|
Pyrethrum Paczoskii
''Pyrethrum'' was a genus of several Old World plants now classified in either ''Chrysanthemum'' or ''Tanacetum'' which are cultivated as ornamentals for their showy flower heads. Pyrethrum continues to be used as a common name for plants formerly included in the genus ''Pyrethrum''. Pyrethrum is also the name of a natural insecticide made from the dried flower heads of ''Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium'' and '' Chrysanthemum coccineum''. The insecticidal compounds present in these species are pyrethrins. Description Some members of the genus ''Chrysanthemum'', such as the following two, are placed in the genus ''Tanacetum'' instead by some botanists. Both genera are members of the daisy (or aster) family, Asteraceae. They are all perennial plants with a daisy-like appearance and white petals. * ''Tanacetum cinerariifolium'' is called the Dalmatian chrysanthemum, denoting its origin in that region of the Balkans (Dalmatia). It looks more like the common daisy than other pyrethrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysanthemum
Chrysanthemums ( ), sometimes called mums or chrysanths, are flowering plants in the Asteraceae family. They are native to East Asia and northeastern Europe. Most species originate from East Asia, and the center of diversity is in China. Countless horticultural varieties and cultivars exist. Description The genus ''Chrysanthemum'' are perennial herbaceous flowering plants, sometimes subshrubs. The leaves are alternate, divided into leaflets and may be pinnatisect, lobed, or serrate (toothed) but rarely entire; they are connected to stalks with hairy bases. The compound inflorescence is an array of several flower heads, or sometimes a solitary head. The head has a base covered in layers of phyllaries. The simple row of ray florets is white, yellow, or red. The disc florets are yellow. Pollen grains are approximately 34 microns. The fruit is a ribbed achene. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Repellent
An insect repellent (also commonly called "bug spray" or "bug deterrent") is a substance applied to the skin, clothing, or other surfaces to discourage insects (and arthropods in general) from landing or climbing on that surface. Insect repellents help prevent and control the outbreak of insect-borne (and other arthropod-bourne) diseases such as malaria, Lyme disease, dengue fever, bubonic plague, river blindness, and West Nile fever. Pest animals commonly serving as vectors for disease include insects such as flea, fly, and mosquito; and ticks (arachnids). Some insect repellents are insecticides (bug killers), but most simply discourage insects and send them flying or crawling away. Effectiveness Synthetic repellents tend to be more effective and/or longer lasting than "natural" repellents. For protection against ticks and mosquito bites, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommends DEET, icaridin (picaridin, KBR 3023), oil of lemon eucalyptus (OLE), para-me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
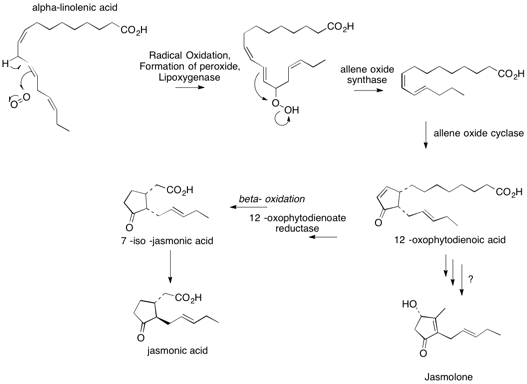
Jasmolone
Jasmolone is an irregular monoterpene. Irregular monoterpenes are derived from two isoprene C5 units, but do not follow the usual head-to-tail coupling mechanism. Jasmolins are found in pyrethrum flowers. They can specifically be found in the flower heads of ''Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium''. Jasmolins act as an insecticide for the flower. It is found in the cytoplasm of plants. Jasmolone is part of the secondary alcohol family. Jasmolone is found in the alcohol portion of pyrethrins. It is thought that jasmolone is a derivative of cyclized and altered fatty acids. The cyclization of the fatty acids is similar to the biosynthetic pathway cyclization of prostaglandins. A precursor of jasmolone could be alpha-linolenic acid with a 12-oxophytodienoic acid intermediate. The chain shortening could be produced by a beta-oxidation then a decarboxylation. 12-Oxophytodienoic acid is also used in the production of jasmonic acid. Jasmonic acid is used in the production of secondary metabo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinerin
The pyrethrins are a class of organic compounds normally derived from '' Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium'' that have potent insecticidal activity by targeting the nervous systems of insects. Pyrethrin naturally occurs in chrysanthemum flowers and is often considered an organic insecticide when it is not combined with piperonyl butoxide or other synthetic adjuvants.Mader, Eric, and Nancy Lee Adamson. "Organic-Approved Pesticides."Organic-Approved Pesticides (n.d.): n. pag. The Xerxes Society. The Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation, Oct. 2012. Web. 10 Mar. 2015. Their insecticidal and insect-repellent properties have been known and used for thousands of years. Pyrethrins are gradually replacing organophosphates and organochlorides as the pesticides of choice as the latter compounds have been shown to have significant and persistent toxic effects to humans. They first appeared on markets in the 1900s and have been continually used since then in products such as bug bombs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Broadcasting Corporation
The Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) is Australia’s principal public service broadcaster. It is funded primarily by grants from the federal government and is administered by a government-appointed board of directors. The ABC is a publicly-owned statutory organisation that is politically independent and accountable; for example, through its production of annual reports, and is bound by provisions contained within the Public Interest Disclosure Act 2013 and the Public Governance, Performance and Accountability Act 2013, with its charter enshrined in legislation, the ''Australian Broadcasting Corporation Act 1983''. ABC Commercial, a profit-making division of the corporation, also helps generate funding for content provision. The ABC was established as the Australian Broadcasting Commission on 1 July 1932 by an Act of Federal Parliament. It effectively replaced the Australian Broadcasting Company, a private company established in 1924 to provide programming for A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell ( cytotoxicity) or an organ such as the liver ( hepatotoxicity). Sometimes the word is more or less synonymous with poisoning in everyday usage. A central concept of toxicology is that the effects of a toxicant are dose-dependent; even water can lead to water intoxication when taken in too high a dose, whereas for even a very toxic substance such as snake venom there is a dose below which there is no detectable toxic effect. Toxicity is species-specific, making cross-species analysis problematic. Newer paradigms and metrics are evolving to bypass animal testing, while maintaining the concept of toxicity endpoints. Etymology In Ancient Greek medical literature, the adjective ''τοξικόν'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperonyl Butoxide
Piperonyl butoxide (PBO) is a pale yellow to light brown liquidNational Toxicology Program, Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health (NTP). 1992. National Toxicology Program Chemical Repository Database. Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. organic compound used as an adjuvant component of pesticide formulations for synergy. That is, despite having no pesticidal activity of its own, it enhances the potency of certain pesticides such as carbamates, pyrethrins, pyrethroids, and rotenone. It is a semisynthetic derivative of safrole and is produced from the condensation of the sodium salt of 2-(2-butoxyethoxy) ethanol and the chloromethyl derivative of hydrogenated safrole (dihydrosafrole); or through 1,2-Methylenedioxybenzene. History PBO was developed in the late 1930s and early 1940s to enhance the performance of the naturally derived insecticide pyrethrum. Pyrethrum is a type of potent insecticide that kills mosquitoes and other disease-ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permethrin
Permethrin is a medication and an insecticide. As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed onto outer clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects that touch them. Side effects include rash and irritation where it is Topical medication, applied. Use during pregnancy appears to be safe, and it is approved for use on and around people over the age of two months in the United States. Permethrin is in the pyrethroid family of medications. It works by disrupting the function of the neurons of lice and scabies mites. Permethrin was discovered in 1972. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2022, it was the 351st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 40,000 prescriptions. Uses Insecticide * In agriculture, to protect crops (a drawback is that it is lethal to bees) * In agricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrethroid
A pyrethroid is an organic compound similar to the natural pyrethrins, which are produced by the flowers of pyrethrums (''Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium'' and ''Chrysanthemum coccineum, C. coccineum''). Pyrethroids are used as commercial and household insecticides. In household concentrations pyrethroids are generally harmless to humans. However, pyrethroids are toxic to insects such as bees, dragonflies, mayflies, Horse-fly, gadflies, and some other invertebrates, including those that constitute the base of aquatic and terrestrial food webs. Pyrethroids are toxic to aquatic organisms, especially fish.Pyrethroids fact sheet from the Illinois Department of Public Health. They have been shown to be an effective control measure for malaria outbreaks, through indoor applications. ...
|
Johann Zacherl
Johann Zacherl (1814 – 30 June 1888) was an Austrian inventor, industrialist and manufacturer who made a fortune in the late 19th century selling dried flower heads of ''Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium'' as an insecticide. Biography Zacherl was born in Munich (Germany) in 1814. After finishing his studies, he left Munich to visit Vienna, St Petersburg and Odessa. He eventually reached Tiflis in the Caucasus, where he discovered villagers used a natural insecticide, Pyrethrum, against vermin. He began to develop the powder's trade with Austria in 1842. The powder received different names: Lowizachek (in Armenia), Bug Flower, Powder of Persia and Persian insect powder. After a longer stay in Tiflis, in 1855 he established his company, ''Mottenfraß-Versicherungsunternehmung Johann Zacherl'', in Vienna's 19th district, and began selling the insect repellent ''Zacherlin''. With the help of his son, Johann Evangelist, he developed the Pyrethrum product line. Zacherl died in Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacherlin
Johann Zacherl (1814 – 30 June 1888) was an Austria-Hungary, Austrian inventor, industrialist and manufacturer who made a fortune in the late 19th century selling dried flower heads of ''Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium'' as an insecticide. Biography Zacherl was born in Munich (Germany) in 1814. After finishing his studies, he left Munich to visit Vienna, St Petersburg and Odessa. He eventually reached Tiflis in the Caucasus, where he discovered villagers used a natural insecticide, Pyrethrum, against vermin. He began to develop the powder's trade with Austria in 1842. The powder received different names: Lowizachek (in Armenia), Bug Flower, Powder of Persia and Persian insect powder. After a longer stay in Tiflis, in 1855 he established his company, ''Mottenfraß-Versicherungsunternehmung Johann Zacherl'', in Vienna's Döbling, 19th district, and began selling the insect repellent ''Zacherlin''. With the help of his son, Johann Evangelist, he developed the Pyrethrum product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Powder
Persian powder is an insecticide powder with natural pyrethrin as the active agent. It is also known as Persian pellitory, insect powder and internationally as pyrethrum. Biological pest control Persian powder is a green pesticide that has been used for centuries for the biological pest extermination of household insects, garden pests, and agricultural pests.''Bioaromatica'The history of pyrethrum It may first have been exported from Persia to Ancient Rome. Pyrethrin and pyrethroids are used indoors, in gardens and the horticulture industry, and in agriculture. It is produced from the powdered flowers of certain species of pyrethrum, plants in the genera ''Chrysanthemum'' and '' Tanacetum''. In more recent times it has had formulations with brand names such as Zacherlin. Synthetic forms Pyrethroids are synthetic insecticides based on natural pyrethrum (pyrethrins), such as permethrin. A common formulation of pyrethrin is in preparations containing the synthetic chemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |