romanisation, romanised as Kwan in Cantonese. In Taiwan, the Wade–Giles spelling Kuan is used. In Macao, the surname is as Kuan due to the Portuguese people, Portuguese influence. In addition the surname Cuan is also used in Mexico. In many overseas Chinese communities, both spellings, Kuan and Kwan, as well as Quan, are common. It is also a Vietnamese surname that uses the same character, romanised as Quan. It is also a Japanese surname, Seki (), that uses the same character. The Vietnamese surname, Quan and the Japanese surname, Seki, were derived from the same Chinese character as the Chinese surname (The Japanese Kanji 関 is a Shinjitai of the Chinese character 關). Origin and timeline A number of groups in different geographic areas are believed to have shared the surname in history. *Guan(关 or 關) - meaning is City Gate, or Close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
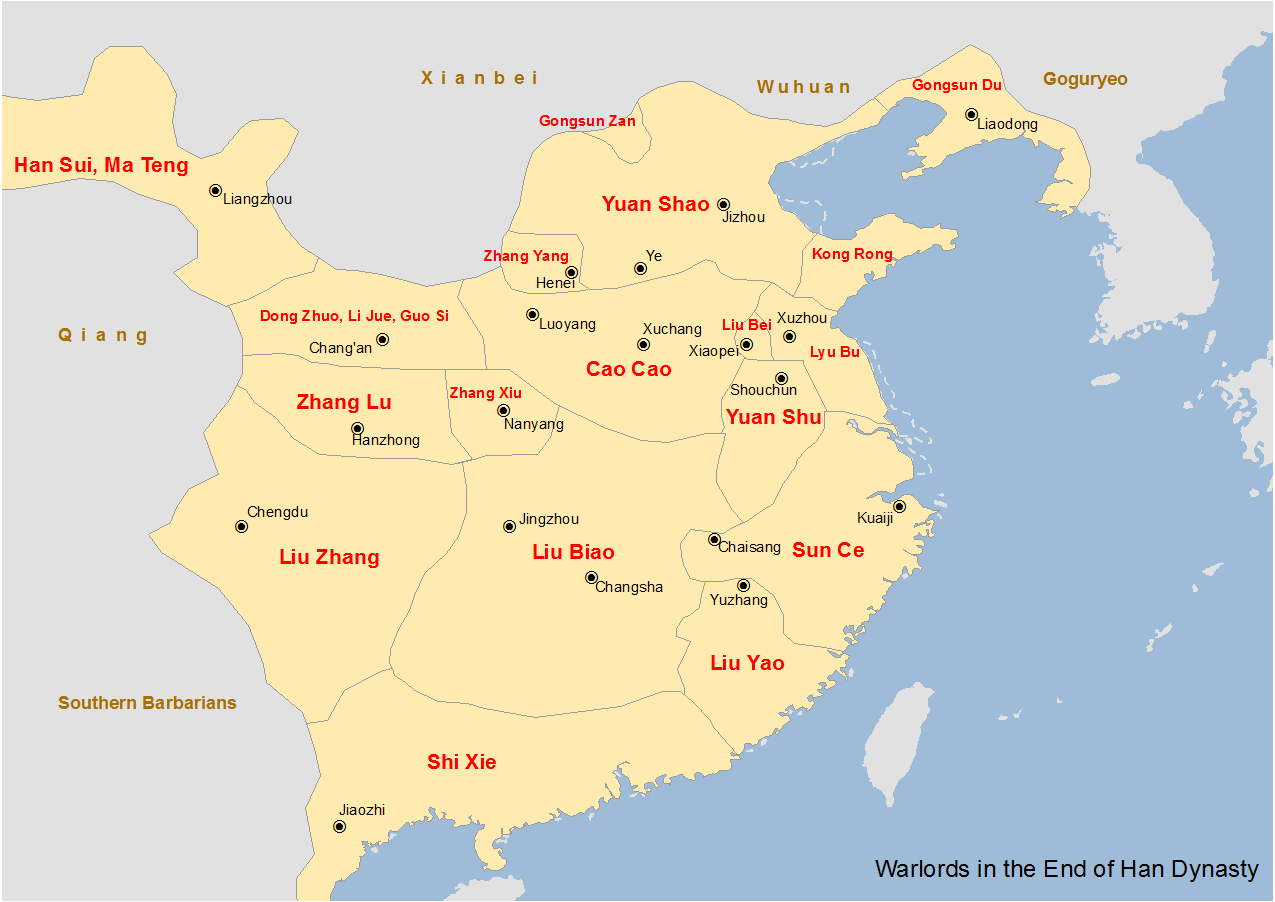
Eastern Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lü Meng
Lü Meng () (178 – January or February 220), courtesy name Ziming, was a Chinese military general and politician who served under the warlord Sun Quan during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Early in his career, he fought in several battles under the banner of Sun Ce, Sun Quan's elder brother and predecessor. Although he had been noted for his bravery, he was still deemed as nothing more than a "mere warrior" for his lack of literacy skills. Later, with encouragement from Sun Quan, Lü Meng took up scholarly pursuits to improve himself, gradually becoming a learned and competent military leader. In 217, he succeeded Lu Su as the frontline commander of Sun Quan's forces in Jing Province. Two years later, in a carefully calculated military operation, Lü Meng led an invasion of Liu Bei's territories in southern Jing Province, swiftly and stealthily capturing all the lands from Liu Bei's general Guan Yu, who was captured and executed after his defeat. Lü Meng enjoyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Quan
Sun Quan (; 182 – 21 May 252), courtesy name Zhongmou (), posthumous name, posthumously known as Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of Eastern Wu, one of the Three Kingdoms of China. He inherited control of the warlord regime established by his elder brother, Sun Ce, in 200. He declared formal independence and ruled from November 222 to May 229 as the King of Wu and from May 229 to May 252 as the Emperor of Wu. Unlike his rivals Cao Cao and Liu Bei, Sun Quan was much younger and governed his state mostly separate of politics and ideology. He is sometimes portrayed as neutral considering he adopted a flexible foreign policy between his two rivals with the goal of pursuing the greatest interests for the country. Sun Quan was born while his father Sun Jian served as the adjutant of Xiapi County. After Sun Jian's death in the early 190s, he and his family lived at various cities on the lower Yangtze, until Sun Ce carved out a warlord regime in the Jiangnan, Jiangdong region, based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Fancheng
The Battle of Fancheng or the Battle of Fan Castle was fought between the warlords Liu Bei and Cao Cao in 219 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. It is named after Fancheng in present-day Xiangyang, Hubei, a fortress that played a significant role in the battle. Background In 218, imperial physician Ji Ben, along with minor treasurer Geng Ji and minister Wei Huang began an insurrection against Cao Cao in his capital of Xuchang, but were quickly quelled and executed. In November 218, Cao Cao sent general Cao Ren to Wan (宛; in present-day Nanyang, Henan) in preparation to launch a strike against Guan Yu. However, due to Cao Ren's wanton policy of conscription and forced labor, Hou Yin (), a military officer under Cao Cao, started a rebellion in with his deputy Wei Kai () and several thousand troops from Wan's citizenry, and requested help from Guan Yu. By February 219, Cao Ren had crushed the rebellion and killed Hou Yin and Wei Kai, and massacred the citizenry of Wan. In the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jing Province
Jingzhou or Jing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China referenced in early Chinese texts such as the ''Yu Gong, Tribute of Yu'', ''Erya'', and ''Rites of Zhou''. Jingzhou became an administrative division during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han, Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BCE) in the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE–9 CE). It usually corresponded with the modern-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan until the Sui dynasty, after which it referred to the city of Jingzhou. History Pre-Qin era In the Warring States period, the Chu (state), Chu state covered most of present-day Hubei and Hunan, the areas that would form Jingzhou in a later era. The Qin (state), Qin state dropped the name "Chu" (楚) (literally "chaste tree") and used its synonym "Jing" (荊) instead to avoid a naming taboo, since the personal name of Qin's King Zhuangxiang of Qin, King Zhuangxiang (281–247 BCE) was "Zichu" (子楚; lit. "son of Chu") because his adoptive mother, Lady Huayang, was fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi Province
Yizhou (益州), Yi Province or Yi Prefecture, was a ''Zhou (country subdivision), zhou'' (province) of ancient China. Its capital city was Chengdu.de Crespigny, p. 256. During the Han dynasty, it included the commanderies Hanzhong Commandery, Hanzhong, Ba commandery, Ba, Guanghan Commandery, Guanghan, Shu Commandery, Shu, Wenshan Commandery, Wenshan, Jianwei Commandery, Jianwei, Zangke Commandery, Zangke, Yuexi Commandery, Yuexi, Yizhou Commandery, Yizhou and Yongchang Commandery, Yongchang. It was bordered in the north by Liang Province and Yong Province. At its greatest extent, Yi covered present-day central and eastern Sichuan, Chongqing, southern Shaanxi and parts of Yunnan and Guizhou. History During the First Great Qiang Rebellion (107–118) in Liang Province,de Crespigny, p. 10–11. unrest also spread to the Hanzhong and Wudu commanderies. In 188, Liu Yan (Han dynasty warlord), Liu Yan was appointed governor of Yi Province. Upon his death in 194, Yi passed to his son L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Boma
The Battle of Boma or Battle of Baima was the first of a series of battles that led to the decisive Battle of Guandu between the warlords Yuan Shao and Cao Cao in northern China in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Although Cao Cao won the battle and Yuan Shao lost his elite general Yan Liang, Cao eventually abandoned his position in Boma to entrench at the strategically important Guandu. Background By the 190s, the Eastern Han dynasty had fractured into warlordism. After years of reconfigurations and annexations, northern China was divided along the Yellow River by two warlords: Yuan Shao to the north and his former ally Cao Cao to the south. As it became obvious that a confrontation was inevitable, the two warlords scrambled to gather their forces in defensive positions along the Yellow River. At the time, Boma (白馬; near present-day Hua County, Henan) lay south of the river across from Liyang (黎陽; north-west of present-day Xun County, Henan), a major base for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Shao
Yuan Shao (, ; died 28 June 202), courtesy name Benchu (), was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. He occupied the northern territories of China during the civil wars that occurred towards the end of the Han dynasty. He was also an elder half-brother of Yuan Shu, a warlord who controlled the Huai River region, though the two were not on good terms with each other. One of the most powerful warlords of his time, Yuan Shao spearheaded a Campaign against Dong Zhuo, coalition of warlords against Dong Zhuo, who held Emperor Xian of Han, Emperor Xian hostage in the imperial capital, Luoyang, but failed due to internal disunity. In 200, he launched a campaign against his rival Cao Cao but was defeated at the Battle of Guandu. He died of illness two years later in Ye (ancient China), Ye. His eventual failure despite his illustrious family background and geographical advantages was commonly blamed on his indecisiveness and inabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yan Liang
Yan Liang () (died 200) was a military general serving under the warlord Yuan Shao during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was slain by Guan Yu at the Battle of Boma. Life Little is known about Yan Liang's life. The only historical records about him could be found in the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'', in the biographies of Yuan Shao, Guan Yu, Xun Yu''Sanguozhi'' vol. 10. and Cao Cao.''Sanguozhi'' vol. 1. By the time he becomes focus of any attention in the records, he had made a name along with Wen Chou as a figure celebrated for his bravery. In 200, the alliance between Cao Cao and Yuan Shao had turned to war with Yuan Shao led a major army against Cao Cao for the campaign of Guandu. Some in Cao Cao's camp where concerned about the war, the scholar and critic Kong Rong listing Yan Liang and Wen Chou's bravery as reasons to worry but Xun Yu dismissed it as bravery of a common sort that could easily be dealt with. As Yuan Shao's forces marched to Liyang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Cao
Cao Cao (; ; ; 15 March 220), courtesy name Mengde, was a Chinese statesman, warlord, and poet who rose to power during the end of the Han dynasty (), ultimately taking effective control of the Han central government. He laid the foundation for the state of Cao Wei (220–265), established by his son and successor Cao Pi, who ended the Eastern Han dynasty and inaugurated the Three Kingdoms period (220–280). Beginning in his own lifetime, a corpus of legends developed around Cao Cao which built upon his talent, his cruelty, and his perceived eccentricities. Cao Cao began his career as an official under the Han government and held various appointments including that of a district security chief in the capital and the chancellor of a Jun (country subdivision), principality. He rose to prominence in the 190s during which he recruited his own followers, formed his own army, and set up a base in Yan Province (covering parts of present-day Henan and Shandong). In 196, he received E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |