|
Qian Xuesen
Qian Xuesen ( zh, s=钱学森; December 11, 1911October 31, 2009; also spelled as Tsien Hsue-shen) was a Chinese aerospace engineer and cyberneticist who made significant contributions to the field of aerodynamics and established engineering cybernetics. He achieved recognition as one of America's leading experts in rockets and high-speed flight theory prior to his deportation to China in 1955. Qian received his undergraduate education in mechanical engineering at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, National Chiao Tung University in Shanghai in 1934. He traveled to the United States in 1935 and attained a master's degree in aeronautical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1936. Afterward, he joined Theodore von Kármán's group at the California Institute of Technology in 1936, received a doctorate in aeronautics and mathematics there in 1939, and became an associate professor at Caltech in 1943. While at Caltech, he co-founded NASA's Jet Propulsion Laborat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qian (surname)
Qian (; Shanghainese: ), also spelt Chin, Chien, Tsien, or Zee in Wu Chinese, is a common Chinese family name. The name literally means "money". Qian is listed at the second place in the Song Dynasty text ''Hundred Family Surnames'', in the line 趙錢孫李 (Zhao (surname) , Zhao, Qian, Sun (surname), Sun, Li (surname 李), Li). As the royal surname of the kingdom of Wuyue, Qian was regarded as second only to Zhao, the imperial surname of the Song. As of 2008, Qian is the 96th most common surname in China, shared by 2.2 million people, with the province with the most people sharing the name being Jiangsu, an area formerly within the Wuyue kingdom. Origins According to the Song dynasty book, ''Tongzhi (encyclopedia), Tongzhi'', the Qian surname is descended from Zhuanxu, one of the legendary Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors, Five Emperors, via Pengzu, the founder of the Peng kingdom in modern-day Jiangsu during the Shang dynasty. A Zhou dynasty official, Fu, was a descendant of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore Von Kármán
Theodore von Kármán ( , May 11, 1881May 6, 1963) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, aerospace engineer, and physicist who worked in aeronautics and astronautics. He was responsible for crucial advances in aerodynamics characterizing supersonic and hypersonic airflow. The human-defined threshold of outer space is named the " Kármán line" in recognition of his work. Kármán is regarded as an outstanding aerodynamic theoretician of the 20th century. Early life Theodore von Kármán was born into a Jewish family in Budapest, then part of Austria-Hungary, as Kármán Tódor, the son of Helene (Konn or Kohn, ) and . Among his ancestors were Rabbi Judah Loew ben Bezalel, who was said to be the creator of the Golem of Prague, and Rabbi , who wrote about Zohar. His father, Mór, was a well-known educator, who reformed the Hungarian school system and founded Minta Gymnasium in Budapest. He became an influential figure and became a commissioner of the Ministry of Educa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Red Scare
McCarthyism is a political practice defined by the political repression and persecution of left-wing individuals and a campaign spreading fear of communist and Soviet influence on American institutions and of Soviet espionage in the United States during the late 1940s through the 1950s, heavily associated with the Second Red Scare, also known as the McCarthy Era. After the mid-1950s, U.S. senator Joseph McCarthy, who had spearheaded the campaign, gradually lost his public popularity and credibility after several of his accusations were found to be false. The U.S. Supreme Court under Chief Justice Earl Warren made a series of rulings on civil and political rights that overturned several key laws and legislative directives, and helped bring an end to the Second Red Scare. Historians have suggested since the 1980s that as McCarthy's involvement was less central than that of others, a different and more accurate term should be used instead that more accurately conveys the breadth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel
Colonel ( ; abbreviated as Col., Col, or COL) is a senior military Officer (armed forces), officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations. In the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of a regiment in an army. Modern usage varies greatly, and in some cases, the term is used as an Colonel (title), honorific title that may have no direct relationship to military. In some smaller military forces, such as those of Monaco or the Holy See, Vatican, colonel is the highest Military rank, rank. Equivalent naval ranks may be called Captain (naval), captain or ship-of-the-line captain. In the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth's air force ranking system, the equivalent rank is group captain. History and origins By the end of the late medieval period, a group of "companies" was referred to as a "column" of an army. According to Raymond Oliver, , the Spanish began explicitly reorganizing part of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of War
The United States Department of War, also called the War Department (and occasionally War Office in the early years), was the United States Cabinet department originally responsible for the operation and maintenance of the United States Army, also bearing responsibility for naval affairs until the establishment of the United States Department of the Navy, Navy Department in 1798, and for most land-based air forces until the creation of the United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the Air Force on September 18, 1947. The United States Secretary of War, secretary of war, a civilian with such responsibilities as finance and purchases and a minor role in directing military affairs, headed the War Department throughout its existence. The War Department existed for 158 years, from August 7, 1789, to September 18, 1947, when it split into the United States Department of the Army, Department of the Army and the United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
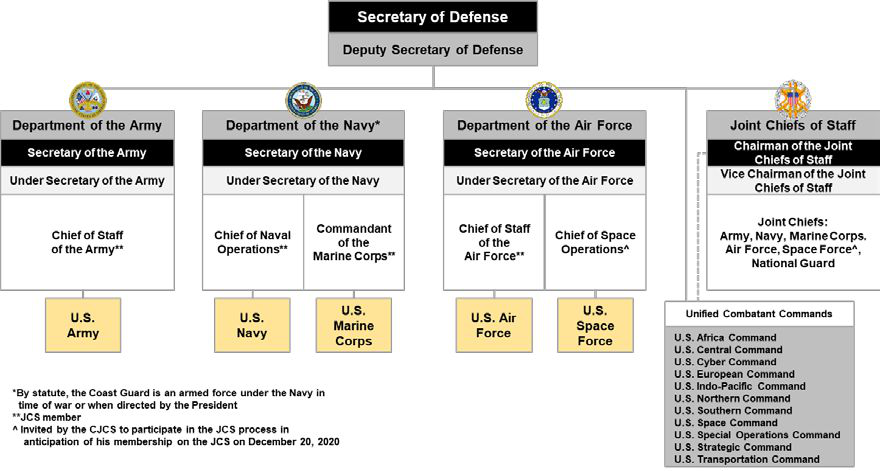
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics () is the study of the motion of atmosphere of Earth, air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics, and is an important domain of study in aeronautics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving Aircraft#Heavier-than-air – aerodynes, heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyberneticist
Cybernetics is the transdisciplinary study of circular causal processes such as feedback and recursion, where the effects of a system's actions (its outputs) return as inputs to that system, influencing subsequent action. It is concerned with general principles that are relevant across multiple contexts, including in engineering, Ecology, ecological, Economy, economic, Biological cybernetics, biological, Cognitive science, cognitive and social systems and also in practical activities such as Design, designing, learning, and Management cybernetics, managing. Cybernetics' transdisciplinary character has meant that it Intersection (set theory), intersects with a number of other fields, leading to it having both wide influence and diverse interpretations. The field is named after an example of circular causal feedback—that of steering a ship (the ancient Greek alphabet, Greek κυβερνήτης (''kybernḗtēs'') refers to the person who steers a ship). In steering a ship, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerospace Engineer
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is similar, but deals with the electronics side of aerospace engineering. "Aeronautical engineering" was the original term for the field. As flight technology advanced to include vehicles operating in outer space, the broader term "aerospace engineering" has come into use. Aerospace engineering, particularly the astronautics branch, is often colloquially referred to as "rocket science". Overview Flight vehicles are subjected to demanding conditions such as those caused by changes in atmospheric pressure and temperature, with structural loads applied upon vehicle components. Consequently, they are usually the products of various technological and engineering disciplines including aerodynamics, air propulsion, avionics, materials science, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang Ying (musician)
Jiang Ying (; August 11, 1919 – February 5, 2012) was a Chinese opera singer and music teacher. She was the wife of Chinese rocket scientist Qian Xuesen, to whom she was married from 1947 until 2009 (his death). Early life On 11 August 1919, Jiang was born in Haining, Jiaxing, Zhejiang province. Jiang was of Chinese and Japanese descent. She was the third daughter of Jiang Baili, a leading military strategist of Chiang Kai-shek, and his Japanese wife, . She was a distant relative of the wuxia novelist Louis Cha. Education In 1936 Jiang went to Europe with her father and studied music in Berlin. Jiang graduated from Universität der Künste Berlin in 1941. When World War II broke out in Europe, Jiang had to move and further studied opera in Switzerland. Jiang graduated from Musikhochschule Luzern in 1944. Career Jiang went back to China (at that time the Republic of China). On 31 May 1947, as a Chinese opera singer, Jiang first performed in Shanghai. In 1947, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two Bombs, One Satellite
Two Bombs, One Satellite ( zh, s=两弹一星, p=liǎng dàn, yī xīng) was a nuclear weapon, intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), and artificial satellite development program by the People's Republic of China. China detonated its first fission and first thermonuclear weapons in 1964 and 1967 respectively, combined a nuclear weapon with a surface-to-surface missile in 1966, and successfully launched its first satellite in 1970. History Proposal In the 1940s and 1950s, a group of notable scientists including Qian Weichang, Qian Xuesen, Deng Jiaxian, Peng Huanwu and Qian Sanqiang returned to mainland China. United States President Dwight D. Eisenhower's threats during the First Taiwan Strait Crisis to use nuclear weapons against military targets in Fujian province prompted Mao to begin China's nuclear program. In January 1955, Mao Zedong expressed the intention of developing atomic bombs during a meeting of the Secretariat of the Chinese Communist Party. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Academy Of Engineering
The Chinese Academy of Engineering (CAE, ) is the national academy of the People's Republic of China for engineering. It was established in 1994 and is an institution of the State Council of China. The CAE and the Chinese Academy of Sciences are often referred to together as the "Two Academies". Its current president is Li Xiaohong. Since its establishment, CAE has provided consultancy to the State on key programs, planning, guidelines, and policies at the request of government ministries and commissions. In response to requests from central and local government ministries, the academy has mobilized its members to conduct surveys, offer strategic opinions, and make proposals. These projects have been instrumental in enhancing member participation in the State's major decision-making processes. Additionally, members have regularly and actively contributed their insights and suggestions based on their experience, perspectives, and awareness of international engineering science a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |