|
Qabala
Qabala () is a city and the administrative centre of the Qabala District of Azerbaijan. The municipality consists of the city of Gabala and the village of Küsnət, Qabala, Küsnat. Before the city was known as Kutkashen, but after the Republic of Azerbaijan's independence the town was renamed in honour of the much older city of Gabala, the former capital of Caucasian Albania, the archaeological site of which is about 20 km southwest. History Antiquity Gabala is the ancient capital of Caucasian Albania. Archaeological evidence indicates that the city functioned as the capital of Caucasian Albania as early as the 4th century BC. Up to the present time, there are the ruins of the ancient city and the main gate of Caucasian Albania. Ongoing excavations near the village Chukhur show that Gabala from the 4th – 3rd centuries BC and up to the 18th century was one of the main cities with developed trade and crafts. The ruins of the ancient town are situated 15 km from the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qabala District
Qabala District () is one of the 66 Administrative divisions of Azerbaijan, districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the north of the country in the Shaki-Zagatala Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Oghuz District, Oghuz, Shaki District, Shaki, Agdash District, Agdash, Goychay District, Goychay, Ismayilli District, Ismayilli, Quba District (Azerbaijan), Quba, Qusar District, Qusar, and the Russian Republic of Dagestan. Its capital and largest city is Qabala. As of 2020, the district had a population of 107,800. History Qabala bears the name of the ancient Gabala, a city which was the capital of the ancient state of Caucasian Albania. The ruins of the old city are located 20 kilometres southwest of the present centre of the district. The remnants of the large buildings, city gates, tower walls and patterns of material culture indicate that Gabala was one of the most prominent cities at that time. Ancient Gabala was founded as a city in the late 4th-early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qutqashen Sultanate
Qutqashen Sultanate () also known as Qabala mahaly () was feudal state which existed from the middle to the end of 18th century in the north of Azerbaijan, in the territories covering the present day Qabala Rayon. Historical background Qabala was ancient capital of the Caucasian Albania. Archeological evidence indicates that the city functioned as the capital of the Caucasian Albania as early as the 4th century BC. Ruins of the ancient town are in 15 km from regional center, allocated on the territory between Garachay and Jourluchay rivers. Qabala was located in the middle of the 2500 old Silk Road and was mentioned in works of Pliny the Younger as "Kabalaka", Greek geographer Ptolemy as "Khabala", Arabic historian Ahmad ibn Yahya al-Baladhuri as "Khazar". In the 19th century, the Azerbaijani historian Abbasgulu Bakikhanov mentioned in his book "Gulistani Irem" that Kbala or Khabala were in fact Qabala. In 60s B.C., Roman troops attacked Caucasian Albania but did not succeed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
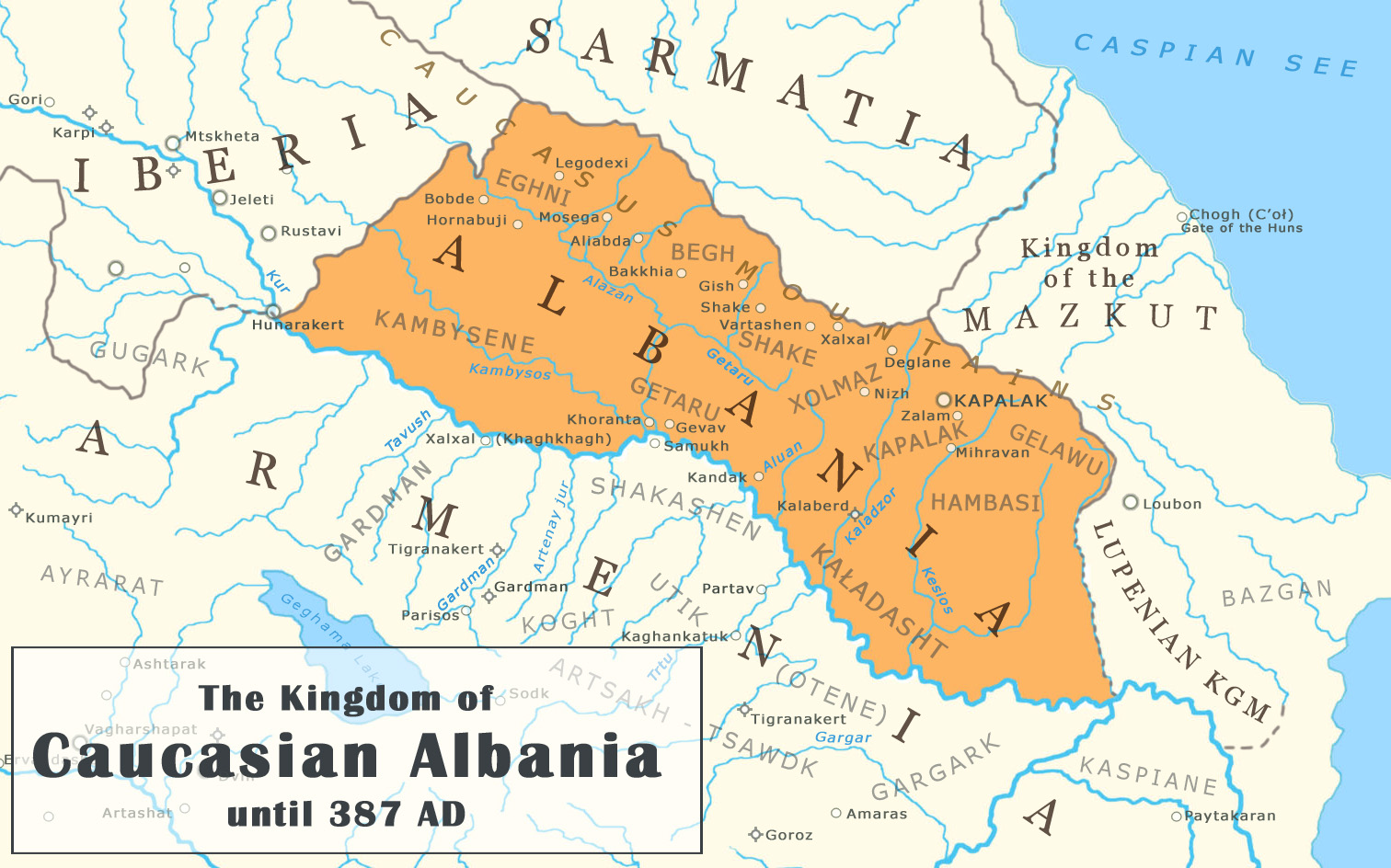
Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus, mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among the Udi people, who regard themselves as descended from the inhabitants of Caucasian Albania. However, its original endonym is unknown. The name Albania is derived from the Ancient Greek name and Latin , created from Greek sources that incorrectly translated the Armenian language. The prefix "Caucasian" is used to avoid confusion with Albania in the Balkans, which has no geographical or historical connections to Caucasian Albania. Little is known of the region's prehistory, including the origins of Caucasian Albania as a geographical and/or ethnolinguistic concept. In the 1st century BC and the 1st century AD, the area south of the Greater Caucasus and north of the Lesser Caucasus was divided between Caucasian Albania in the east, Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Küsnət, Qabala
Küsnət is a village in the Qabala Rayon of Azerbaijan Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by .... The village forms part of the municipality of Qəbələ. References * Populated places in Qabala District {{Qabala-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 67 districts () and 11 cities () that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these districts and cities, 7 districts and 1 city are located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into Municipalities of Azerbaijan, municipalities (). Additionally, the districts of Azerbaijan are grouped into 14 Economic regions of Azerbaijan, Economic Regions (). On 7 July 2021, President of Azerbaijan Ilham Aliyev signed a decree "On the new division of economic regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan". Administrative divisions Contiguous Azerbaijan The list below represents the districts of contiguous Azerbaijan. For those of the Nakhchivan exclave, see further below. Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic The seven districts and one municipality of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic are listed below. Economic regions Nagorno-Karabakh The territory of former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast presently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garachay
The Garachay () is a river in Quba district of Azerbaijan. It flows through the western end of an ancient city of Qabala. In the suburbs of Qabala, it joins other small rivers Hamzali, Mirazabeyli and Gojalan. It flows into the Turyan near the village Savalan.It originates from the northern slopes of the eastern part of the Greater Caucasus Range, near the peak of Babadag and eventually flows into the Caspian Sea. See also *Rivers and lakes in Azerbaijan *Nature of Azerbaijan The environment of Azerbaijan includes a wide diversity of climates, animals, plants, and habitats. National protection Due to the tapping of oil reserves in the early 20th century, Azerbaijan has had sufficient resources to develop an indus ... References External linksQabala Executive Power: Rivers section Rivers of Azerbaijan Qabala District {{Azerbaijan-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaki, Azerbaijan
Shaki (, ) is a city in northwestern Azerbaijan, surrounded by the district of the same name. It is located in the southern part of the Greater Caucasus mountain range, from Baku. As of 2020, it has a population of 68,400. The center of the city and the Palace of Shaki Khans were inscribed in the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2019 because of their unique architecture and history as an important trading center along the Silk Road. Etymology According to the Azerbaijani historians, the name of the town goes back to the ethnonym of the Sakas, who reached the territory of modern-day Azerbaijan in the 7th century B.C. and populated it for several centuries. In the medieval sources, the name of the town is found in various forms such as Sheke, Sheki, Shaka, Shakki, Shakne, Shaken, Shakkan, Shekin. The city was known as ''Nukha'' (; ) until 1968. History Antiquity There are traces of large-scale settlements in Shaki dating back to more than 2700 years ago. The Sakas were an I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David IV Of Georgia
David IV, also known as David IV the Builder ( ka, დავით IV აღმაშენებელი, tr; 1073 – 24 January 1125), of the Bagrationi dynasty, was the 5th king ('' mepe'') of the Kingdom of Georgia from 1089 until his death in 1125. Popularly considered to be the greatest and most successful Georgian ruler in history and an original architect of the Georgian Golden Age, he succeeded in driving the Seljuk Turks out of the country, winning the Battle of Didgori in 1121. His reforms of the army and administration enabled him to reunite the country and bring most of the lands of the Caucasus under Georgia's control. A friend of the Church and a notable promoter of Christian culture, he was canonized by the Georgian Orthodox Church. Sobriquet and regnal ordinal The epithet (), which is translated as (in the sense of "built completely"), , or , first appears as the sobriquet of David in the charter issued in the name of "King of Kings Bagrat" in 1452 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirvanshah
The Shirvanshahs (Arabic/) were the rulers of Shirvan (in present-day Azerbaijan) from 861 to 1538. The first ruling line were the Yazidids, an originally Arab and later Persianized dynasty, who became known as the Kasranids (also referred to as the Khaqanids). The second ruling line were the Darbandi, distant relatives of the Yazidids/Kasranids. The Shirvanshahs ruled from 861 to 1538, one of the most enduring dynasties of the Islamic world. At times they were independent, often they had to recognize the overlordship of neighbouring empires. The dynasty is known for its patronage of culture, such as during the 12th-century, when their realm served as the focal point for Persian literature, attracting distinguished poets such as Khaqani, Nizami Ganjavi, Falaki Shirvani, etc. In 1382, the Shirvanshah throne was taken by Ibrahim I (), thus marking the start of the Darbandi line. The Shirvanshah realm flourished in the 15th century, during the long reigns of Khalilullah I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barda, Azerbaijan
Barda ( ) is a city and the capital of the Barda District in Azerbaijan, located south of Yevlax and on the left bank of the Tartar river. It served as the capital of Caucasian Albania by the end of the 5th century. Barda became the chief city of the Islamic province of Arran, the classical Caucasian Albania, remaining so until the 10th century. Etymology The name of the town derives from () which derives from Old Armenian ''Partaw'' ( Պարտաւ). The etymology of the name is uncertain. According to the Iranologist Anahit Perikhanian, the name is derived from Iranian *''pari-tāva-'' 'rampart', from *''pari-'' 'around' and *tā̆v- 'to throw; to heap up'. According to the Russian-Dagestani historian Murtazali Gadjiev, however, the name means "Parthian/Arsacian" (cf. Parthian ''*Parθaυ''; Middle Persian: ''Pahlav''; Old Persian: ''Parθaυa-''). The name is attested in Georgian as ''Bardav ' (ბარდავი). History Ancient According to '' The History of the Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by the Caspian Sea to the east, Russia's republic of Dagestan to the north, Georgia (country), Georgia to the northwest, Armenia and Turkey to the west, and Iran to the south. Baku is the capital and largest city. The territory of what is now Azerbaijan was ruled first by Caucasian Albania and later by various Persian empires. Until the 19th century, it remained part of Qajar Iran, but the Russo-Persian wars of Russo-Persian War (1804–1813), 1804–1813 and Russo-Persian War (1826–1828), 1826–1828 forced the Qajar Empire to cede its Caucasian territories to the Russian Empire; the treaties of Treaty of Gulistan, Gulistan in 1813 and Treaty of Turkmenchay, Turkmenchay in 1828 defined the border between Russia and Iran. The region north o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |