|
Qena Mosque
Qena ( ' , locally: ) is a city in Upper Egypt, and the capital of the Qena Governorate. Situated on the east bank of the Nile, it was known in antiquity as Kaine (Greek Καινή, meaning "new (city)"; Latinized transliteration: Caene) and Maximianopolis. Gauthier identifies Qena with ancient Shabt. Qena meaning in Arabic "very red" of fertile land. Overview This provincial capital is located about 95 km from El Balyana and 63 km north of Luxor. It is most famous for its proximity to the ruins of Dendara. It owes its modern prosperity to the opening of the Wadi Qena towards the Red Sea, which is a major traffic route between Upper Egypt and the Red Sea. Tourists traveling between Luxor and the Red Sea will assuredly pass through this city since there is only one good road connection. Qena is noted for its pottery. Qena is also known for its beautiful huge mountains and green nature. South Valley University has a campus in Qena. Qena is a large market town on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quena
The quena (hispanicized spelling of Quechua ''qina'', sometimes also written ''kena'' in English) is the traditional flute of the Andes. Traditionally made of cane or wood, it has 6 finger holes and one thumb hole, and is open on both ends or the bottom is half-closed (choked). To produce sound, the player closes the top end of the pipe with the flesh between the chin and lower lip, and blows a stream of air downward, along the axis of the pipe, over an elliptical notch cut into the end. It is normally in the key of G, with G4 being the lowest note. It produces a very "textured" and "dark" timbre because of the length-to-bore ratio of about 16 to 20 (subsequently causing difficulty in the upper register), which is very unlike the tone of the Western concert flute with a length-to-bore ratio of about 38 to 20. The quenacho (also "kenacho" in English) is a greater, lower-toned version of the quena and made the same way. It is in the key of D, with D4 being the lowest note, a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Valley University
South Valley University (SVU) () is a university in Egypt that provides teaching and research facilities. The President of South Valley University is Prof. Dr. Ahmed Akkawy Abdulaziz. South Valley University is one of Egypt's more modern higher education institutions. It has 16 faculties split between its two campuses in Qena and Hurghada. Initially a branch of Assiut University, SVU was established in 1995. It has a second campus in the coastal city of Hurghada, just south of where the Gulf of Suez meets the Red Sea The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th .... Hurghada is home to the faculty of education. SVU has placed strongly among similar universities in the country in national rankings. Tuition fees are low for domestic and international students alike. More ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
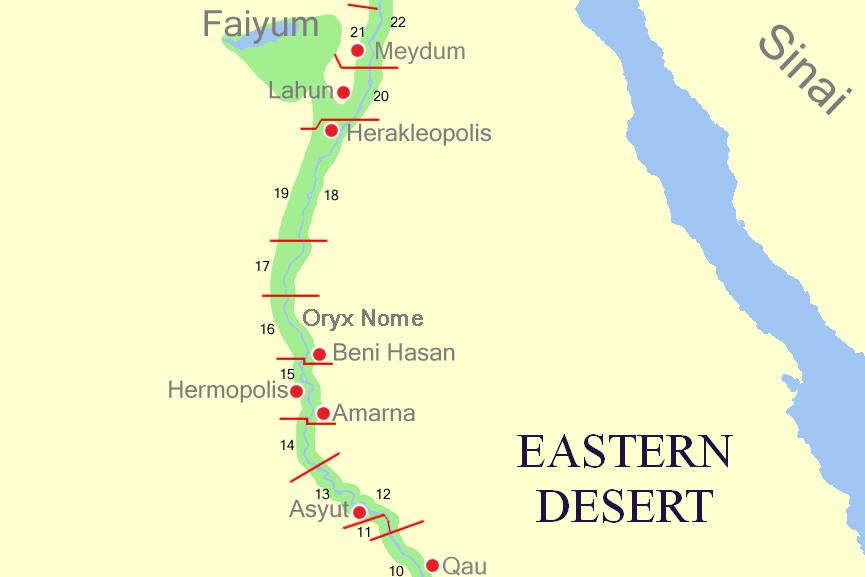
Asyut
AsyutAlso spelled ''Assiout'' or ''Assiut''. ( ' ) is the capital of the modern Asyut Governorate in Egypt. It was built close to the ancient city of the same name, which is situated nearby. The modern city is located at , while the ancient city is located at . The city is home to one of the largest Coptic Christian communities in the country. History Names and etymology The name of the city is derived from Egyptian language, early Egyptian (late Egyptian, Səyáwt) which became Coptic language, Coptic , meaning "''Guardian''" of the northern approach of Upper Egypt. In Graeco-Roman Ægyptus, Egypt, it was called Lycopolis or Lykopolis (, ""), ('wolf city') Lycon, or Lyco. Ancient Asyut Ancient Asyut was the capital of the Thirteenth Nome (Egypt), Nome of Upper Egypt (''Lycopolites Nome'') around 3100 BC. It was located on the western bank of the Nile. The two most prominent Egyptian pantheon, gods of ancient Egyptian Asyut were Anubis and Wepwawet, both funerary deities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minya, Egypt
MinyaAlso spelled '' el...'' or ''al...'' ''...Menia, ...Minia'' or ''...Menya'' ( ) is the capital of the Minya Governorate in Upper Egypt. It is located approximately south of Cairo on the western bank of the Nile River, which flows north through the city. Minya has one of the highest concentration of Coptic Christians in Egypt (approximately 50% of total population). It is the home city of the Minya University, Suzanne Mubarak Center for Arts, the new Minya Museum, and the regional North of Upper Egypt Radio and Television. Etymology The city's Arabic name comes from the Coptic, rendered in as ⲧⲙⲱⲛⲏ in Bohairic and ⲧⲙⲟⲟⲛⲉ in Sahidic, which in turn came from . The modern city of Minya is often identified with the Ancient Egyptian settlement of Men'at Khufu based on the resemblance of two names, although this claim, proposed by Gauthier and Drew-Bear, is denied by modern Egyptology as the former has a clear Greek etymology. Minya is dubbed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwealth usage), snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation; their water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate, so fog and mist do not fall. (Such a non-precipitating combination is a colloid.) Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated with water vapor: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called shower (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Desert Climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk'') is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert climates are dry and hold little moisture, quickly evaporating the already little rainfall they receive. Covering 14.2% of Earth's land area, hot deserts are the second-most common type of climate on Earth after the Polar climate. There are two variations of a desert climate according to the Köppen climate classification: a hot desert climate (''BWh''), and a cold desert climate (''BWk''). To delineate "hot desert climates" from "cold desert climates", a mean annual temperature of is used as an isotherm so that a location with a ''BW'' type climate with the appropriate temperature above this isotherm is classified as "hot arid subtype" (''BWh''), and a location with the appropriate temperature below the isotherm is classified as "cold ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International security, security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 194 Member states of UNESCO, member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the Non-governmental organization, non-governmental, Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 National Commissions for UNESCO, national commissions. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the events of World War II, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosque
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard. Originally, mosques were simple places of prayer for the early Muslims, and may have been open spaces rather than elaborate buildings. In the first stage of Islamic architecture (650–750 CE), early mosques comprised open and closed covered spaces enclosed by walls, often with minarets, from which the Adhan, Islamic call to prayer was issued on a daily basis. It is typical of mosque buildings to have a special ornamental niche (a ''mihrab'') set into the wall in the direction of the city of Mecca (the ''qibla''), which Muslims must face during prayer, as well as a facility for ritual cleansing (''wudu''). The pulpit (''minbar''), from which public sermons (''khutbah'') are delivered on the event of Friday prayer, was, in earlier times, characteristic of the central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world's Major religious groups, second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a Fitra, primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets and messengers, including Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, and Jesus in Islam, Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God in Islam, God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Torah in Islam, Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Gospel in Islam, Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad in Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenepolis (Egypt)
Kainepolis or Caenepolis (), also called Caene or Kaine (Καινή), was a town of ancient Egypt. It was the southernmost town of the Panopolite nome in the Thebaid of Egypt. It stood upon the eastern bank of the Nile, northwest of Coptos. Herodotus mentions a town Neapolis (Νέη πόλις), near Chemmis in Upper Egypt, which is probably the same with Caenepolis. The town later bore the name Maximianopolis (Μαξιμιανοῦ Πόλις). Panopolis, which was north of Chemmis, at one period went by the name of Caene or Caenepolis. Its site is located near the modern Qena. According to the Notitia Dignitatum the town was the station of Ala III Dromedariorum (a Roman auxiliary unit consisting of Dromedarii)., p. 444 See also * List of ancient Egyptian towns and cities This is a list of known ancient Egyptian towns and cities. http://www.u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |