|
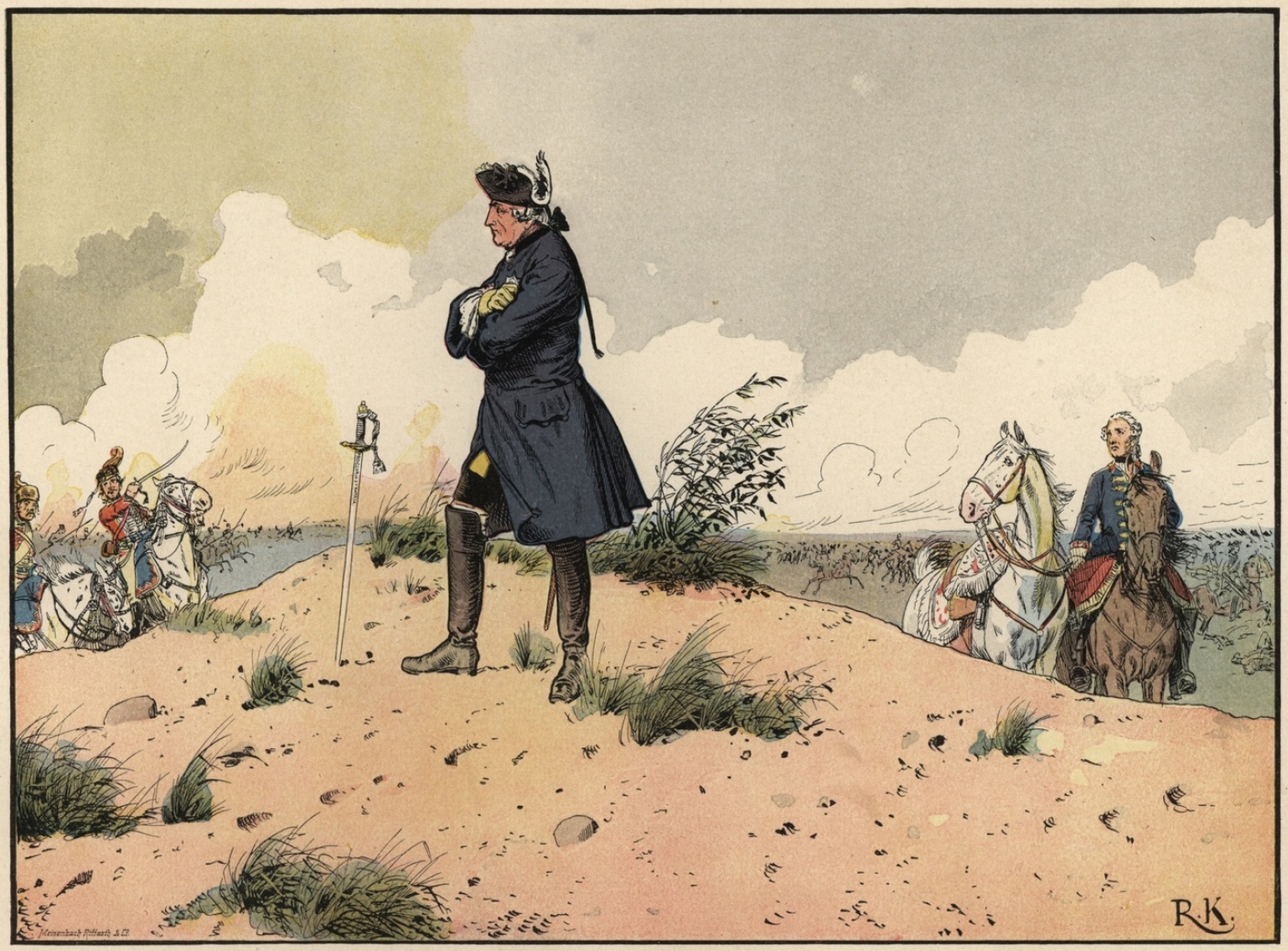
Pyotr Rumyantsev
Count Pyotr Alexandrovich Rumyantsev-Zadunaisky (; – ) was one of the foremost Russian generals of the 18th century, and is widely considered to be one of Russia's greatest military leaders, and one of the greatest military commanders in military history. He is noted as one of the three best and most talented Russian military leaders of the time period, along with Alexander Suvorov and Grigory Potemkin. Rumyantsev used mobile divisional squares for the first time in history as opposed to linear battle orders and initiated the formation of light ( ''jaeger'') battalions in the Russian Army, which operated in a scattered order. He governed Little Russia in the name of Empress Catherine the Great from the abolition of the Cossack Hetmanate in 1764 until Catherine's death 32 years later. Monuments to his victories include the Kagul Obelisk in Tsarskoye Selo (1772), the Rumyantsev Obelisk on Vasilievsky Island (1798–1801), and a galaxy of Derzhavin's odes. Early life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Little Russia Governorate (1764-1781)
Little Russia Governorate may refer to: 1764–1781 The First Little Russia Governorate or Malorossiya Governorate, was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1764–1781. It was created after the abolition of Cossack Hetmanate and was governed by Pyotr Rumyantsev. With another administrative reform of 1781 the governorate and its subdivisions (regiments) were liquidated and replaced with vice-royalties divided into counties ( uezds). Subdivisions The governorate was divided into 10 regiments (polk) which were equivalent to counties (uezd). * (1663–1782) * * * Nizhyn Regiment * Chernihiv Regiment * Pryluky Regiment * Lubny Regiment * Myrhorod Regiment * Hadiach Regiment * Poltava Regiment Coat of arms Until 1767 the coat of arms for the governorate was Cossack with musket when it was replaced with the Russian double headed eagle. 1796–1802 Little Russia Governorate or Malorossiya Governorate was an administrative-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
War Of The Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King George's War in North America, the War of Jenkins' Ear, the First Carnatic War, and the First Silesian War, First and Second Silesian Wars. Its pretext was the right of Maria Theresa to succeed her father, Charles VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Charles VI, as ruler of the Habsburg monarchy. Kingdom of France, France, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, and Electorate of Bavaria, Bavaria saw it as an opportunity to challenge Habsburg power, while Maria Theresa was backed by Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain, the Dutch Republic, and Electorate of Hanover, Hanover, collectively known as the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713, Pragmatic Allies. As the conflict widened, it drew in other participants, among them History of Spain (1700–1810), Spain, Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
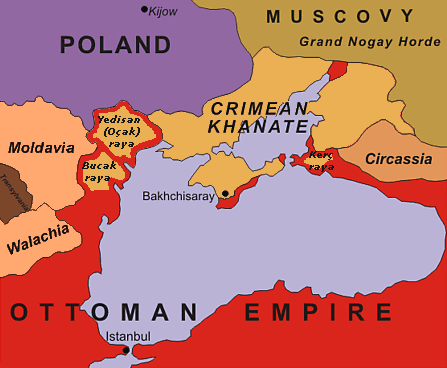
Siege Of Silistra (1773)
The siege of Silistra was a military siege undertaken by Russia between 18 and 29 June 1773 against the Ottoman city of Silistria. The siege was an important phase of the Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774), and resulted in an Ottoman victory. Prelude In 1773, Catherine the Great ordered for Pyotr Rumyantsev to march with his army onto Silistra to pressure the Ottoman Empire into peace. With this, he crossed the Danube with a tens-of-thousands-strong force after a pontoon bridge was built across the Galitsa. Grigory Potemkin and Otto Weismann's forces were at the front of this army. Rumyantsev ordered Major-general to have roads built out to Silistra. On 12 June, Potemkin and Weismann were sent in two columns towards Silistra. They were both under the command of . There was constant fighting between Ottoman and Russian troops before they reached the fortress on 15 June. Stupishin sent a letter the same day to Serasker Halıcı Osman Pasha (the ethnically Armenian pasha defendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Kagul
The Battle of Kagul or Cahul (, ) occurred on 1 August 1770 (21 July 1770 in Julian Calendar) during the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774. It was the decisive and most important land battle of the war and one of the largest battles of the 18th century. It was fought in Moldavia, near the village of Frumoasa (now Cahul, Moldova), nearly a month after the Russian victory at Larga. While the army of the Ottomans and its Crimean Tatar vassals greatly outnumbered the Russian force opposite them, the Russian commander, Field Marshal Pyotr Rumyantsev, deftly arranged his far smaller army in solid infantry squares and surprisingly chose to go on the offensive against the allied forces. Assisting it is the superb coordination and firing rapidity of the Russian artillery, which effectively neutralized the Ottoman artillery and largely negated the numerical superiority of the Ottoman army. The result was a decisive Russian victory. Background The Russian empress Catherine II ordered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Larga
The Battle of (the) Larga was fought between 65,000 Crimean Tatars and 15,000 Ottomans under Qaplan II Giray against 38,000 Russians under Field-Marshal Rumyantsev on the banks of the Larga River, a tributary of the Prut River, in Moldavia (now in Moldova), for eight hours on 7 July 1770. It was fought on the same day as Battle of Chesma, a key naval engagement of the Russo-Turkish War, 1768–1774. The battle was a decisive victory for the Russians who captured 33 Turkish cannons and the vast enemy camp. For this victory, Rumyantsev was awarded the Order of Saint George of the 1st degree. Two weeks later, the Russians scored an even greater victory in the Battle of Kagul The Battle of Kagul or Cahul (, ) occurred on 1 August 1770 (21 July 1770 in Julian Calendar) during the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774. It was the decisive and most important land battle of the war and one of the largest battles of the 18th ce .... References The Battles of Larga and Kagul {{Ottoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Ryabaya Mogila
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
The Russo-Turkish wars ( ), or the Russo-Ottoman wars (), began in 1568 and continued intermittently until 1918. They consisted of twelve conflicts in total, making them one of the longest series of wars in the history of Europe. All but four of these wars ended in losses for the Ottoman Empire, which was undergoing a period of stagnation and decline. Conversely, they showcased the ascendancy of the Russian Empire as a significant European power after Peter the Great oversaw extensive modernization efforts in the early 18th century. Ultimately, however, the end of the Russo-Turkish wars came about with the dissolution of the two belligerents' respective states as a consequence of World War I: the Russian Empire collapsed in 1917 and was ultimately succeeded by the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in 1922; while the Ottoman Empire was partitioned between 1918 and 1922 and succeeded by the Republic of Turkey in 1923. History Initial and intermediate phases (1568–1739) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Kolberg (Seven Years' War)
During the Seven Years' War, the Prussian-held town of Kolberg in Brandenburg-Prussian Pomerania (now Kołobrzeg) was besieged by Russian forces three times. The first two sieges, in late 1758 and from 26 August to 18 September 1760, were unsuccessful. A final and successful siege took place from August to December 1761.Buchholz (1999), pp.352–354 In the sieges of 1760 and 1761, the Russian forces were supported by Swedish auxiliaries.Szabo (2008), pp.290, 370 As a consequence of the fall of the city, Prussia lost its last major port on the Baltic Coast,West (2001), p.492 while at the same time the Russian forces were able to take winter quarters in Pomerania. However, when Empress Elizabeth of Russia died only weeks after the Russian victory, her successor, Peter III of Russia, made peace and returned Kolberg to Prussia.Stone (2006), p.75 First siege (1758) A first siege in 1758 was repelled by the Prussian defenders. Russian Count Fermor was ordered to expel the Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pomeranian War
The Pomeranian War was a theatre of the Seven Years' War. The term is used to describe the fighting between Sweden and Prussia between 1757 and 1762 in Swedish Pomerania, Prussian Pomerania, northern Brandenburg and eastern Mecklenburg-Schwerin. The war was characterized by a back-and-forth movement of the Swedish and Prussian armies, neither of whom would score a decisive victory. It started when Swedish forces advanced into Prussian territory in 1757, but were repelled and blockaded at Stralsund until their relief by a Russian force in 1758. In the course of the following, renewed Swedish incursion into Prussian territory, the small Prussian fleet was destroyed and areas as far south as Neuruppin were occupied, yet the campaign was aborted in late 1759 when the undersupplied Swedish forces succeeded neither in taking the major Prussian fortress of Stettin (now Szczecin) nor in combining with their Russian allies. A Prussian counter-attack of Swedish Pomerania in January 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Kunersdorf
The Battle of Kunersdorf occurred on 12 August 1759 near Kunersdorf (now Kunowice, Poland) immediately east of Frankfurt an der Oder. Part of the Third Silesian War and the wider Seven Years' War, the battle involved over 100,000 men. An Allied army commanded by Pyotr Saltykov and Ernst Gideon von Laudon that included 41,000 Russians and 18,500 Austrians defeated Frederick the Great's army of 50,900 Prussians. The terrain complicated battle tactics for both sides, but the Russians and the Austrians, having arrived in the area first, were able to overcome many of its difficulties by strengthening a causeway between two small ponds. They had also devised a solution to Frederick's deadly ''modus operandi'', the oblique order. Although Frederick's troops initially gained the upper hand in the battle, his limited scouting, combined with the strong defensive preparations of the Allied troops, gave the Russians and Austrians an advantage. By afternoon, when the combatants were exh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Third Silesian War
The Third Silesian War () was a war between Prussia and Austria (together with its allies) that lasted from 1756 to 1763 and confirmed Prussia's control of the region of Silesia (now in south-western Poland). The war was fought mainly in Silesia, Bohemia and Upper Saxony and formed one theatre of the Seven Years' War. It was the last of three Silesian Wars fought between Frederick the Great's Prussia and Maria Theresa's Austria in the mid-18th century, all three of which ended in Prussian control of Silesia. This conflict can be viewed as a continuation of the First and Second Silesian Wars of the previous decade. After the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle ended the War of the Austrian Succession, Austria enacted broad reforms and upended its traditional diplomatic policy to prepare for renewed war with Prussia. As with the previous Silesian Wars, no particular triggering event initiated the conflict; rather, Prussia struck opportunistically to disrupt its enemies' plans. The war' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Gross-Jägersdorf
The Battle of Gross-Jägersdorf (30 August 1757) was a victory for the Russian force under Field Marshal Stepan Fyodorovich Apraksin over a smaller Prussian force commanded by Field Marshal Hans von Lehwaldt, during the Seven Years' War. This was the first battle in which Russia engaged during the Seven Years' War. Despite the tactical success, supply problems made a successful advance further into East Prussia impractical. Apraksin decided not to take Königsberg and ordered a withdrawal soon after the battle. Suspecting collusion between Apraksin and Chancellor Alexey Bestuzhev-Ryumin, who had opposed the invasion, Elizabeth of Russia removed Apraksin from command, ordered Bestuzhev-Ryumin to face trial for treason, and appointed William Fermor as the head of the army. Femor led the army back into East Prussia in the following year. Seven Years' War Although the Seven Years' War was a global conflict, it took a specific intensity in the European theater based on the rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |