|
Pyramid Of Hellinikon
Greek pyramids, also known as the Pyramids of Argolis, refers to several ancient structures located in the plains of Argolid, Greece. The best known of these is known as the Pyramid of Hellinikon (). During the time of the geographer Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias it was considered to be a tomb. Twentieth century researchers have suggested other possible uses. The surrounding country of Apobathmi was termed Pyramia (Πυράμια), from the monuments in the form of pyramids found there. Background In addition to at least two pyramids which no longer exist, there are two surviving pyramid-like structures, the Pyramid of Hellinikon and another at Lygourio, a village near the Ancient Theatre of Epidaurus. At the southeastern edge of the plain of Argos, near the springs of river Erasinos (spring of Kefalari (Argolis), Kefalari) and on the main arterial road which during classical antiquity, antiquity led from Ancient Argos, Argos to Tegea and the rest of Arcadia (ancient region) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argolis
Argolis or Argolida ( , ; , in ancient Greek and Katharevousa) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, situated in the eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula and part of the tripoint area of Argolis, Arcadia (ancient region), Arcadia and Corinthia. Much of the territory of this region is situated in the Argolid Peninsula. Geography Most arable land lies in the central part of Argolis. Its primary agricultural resources are orange (fruit), oranges and olives. Argolis has a coastline on the Saronic Gulf in the northeast and on the Argolic Gulf in the south and southeast. Notable mountains ranges are the Oligyrtos in the northwest, Lyrkeio and Ktenia in the west, and Arachnaio and Didymo (mountain), Didymo in the east. Argolis has land borders with Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia to the west and southwest, Corinthia to the north, and the Islands (regional unit), Islands regional unit (Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tegea
Tegea (; ) was a settlement in ancient Arcadia, and it is also a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the Tripoli municipality, of which it is a municipal unit with an area of 118.350 km2. It is near the modern villages of Alea and Episkopi. The legendary founder of Tegea was Tegeates, a son of Lycaon. History Tegea (; ) was one of the most ancient and powerful towns of ancient Arcadia, situated in the southeast of the country. Its territory, called Tegeatis (Τεγεᾶτις), was bounded by Cynuria and Argolis on the east, from which it was separated by Mount Parthenium, by Laconia on the south, by the Arcadian district of Maenalia on the west, and by the territory of Mantineia on the north. The Tegeatae are said to have derived their name from Tegeates, a son of Lycaon, and to have dwelt originally in eight, afterwards nine, demoi or townships. In the Archaic period the nine demoi that und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
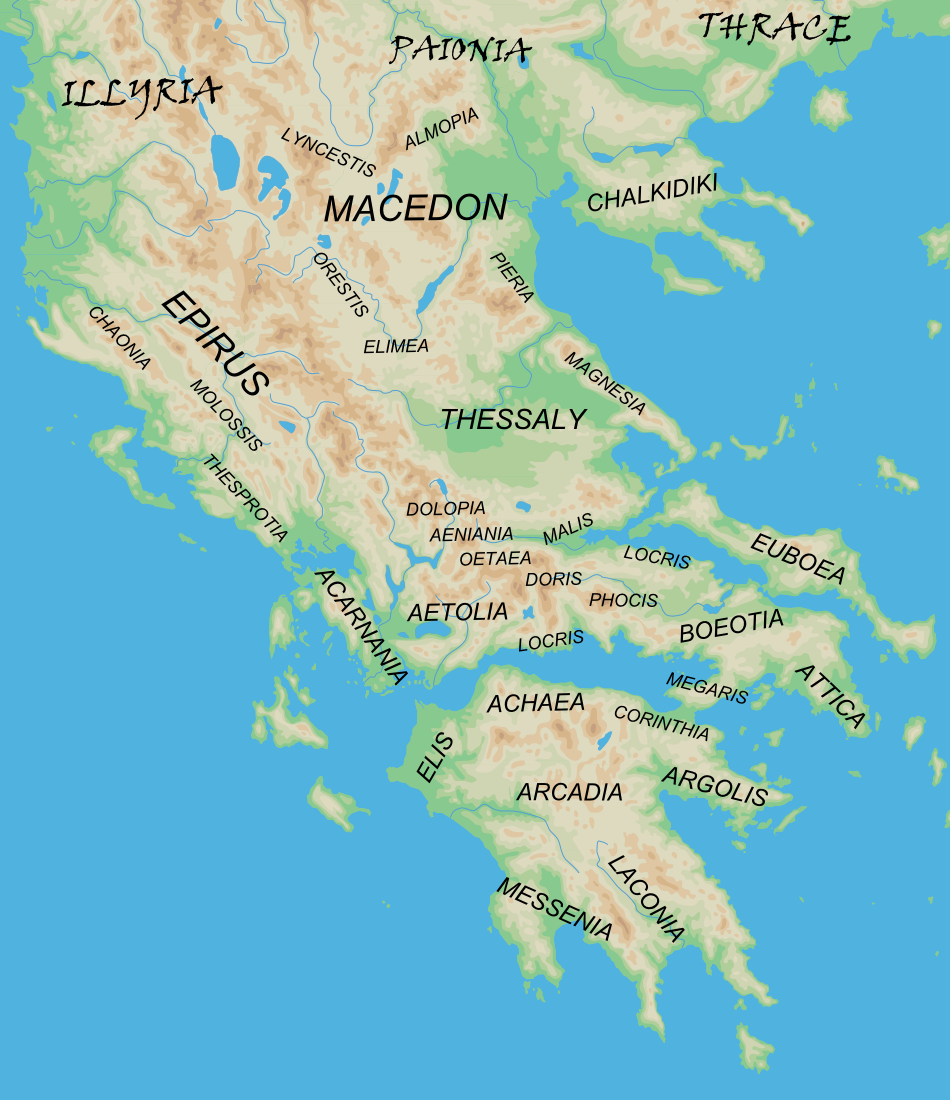
Ancient Argolis
The regions of ancient Greece were sub-divisions of the Hellenic world as conceived by the ancient Greeks, shown by their presence in the works of ancient historians and geographers or in surviving legends and myths. Conceptually, there is no clear theme to the structure of these regions. Some, particularly in the #Peloponnese, Peloponnese, can be seen primarily as distinct geo-physical units, defined by physical boundaries such as mountain ranges and rivers. Conversely, the division of #Central Greece, central Greece between #Boeotia, Boeotia, #Phocis, Phocis, #Doris, Doris and the three parts of #Locris, Locris, seems to be attributable to ancient tribal divisions and not major geographical features. Both types of regions retained their identity throughout the Greek Dark Ages and its tumultuous changes in the local population and culture, giving them a less political and more symbolic presence. Other geographical divisions not identified with the aforementioned areas did, howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramids In Greece
A pyramid () is a structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be of any polygon shape, such as triangular or quadrilateral, and its surface-lines either filled or stepped. A pyramid has the majority of its mass closer to the ground with less mass towards the pyramidion at the apex. This is due to the gradual decrease in the cross-sectional area along the vertical axis with increasing elevation. This offers a weight distribution that allowed early civilizations to create monumental structures.Ancient civilizations in many parts of the world pioneered the building of pyramids. The largest pyramid by volume is the Mesoamerican Great Pyramid of Cholula, in the Mexican state of Puebla. For millennia, the largest structures on Earth were pyramids—first the Red Pyramid in the Dashur Necropolis and then the Great Pyramid of Khufu, both in Egyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Lefkowitz
Mary R. Lefkowitz (born April 30, 1935) is an American scholar of Classics. She is the Professor Emerita of Classical Studies at Wellesley College in Wellesley, Massachusetts, where she previously worked from 1959 to 2005. She has published ten books over the course of her career. Lefkowitz studied at Wellesley College before obtaining a Ph.D. in Classical Philology from Radcliffe College in 1961. During the 1980s much of her research focused on the place of women in the Classical world. She attracted broader attention for her 1996 book ''Not Out of Africa'', a criticism of Afrocentric claims that ancient Greek civilization derived largely from that of ancient Egypt. She argued that such claims owed more to an American black nationalist political agenda than historical evidence. That decade, she also entered into a publicised argument with Africana studies scholar Tony Martin. She served on the advisory board of the conservative advocacy group the National Association of Schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ioannis Liritzis
Ioannis Liritzis (Greek: Ιωάννης Λυριντζής; born 2 November 1953) is professor of physics in archaeology ( archaeometry) and his field of specialization is the application of natural sciences to archaeology and cultural heritage. He studied physics at the University of Patras and continued at the University of Edinburgh, where he obtained his Ph.D. in 1980. Since then, he undertook postgraduate work at the University of Oxford, Université Bordeaux III, University of Edinburgh and the Academy of Athens. Currently he is distinguished professor of archaeometry-Natural Sciences at the Henan University, Kaifeng, China and was professor in Archaeometry & Natural Sciences at the University of the Aegean and he directed and founded the Laboratory of Archaeometry (founded by him at 1999) and Lab of Environmental Archaeology. Director and initiator of the Masters course Applied Archaeological Sciences. In the past he served as Head of the Department of Mediterranean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoluminescence Dating
Thermoluminescence dating (TL) is the determination, by means of measuring the accumulated radiation dose, of the time elapsed since material containing crystalline minerals was either heated (lava, ceramics) or exposed to sunlight (sediments). As a crystalline material is heated during measurements, the process of thermoluminescence starts. Thermoluminescence emits a weak light signal that is proportional to the radiation dose absorbed by the material. It is a type of luminescence dating. The technique has wide application, and is relatively cheap at some US$300–700 per object; ideally a number of samples are tested. Sediments are more expensive to date. , University of Wollongong, Australia [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy (lithologic stratigraphy), biostratigraphy (biologic stratigraphy), and chronostratigraphy (stratigraphy by age). Historical development Catholic priest Nicholas Steno established the theoretical basis for stratigraphy when he introduced the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality and the principle of lateral continuity in a 1669 work on the fossilization of organic remains in layers of sediment. The first practical large-scale application of stratigraphy was by William Smith in the 1790s and early 19th century. Known as the "Father of English geology", Smith recognized the significance of strata or rock layering and the importance of fossil markers for correlating strata; he created the first geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helladic Chronology
Helladic chronology is a relative dating system used in archaeology and art history. It complements the Minoan chronology scheme devised by Sir Arthur Evans for the categorisation of Bronze Age artefacts from the Minoan civilization within a historical framework. Whereas Minoan chronology is specific to Crete, the cultural and geographical scope of Helladic chronology is confined to mainland Greece during the same timespan (c. 3200 – c. 1050 BC). Similarly, a Cycladic chronology system is used for artifacts found in the Aegean islands. Archaeological evidence has shown that, broadly, civilisation developed concurrently across the whole region and so the three schemes complement each other chronologically. They are grouped together as "Aegean" in terms such as Aegean art and, rather more controversially, Aegean civilization. The systems derive primarily from changes in the style of pottery, which is a benchmark for relative dating of associated artifacts such as tools and wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American School Of Classical Studies At Athens
The American School of Classical Studies at Athens (ASCSA; ) is one of 19 foreign archaeological institutes in Athens, Greece. It is a member of the Council of American Overseas Research Centers (CAORC). CAORC is a private not-for-profit federation of independent overseas research centers that promote advanced research, particularly in the humanities and social sciences, with focus on the conservation and recording of cultural heritage and the understanding and interpretation of modern societies. General information With an administrative base in Princeton, New Jersey, and a campus in Athens, the American School of Classical Studies at Athens is one of the leading American research and teaching institutions in Greece, dedicated to the advanced study of all aspects of Greek culture, from antiquity to the present. Founded in 1881, the School is a consortium of nearly 200 colleges and universities in the United States and Canada. It was the first American overseas research center, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Wiegand
Theodor Wiegand (30 October 1864 – 19 December 1936) was a German archaeologist. Wiegand was born in Bendorf, Rhenish Prussia. He studied at the universities of Munich, Berlin, and Freiburg. In 1894 he worked under Wilhelm Dörpfeld at the excavation of the Athenian Acropolis. From 1895 until 1899 he excavated the ancient Greek city of Priene, and from 1899 to 1911 he worked at Miletus. He took part in the excavations of the sanctuary of Didyma (1905–11) and of Samos (1910–11). In Pergamon he discovered, in 1927, the arsenals of the castle at the acropolis and excavated the large sanctuary of Asklepios outside the city. He also finished the excavations at Baalbek in Lebanon and published the results. From 1899 until 1911, he worked for the museums of Berlin as a foreign director in Constantinople, the capital of the Ottoman Empire, and was the science attaché of the German Embassy there. From 1912 to 1930 he worked as the director of the Department of Antiqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |