|
Q-Chem Postcard
Q-Chem is a general-purpose electronic structure package featuring a variety of established and new methods implemented using innovative algorithms that enable fast calculations of large systems on various computer architectures, from laptops and regular lab workstations to midsize clusters and HPCC, using density functional and wave-function based approaches. It offers an integrated graphical interface and input generator; a large selection of functionals and correlation methods, including methods for electronically excited states and open-shell systems; solvation models; and wave-function analysis tools. In addition to serving the computational chemistry community, Q-Chem also provides a versatile code development platform. History Q-Chem software is maintained and distributed by Q-Chem, Inc., located in Pleasanton, California, USA. It was founded in 1993 as a result of disagreements within the Gaussian company that led to the departure (and subsequent "banning") of John Pople ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Head-Gordon
Martin Philip Head-Gordon (''né'' Martin Philip Head) is a professor of chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory working in the area of computational quantum chemistry. He is a member of the International Academy of Quantum Molecular Science. Education A native of Australia, Head-Gordon received his Bachelor of Science and Master of Science degrees from Monash University, followed by a PhD from Carnegie Mellon University working under the supervision of John Pople developing a number of useful techniques including the Head-Gordon-Pople scheme for the evaluation of integrals, and the orbital rotation picture of orbital optimization. Career and research At Berkeley, Martin supervises a group interested in pairing methods, local correlation methods, dual-basis methods, scaled MP2 methods, new efficient algorithms, and very recently corrections to the Kohn-Sham density functional framework. Broadly speaking, wavefunction bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Møller–Plesset Perturbation Theory
Møller–Plesset perturbation theory (MP) is one of several quantum chemistry post–Hartree–Fock ab initio methods in the field of computational chemistry. It improves on the Hartree–Fock method by adding electron correlation effects by means of Rayleigh–Schrödinger perturbation theory (RS-PT), usually to second (MP2), third (MP3) or fourth (MP4) order. Its main idea was published as early as 1934 by Christian Møller and Milton S. Plesset. Rayleigh–Schrödinger perturbation theory The MP perturbation theory is a special case of RS perturbation theory. In RS theory one considers an unperturbed Hamiltonian operator \hat_, to which a small (often external) perturbation \hat is added: :\hat = \hat_ + \lambda \hat. Here, ''λ'' is an arbitrary real parameter that controls the size of the perturbation. In MP theory the zeroth-order wave function is an exact eigenfunction of the Fock operator, which thus serves as the unperturbed operator. The perturbation is the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-dependent Density Functional Theory
Time-dependent density-functional theory (TDDFT) is a quantum mechanical theory used in physics and chemistry to investigate the properties and dynamics of many-body systems in the presence of time-dependent potentials, such as electric or magnetic fields. The effect of such fields on molecules and solids can be studied with TDDFT to extract features like excitation energies, frequency-dependent response properties, and photoabsorption spectra. TDDFT is an extension of density-functional theory (DFT), and the conceptual and computational foundations are analogous – to show that the (time-dependent) wave function is equivalent to the (time-dependent) electronic density, and then to derive the effective potential of a fictitious non-interacting system which returns the same density as any given interacting system. The issue of constructing such a system is more complex for TDDFT, most notably because the time-dependent effective potential at any given instant depends o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
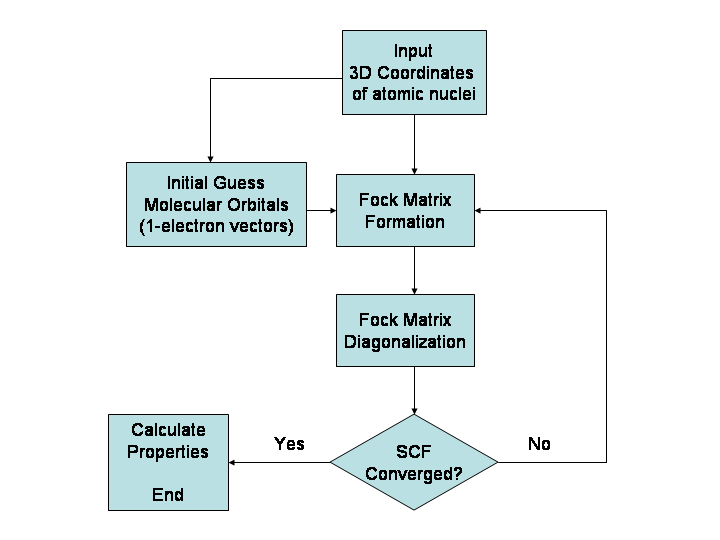
Hartree–Fock Method
In computational physics and chemistry, the Hartree–Fock (HF) method is a method of approximation for the determination of the wave function and the energy of a quantum many-body system in a stationary state. The Hartree–Fock method often assumes that the exact ''N''-body wave function of the system can be approximated by a single Slater determinant (in the case where the particles are fermions) or by a single permanent (in the case of bosons) of ''N'' spin-orbitals. By invoking the variational method, one can derive a set of ''N''-coupled equations for the ''N'' spin orbitals. A solution of these equations yields the Hartree–Fock wave function and energy of the system. Especially in the older literature, the Hartree–Fock method is also called the self-consistent field method (SCF). In deriving what is now called the Hartree equation as an approximate solution of the Schrödinger equation, Hartree required the final field as computed from the charge distributi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
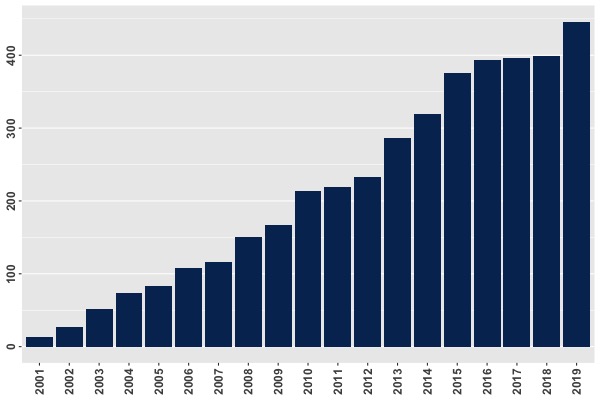
Q-Chem Developer Activity (2019)
Q-Chem is a general-purpose electronic structure package featuring a variety of established and new methods implemented using innovative algorithms that enable fast calculations of large systems on various computer architectures, from laptops and regular lab workstations to midsize clusters and HPCC, using density functional and wave-function based approaches. It offers an integrated graphical interface and input generator; a large selection of functionals and correlation methods, including methods for electronically excited states and open-shell systems; solvation models; and wave-function analysis tools. In addition to serving the computational chemistry community, Q-Chem also provides a versatile code development platform. History Q-Chem software is maintained and distributed by Q-Chem, Inc., located in Pleasanton, California, USA. It was founded in 1993 as a result of disagreements within the Gaussian company that led to the departure (and subsequent "banning") of John Pople ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Community Grid
World Community Grid (WCG) is an effort to create the world's largest volunteer computing platform to tackle scientific research that benefits humanity. Launched on November 16, 2004, with proprietary Grid MP client from United Devices and adding support for Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing (BOINC) in 2005, World Community Grid eventually discontinued the Grid MP client and consolidated on the BOINC platform in 2008. In September 2021, it was announced that IBM transferred ownership to the Krembil Research Institute of University Health Network in Toronto, Ontario. World Community Grid utilizes unused processing power of consumer devices (PCs, Laptops, Android Smartphones, etc.) to analyse data created by the research groups that participate in the grid. WCG projects have analysed data related to the human genome, the human microbiome, HIV, dengue, muscular dystrophy, cancer, influenza, Ebola, Zika virus, virtual screening, rice crop yields, clean energy, wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clean Energy Project
The Clean Energy Project (CEP) was a virtual high-throughput discovery and design effort for the next generation of plastic solar cell materials that has finished. It studies millions of candidate structures to identify suitable compounds for the harvesting of renewable energy from the sun and for other organic electronic applications. It ran on the BOINC platform. Project purpose The project searched for the most suitable organic compounds with which to make solar cells, the best polymeric membranes with which to make fuel cells, and how best to assemble the molecules for such devices. Current project status On June 24, 2013, the Clean Energy Project released its database to the public and the research community. The release was featured on the White House Blog and by several news organizations including the MIT Technology Review. The database contains 150 million density functional theory calculations on 2.3 million molecules. Publications * C. Amador-Bedolla, R. Olivares-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citations
A citation is a reference to a source. More precisely, a citation is an abbreviated alphanumeric expression embedded in the body of an intellectual work that denotes an entry in the bibliographic references section of the work for the purpose of acknowledging the relevance of the works of others to the topic of discussion at the spot where the citation appears. Generally, the combination of both the in-body citation and the bibliographic entry constitutes what is commonly thought of as a citation (whereas bibliographic entries by themselves are not). Citations have several important purposes. While their uses for upholding intellectual honesty and bolstering claims are typically foregrounded in teaching materials and style guides (e.g.,), correct attribution of insights to previous sources is just one of these purposes. Linguistic analysis of citation-practices has indicated that they also serve critical roles in orchestrating the state of knowledge on a particular topic, identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Krylov
Anna I. Krylov (Russian: Анна Игоревна Крылова) is a Professor of Chemistry at the University of Southern California (USC), working in the field of theoretical and computational quantum chemistry. She is the inventor of the spin-flip method. Krylov is the president of Q-Chem, Inc. and an elected member of the International Academy of Quantum Molecular Science and the Academia Europaea. Life and education Born in Donetsk, Ukraine (May 6, 1967), Krylov received her M.Sc. (with honors) in Chemistry from Moscow State University in 1990 and her Ph.D. (summa cum laude) from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem working under the supervision of Professor Robert Benny Gerber. Her Ph.D. research at the Fritz Haber Center focused on molecular dynamics in rare gas clusters and matrices. Career Upon completing her Ph.D. in 1996, she joined the group of Prof. Martin Head-Gordon at the University of California, Berkeley, as a postdoctoral research associate, where she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry F
Henry may refer to: People * Henry (given name) * Henry (surname) * Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry Royalty * Portuguese royalty ** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal ** Henry, Count of Portugal, Henry of Burgundy, Count of Portugal (father of Portugal's first king) ** Prince Henry the Navigator, Infante of Portugal ** Infante Henrique, Duke of Coimbra (born 1949), the sixth in line to Portuguese throne * King of Germany **Henry the Fowler (876–936), first king of Germany * King of Scots (in name, at least) ** Henry Stuart, Lord Darnley (1545/6–1567), consort of Mary, queen of Scots ** Henry Benedict Stuart, the 'Cardinal Duke of York', brother of Bonnie Prince Charlie, who was hailed by Jacobites as Henry IX * Four kings of Castile: ** Henry I of Castile ** Henry II of Castile ** Henry III of Castile ** Henry IV of Castile * Five kings of France, spelt ''Henri'' in Modern French since the Renaissance to italianize the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Chemistry
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions to physical and chemical properties of molecules, materials, and solutions at the atomic level. These calculations include systematically applied approximations intended to make calculations computationally feasible while still capturing as much information about important contributions to the computed wave functions as well as to observable properties such as structures, spectra, and thermodynamic properties. Quantum chemistry is also concerned with the computation of quantum effects on molecular dynamics and chemical kinetics. Chemists rely heavily on spectroscopy through which information regarding the quantization of energy on a molecular scale can be obtained. Common methods are infra-red (IR) spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |