|
Qiao Zhou
Qiao Zhou (199 - 270), courtesy name Yunnan, was a Chinese astronomer, historian, politician, and writer of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He previously served under Liu Zhang, the Governor of Yi Province (covering present-day Sichuan and Chongqing) in the late Eastern Han dynasty before becoming a subject of the warlord Liu Bei, who established the Shu Han regime in 221. He is particularly notable for being the teacher of many Shu Han (and later Cao Wei / Western Jin) officials. Among them are Chen Shou, Luo Xian, Du Zhen, Wen Li and Li Mi. During his lifetime, Qiao Zhou was regarded as lacking talent and was not respected by many of his peers. Only Yang Xi regarded Qiao Zhou highly. Yang Xi even once said: "Like us, the later generations can never be as good as this great man." Because of this, Yang Xi earned praise from those individuals who also recognised Qiao Zhou for his talent. Qiao Zhou served in the Shu Han government from the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Huan
Cao Huan () (246 – 302/303), courtesy name Jingming, was the fifth and last emperor of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period. On 4 February 266, he abdicated the throne in favour of regent Sima Yan (later Emperor Wu of the Jin dynasty), and brought an end to the Wei regime. After his abdication, Cao Huan was granted the title " Prince of Chenliu" and held it until his death, after which he was posthumously honoured as "Emperor Yuan (of Cao Wei)". Family background and accession to the throne Cao Huan's birth name was "Cao Huang" (). His father, Cao Yu, the Prince of Yan, was a son of Cao Cao, the father of Wei's first emperor, Cao Pi. In 258, at the age of 12, in accordance with Wei's regulations that the sons of princes (other than the first-born son of the prince's spouse or wife, customarily designated the prince's heir) were to be instated as dukes, Cao Huan was instated as the "Duke of Changdao District" (). In June 260, after the ruling emperor Cao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luo Xian
Luo Xian (died 270), courtesy name Lingze, was a Chinese military general and politician of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period of China. After the fall of Shu in 263, he continued serving under the Cao Wei state, then the succeeding Jin dynasty in 266. He is best known for defending his position at Yong'an (present-day Fengjie County, Chongqing) for about six months against attacks from Shu's former ally state Wu after the fall of Shu. Historical sources Despite his prominence, Luo Xian is only mentioned in the biographies of others as Chen Shou did not write a exclusive biography for him in the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi''). Jin dynasty historian, Xi Zuochi wrote his biography in the ''Records of the Elders of Xiangyang'' (). In the 5th century, Pei Songzhi annotated Luo Xian's biography to Huo Yi's. His later biography in volume 57 of ''Book of Jin'' (''Jin Shu'') is nearly identical to the one wrote earlier. Early life Luo Xian's ancestral home (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astrology
Chinese astrology is based on traditional Chinese astronomy and the Chinese calendar. Chinese astrology flourished during the Han dynasty (2nd century BC to 2nd century AD). Chinese astrology has a close relation with Chinese philosophy (theory of the three harmonies: heaven, earth, and human), and uses the principles of yin and yang, '' wuxing'' (five phases), the ten Heavenly Stems, the twelve Earthly Branches, the lunisolar calendar (moon calendar and sun calendar), and the time calculation after year, month, day, and '' shichen'' (, double hour). These concepts are not readily found or familiar in Western astrology or culture. History and background Chinese astrology was elaborated during the Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) and flourished during the Han dynasty (2nd century BC to 2nd century AD). During the Han period, the familiar elements of traditional Chinese culture—the yin-yang philosophy, the theory and technology of the five elements ( Wuxing), the concepts of heav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romance Of The Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD and ending with the reunification of the land in 280 by the Western Jin. The novel is based primarily on the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'', written by Chen Shou in the 3rd century. The story – part historical and part fictional – romanticises and dramatises the lives of feudal lords and their retainers, who tried to supplant the dwindling Han dynasty or restore it. While the novel follows hundreds of characters, the focus is mainly on the three power blocs that emerged from the remnants of the Han dynasty, and would eventually form the three states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The novel deals with the plots, personal and military battles, intrigues, and struggles of these states to achieve dominance for almost 100 years. ''Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Wei
Wei () was one of the major Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic states in China during the Three Kingdoms period. The state was established in 220 by Cao Pi based upon the foundations laid by his father Cao Cao during the end of the Han dynasty. Its capital was initially located at Xuchang, and was later moved to Luoyang. The name ''Wei'' first became associated with Cao Cao when he was named the Duke of Wei by the Eastern Han government in 213, and became the name of the state when Cao Pi proclaimed himself emperor in 220. Historians often add the prefix "Cao" to distinguish it from other Chinese states known as ''Wei (other), Wei''. The authority of the ruling Cao family dramatically weakened following the deposition and execution of Cao Shuang, a regent for the dynasty's third emperor Cao Fang. Beginning in 249, another regent in Sima Yi gradually consolidated state authority for himself and his relatives, with the last Wei emperors largely being puppet ruler, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine-rank System
The nine-rank system, also known as the nine-grade controller system, was used to categorize and classify government officials by rank in Imperial China. Their accorded rank signified their status in the government hierarchy and the amount of wages they earned. Created by the politician Chen Qun in the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms, it was used until the Song dynasty, and similar ranking systems were also present in the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty. A similar system was also used in Korea. In Japan, the Twelve Level Cap and Rank System was adopted in 603 during the reign of Empress Suiko. History Background Prior to the nine-rank system, official positions were denoted by their salary paid in number of bushels of grain. For example, during the Han dynasty, the highest-ranking officials were classed as ''wandan'' (萬石), meaning ten thousand bushels, and were paid 350 bushels of grain per month. The lowest ranking petty subofficials were paid in pecks, worth le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi Zhongtian
Yi Zhongtian (born 8 February 1947) is a Chinese historian. He is also a professor and Ph.D. supervisor at the Department of Chinese Language and Literature at Xiamen University's School of Humanities. Life and career Yi's grandfather, Yi Silin (易思麟; 1885–1983), graduated from the Hunan Law School (湖南法政学堂; now part of Hunan University) and served as the acting county magistrate of Dao County, Hunan Province. He became a self-taught physician after leaving office. Yi's uncle, Yi Rengai (易仁荄; 1908–1990), graduated from Tsinghua University's Department of History in 1935. Yi's father, Yi Tingyuan (易庭源; 1919–2011), was an accountant. Yi spent his childhood in his birthplace, Changsha, Hunan Province, before moving to Wuhan, Hubei province at the age of six. He attended Yuemachang Primary School () and No. 1 Middle School attached to Central China Normal University (). Between 1965 and 1975, Yi went to Xinjiang to join the Xinjiang Product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Sheng (Jin Dynasty)
Sun Sheng (302–373), courtesy name Anguo, was a Chinese historian and politician of the Jin dynasty. He was a native of Pingyao County, Jinzhong, Shanxi. He was described to be very studious, and was never seen without holding a book in his hand from his youth to his old age. Life Sun Sheng's father Sun Xun (孫恂) was Grand Administrator of Yingchuan (潁川), in present-day Henan and Anhui. He was killed by bandits when Sun Sheng was nine, and the rest of the family fled to safety across the Yangtze River. In his young adulthood, Sun Sheng achieved fame as a serious scholar of the ''I Ching'', composing an essay which some of the leading luminaries of the time, including Yin Hao, Wang Meng, and Xie Shang were unable to debate with him. Parts of the essay, "''The Symbols of the Book of Changes are More Subtle than the Visible Shapes of Nature''", survive and have been translated by Richard B. Mather. After entering politics, Sun Sheng served under Tao Kan, Yu Liang, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Jin
Western may refer to: Places *Western, Nebraska, a village in the US * Western, New York, a town in the US * Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia * Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia *Western world, countries that identify with shared "Western" culture *Western United States, a region of the United States Arts and entertainment Films * ''Western'' (1997 film), a French road movie directed by Manuel Poirier * ''Western'' (2017 film), a German-Austrian film Genres *Western (genre), a category of fiction and visual art centered on the American Old West **Western fiction, the Western genre as featured in literature **Western film, the western genre in film **Western music (North America), a type of American folk music Music * ''Westerns'' (EP), an EP by Pete Yorn * WSTRN, a British hip hop group from west London *"Western" a song by Black Midi from ''Schlagenheim'' Business * The Western, a closed hotel/casino in Las Vegas, United States *Western C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanguozhi
The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is a Chinese official history written by Chen Shou in the late 3rd century CE, covering the end of the Han dynasty (220 CE) and the subsequent Three Kingdoms period (220–280 CE). It is regarded as to be the authoritative source text for these periods. Compiled following the reunification of China under the Jin dynasty (266–420), the work chronicles the political, social, and military events within rival states Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu into a single text organized by individual biography. The ''Records'' are the primary source of information for the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', considered to be one of the four classic novels emblematic of written vernacular Chinese. While large subsections of the work have been selected and translated into English, the entire corpus has yet to receive an unabridged English translation. Origin and structure The ''Book of Han'' and ''Records of the Thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
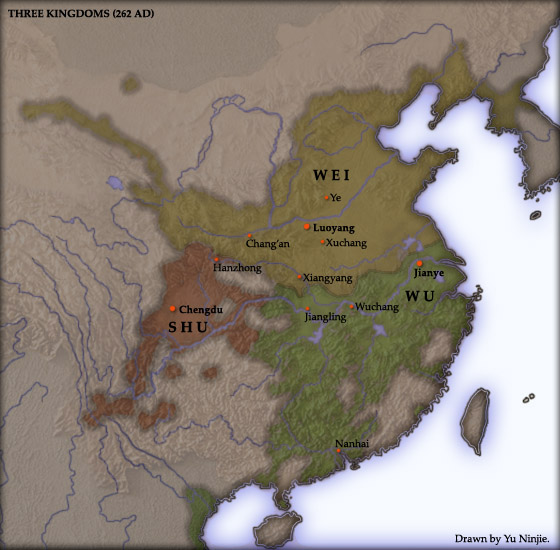
Conquest Of Shu By Wei
The Conquest of Shu by Wei was a military campaign launched by the dynastic state of Cao Wei against its rival Shu Han in late 263 during the Three Kingdoms period of China. The campaign culminated in the fall of Shu Han and the tripartite equilibrium maintained in China for over 40 years since the End of the Han dynasty, end of the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty in 220. The conquest laid the foundation for an eventual reunified China under the Jin dynasty (266–420)#Western Jin (266–316), Western Jin dynasty in 280. Background Following the End of the Han dynasty, end of the Eastern Han dynasty in 220, three contending states emerged in China and fought for control over the territories of the former Han Empire. Among the three, Cao Wei, Wei was the most powerful one in terms of military prowess, economic resources, manpower and geographical size. The other two, Shu Han, Shu and Eastern Wu, Wu, re-established their alliance against Wei in 223. Between 228 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Xi (Three Kingdoms)
Yang Xi (late 200s - 261), courtesy name Wenran, was a Chinese politician of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He is best known for writing the ''Ji Han Fuchen Zan'' (季漢輔臣贊; pub. 241), a collection of praises of notable persons who served in the Shu Han state. Chen Shou, the third-century historian who wrote the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi''), extensively quoted and annotated Yang Xi's collection. Life Yang Xi was from Wuyang County (武陽縣), Qianwei Commandery (犍為郡), which is present-day Pengshan District, Meishan, Sichuan. At a young age, Yang Xi was already quite well known in Shu. His fame put him on par with others such as Cheng Qi from Baxi Commandery, Yang Tai (楊汰) from Ba Commandery, and Zhang Biao from Shu Commandery. Yang Xi also often praised Cheng Qi as the most brilliant among the four of them. Zhuge Liang, the Imperial Chancellor of Shu, recognised and appreciated their talents. When Yang X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |