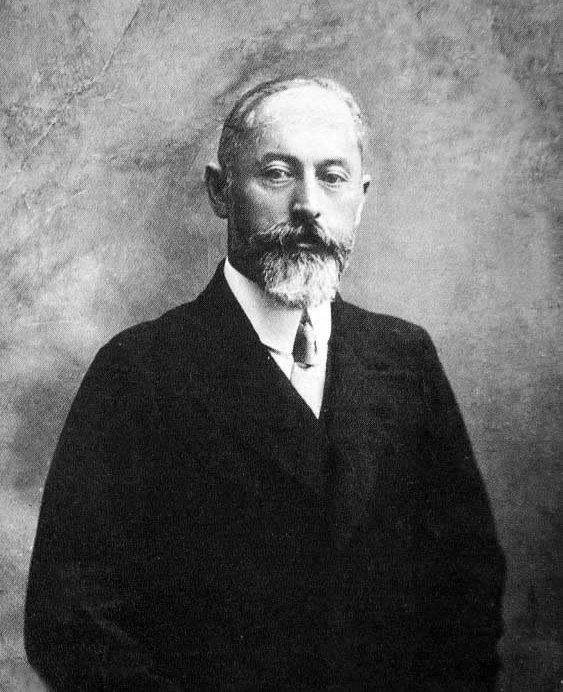|
Pyotr Krasikov
Pyotr Ananyevich Krasikov (; 17 October Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O.S. 5 October1870 – 20 August 1939) was a Russians">Russian revolutionary and Soviet statesman, as well as a jurist and writer on political and religious affairs. He was the first Procurator General of the Soviet Union, serving from 1924 to 1933. Career Pyotr Krasikov was born in Krasnoyarsk, where he was brought up from the age of 12 by his grandfather, an Archpriest, after the early death of his father, a lawyer. He was expelled from the Krasnoyarsk gymnasium for bad behaviour, but reinstated after his grandfather intervened. In the years 1892–1893, Krasikov visited Switzerland and met with Russian Marxists, met with the leaders of the " Emancipation of Labor" group of Georgy Plekhanov, Pavel Axelrod and Vera Zasulich and joined Emancipation of Labour group in 1892. After returning home in 1894, he was arrested and kept in a solitary confine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archpriest
The ecclesiastical title of archpriest or archpresbyter belongs to certain priests with supervisory duties over a number of parishes. The term is most often used in Eastern Orthodoxy and the Eastern Catholic Churches and may be somewhat analogous to a monsignor, vicar forane or dean in the Latin Church, but in the Eastern churches an archpriest wears an additional vestment and, typically, a pectoral cross, and becomes an archpriest via a liturgical ceremony. The term may be used in the Latin Catholic Church in certain historical titles and may replace in popular usage the title of ''vicar forane'', otherwise often known as a dean. Antiquity In ancient times, the archdeacon was the head of the deacons of a diocese, as is still the case in the Eastern Orthodox Church, while the archpriest was the chief of the presbyterate of the diocese, i.e. of the priests as a body. The latter's duties included deputising for the bishop in spiritual matters when necessary. Western C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mensheviks
The Mensheviks ('the Minority') were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with Vladimir Lenin's Bolshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903. Mensheviks held more moderate and reformist views as compared to the Bolsheviks, and were led by figures including Julius Martov and Pavel Axelrod. The initial point of disagreement was the Mensheviks' support for a broad party membership, as opposed to Lenin's support for a smaller party of professional revolutionaries. The Bolsheviks gained a majority on the Central Committee in 1903, although the power of the two factions fluctuated in the following years. Mensheviks were associated with Georgi Plekhanov's position that a bourgeois-democratic revolution and period of capitalism would need to occur before the conditions for a socialist revolution emerged. Some Mensheviks, notably Alexander Potresov, called for the party to suspend illegal revolutionary work to focus more on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Congress Of The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
The 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party was held from July 30 to August 23 (July 17 – August 10, O.S.) 1903, starting in Brussels, Belgium (until August 6) and ending in London, England. Probably as a result of diplomatic pressure from the Russian Embassy, Belgian police had forced the delegates to leave the country on August 6. The congress finalized the creation of the Marxist party in Russia proclaimed at the 1st Congress of the RSDLP. This congress brought the first split within the party, between the Bolshevik faction led by Lenin, and the Menshevik faction led by Martov. Preparation The Organising Committee for convening the Second Congress of the RSDLP was originally elected at the Białystok Conference held in March (April) 1902, but soon after the conference all the committee members but one were arrested. At Lenin's suggestion, a new Organising Committee was set up at a conference of Social-Democratic committees held in November 1902 in Psko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
The Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP), also known as the Russian Social Democratic Workers' Party (RSDWP) or the Russian Social Democratic Party (RSDP), was a socialist political party founded in 1898 in Minsk, Russian Empire. The party emerged from the merger of various Marxist groups operating under Tsarist repression, and was dedicated to the overthrow of the autocracy and the establishment of a socialist state based on the revolutionary leadership of the Russian proletariat. The RSDLP's formative years were marked by ideological and strategic disputes culminating at its Second Congress in 1903, where the party split into two main factions: the Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, who advocated a tightly organized vanguard of professional revolutionaries; and the Mensheviks, led by Julius Martov and others, who favored a more moderate, broad-based model. During and in the years after the 1905 Revolution, the RSDLP operated both legally and underground, publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iskra
''Iskra'' (, , ''the Spark'') was a fortnightly political newspaper of Russian socialist emigrants established as the official organ of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP). History ''Iskra'' was published in exile and then smuggled into Russia. Initially, it was managed by Vladimir Lenin, moving as he moved. The first edition was published in Leipzig, Germany, on 1 December 1900 (other sources say 11 December). Other editions were published in Munich (1900–1902) and Geneva from 1903. When Lenin was in London (1902–1903) the newspaper was edited from a small office at 37a Clerkenwell Green, EC1, with Henry Quelch arranging the necessary printworks. ''Iskra'' quickly became the most successful underground Russian newspaper since 1850s. It was smuggled into Russia via Romania, and reprinted on secret presses in Kishinev and the Caucasus. Using the networks created to write for and distribute the paper, Lenin and Julius Martov prepared organisationally for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=Ru-Псков.oga, p=psˈkof; see also Names of Pskov in different languages, names in other languages) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya, Velikaya River. Population: Pskov is one of the oldest cities in Russia. During the Middle Ages, it served as the capital of the Pskov Republic and was a trading post of the Hanseatic League before it was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Moscow and became an important border fortress in the Tsardom of Russia. History Early history Pskov is one of the oldest cities in Russia. The name of the city, originally Pleskov (historic Russian spelling , ), may be loosely translated as "[the town] of :wikt:purling, purling waters". It was historically known in English as Plescow. Its earliest mention comes in 903, which records that Igor of Kiev married a local lady, Olga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League Of Struggle For The Emancipation Of The Working Class
The League of Struggle for the Emancipation of the Working Class (LSEWC) was a Marxist group in the Russian Empire. It was founded in St. Petersburg by Vladimir Lenin, Julius Martov, Gleb Krzhizhanovsky, Anatoly Vaneyev, Alexander Malchenko, P. Zaporozhets and V. Starkov in the autumn of 1895.Tony Cliff (1986) ''Lenin: Building the Party 1893-1914''. London, Bookmarks: 52-59 It united twenty different Marxist study circles, but Lenin dominated the league through the 'central group'. Its main activity was Political demonstration, agitation amongst the workers of St Petersburg and the distribution of socialist leaflets to the factories there. Towards the end of 1895, the League had prepared the first issue of their new newspaper, ''Rabocheye Delo''; it was ready to go to press when it was seized by the gendarmes during a raid on the house of Vaneyev, on December 20. Six League members were arrested, Lenin among them. While in prison, Lenin continued to guide the work of the Leagu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Police Supervision
Police supervision or police monitoring is a form of additional punishment and crime prevention. The regulations vary for various countries. A common feature was restriction and control of the place of residence of the supervised person. In certain situations a released convict was placed under police supervision. In some countries "unreliable persons" (usually in political sense) could be placed under police supervision.С.А. НЕВСКИЙПОЛИЦЕЙСКИЙ НАДЗОР В СТРАНАХ ЗАПАДНОЙ ЕВРОПЫ И В РОССИИ В XIX В. (ПО МАТЕРИАЛАМ ЗАПИСКИ, СОСТАВЛЕННОЙ Н.Д. РЫЧКОВЫМ)/ref> In 1871 regulations for police supervision were summarized in an internal report of Russian chief prosecutor deputy Nikolay Rychkov () for Russian Empire, France, Belgium, Prussia, Bavaria, and German Empire The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter And Paul Fortress
The Peter and Paul Fortress () is the original citadel of Saint Petersburg, Russia, founded by Peter the Great in 1703 and built to Domenico Trezzini's designs from 1706 to 1740 as a star fortress. Between the first half of the 1700s and early 1920s it served as a prison for political criminals. It has been a museum since 1924. History From foundation until 1917 The fortress was established by Peter the Great on , on small Hare Island by the north bank of the Neva River. From around 1720, the fort served as a base for the city garrison and also as a prison for high-ranking or political prisoners. Russian Revolution and beyond During the February Revolution of 1917, it was attacked by mutinous soldiers of the Pavlovsky Life Guards Regiment on February 27 (O.S.) and the prisoners were freed. Under the Provisional Government, hundreds of Tsarist officials were held in the Fortress. The tsar was threatened with being incarcerated at the fortress on his return from Mogile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vera Zasulich
Vera Ivanovna Zasulich (; – 8 May 1919) was a Russian socialist activist, Menshevik writer and revolutionary. She is widely known for her correspondence with Karl Marx, in which she put into question the necessity of a capitalist industrialisation prior to socialism, in the context of the fact that there already were living farmer communities in Russia that had developed practices and cultures that had a communist component. Radical beginnings Zasulich was born in Mikhaylovka, in the Smolensk Governorate of the Russian Empire, as one of four daughters of an impoverished minor Polish nobleman. When she was three years old, her father died and her mother sent her to live with her wealthier relatives, the Mikulich family, in Byakolovo. After graduating from high school in 1866, she moved to Saint Petersburg, where she worked as a clerk. Soon she became involved in radical politics and taught literacy classes for factory workers. Her contacts with the Russian revolutionary le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavel Axelrod
Pavel Borisovich Axelrod (; 25 August 1850 – 16 April 1928) was an early Russian Marxist revolutionary. Along with Georgi Plekhanov, Vera Zasulich, and Leo Deutsch, he was one of the members of the first organization of Russian Marxists, Emancipation of Labor. After the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, he was part of the Menshevik faction, with which he was identified until his death. Early life and career Pavel Axelrod was the son of a Jewish innkeeper. His parents lived in the Jewish poorhouse. He was forced to work for a living from a young age; though while still in his early teens, he produced his first political essay, on the condition of the Jewish poor in the Mogilev Region, in modern-day Belarus. At the age of 16, he discovered the writings of the German socialist Ferdinand Lassalle, which had a major influence on him. Later, he obtained a place at Kiev University, with financial help from wealthy Jews, and organised a political discussio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |