|
Pyotr Kolodin
Pyotr Ivanovich Kolodin (; 23 September 1930 – 4 February 2021) was a Soviet cosmonaut. Although he retired in 1983 without flying in space, Kolodin served non-flying assignments on several spaceflights. Biography Kolodin was born in Novovasilyevka, Soviet Union (now in Zaporizhia Oblast, Ukraine). In 1959, he graduated from Military Academy of Engineering and Radioengineering with gold medal. Kolodin then became an engineer-officer in the Soviet Armed Forces until his selection as a cosmonaut. He was selected as a Soviet cosmonaut as part of the TsPK Group 2 in 1963. He entered cosmonaut training in January 1963 and completed training in January 1966. After completing his training, Kolodin served non-flight (backup) roles on the Voskhod 2, Soyuz 5, Soyuz 7, Soyuz 11, and Soyuz 12 spaceflights. He trained as test engineer of the 1st crew to fly on Soyuz 11 to 1st visit the Salyut 1 space station, but the entire crew was bumped when it was suspected that flight engineer V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut 1
Salyut 1 (), also known as DOS-1 (Durable Orbital Station 1), was the world's first space station. It was launched into low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on April 19, 1971. The Salyut programme, ''Salyut'' program subsequently achieved five more successful launches of seven additional stations. The program's final module, Zvezda (ISS module), ''Zvezda'' (DOS-8), became the core of the Russian Orbital Segment of the International Space Station and remains in orbit today. Salyut 1 was adapted from an Almaz airframe and comprised five components: a transfer compartment, a main compartment, two auxiliary compartments, and the Orion (space telescope), Orion 1 Space Observatory. It was visited by the Soyuz 10 and Soyuz 11 missions. While the crew of Soyuz 10 was able to soft dock, the Docking and berthing of spacecraft#Docking states, hard-docking failed, forcing the crew to abort their mission. The Soyuz 11 crew successfully docked, spending 23 days aboard Salyut 1 conducting exper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Deaths
This is a list of lists of deaths of notable people, organized by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked below. 2025 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 Earlier years ''Deaths in years earlier than this can usually be found in the main articles of the years.'' See also * Lists of deaths by day * Deaths by year (category) {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1930 Births
Events January * January 15 – The Moon moves into its nearest point to Earth, called perigee, at the same time as its fullest phase of the Lunar Cycle. This is the closest moon distance at in recent history, and the next one will be on January 1, 2257, at . * January 26 – The Indian National Congress declares this date as Independence Day, or as the day for Purna Swaraj (Complete Independence). * January 28 – The first patent for a field-effect transistor is granted in the United States, to Julius Edgar Lilienfeld. * January 30 – Pavel Molchanov launches a radiosonde from Pavlovsk, Saint Petersburg, Slutsk in the Soviet Union. February * February 10 – The Việt Nam Quốc Dân Đảng launch the Yên Bái mutiny in the hope of ending French Indochina, French colonial rule in Vietnam. * February 18 – While studying photographs taken in January, Clyde Tombaugh confirms the existence of Pluto, a celestial body considered a planet until redefined as a dwarf planet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oleg Grigoryevich Makarov
Oleg Grigoryevich Makarov (; 6 January 1933 28 May 2003) was a Soviet Union, Soviet astronaut, cosmonaut. Early life and education Makarov was born in Udomlya, Tver Oblast, USSR. He graduated from Moscow State Technical University, Bauman Moscow Higher Technical School in 1957 and started working at the Special Design Bureau Number One (which is now RSC Energia) as an engineer, working on the Vostok spacecraft. In 1966, he was selected for cosmonaut training. Space program He was originally part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs, Soviet lunar program and was training with Alexei Leonov for the first human circumlunar trajectory, circumlunar flight. After the success of Apollo 8, however, the flight was cancelled. His first spaceflight was Soyuz 12 in 1973, a test flight to check the changes made to the Soyuz spacecraft after the Soyuz 11 disaster. His second flight was the abortive Soyuz 18a that made an emergency landing in the Altay Mountains, 21 minutes after launch. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 25
Soyuz 25 (, ''Union 25'') was an October 1977 Soviet crewed space flight, the first to the new Salyut 6 space station, which had been launched 10 days earlier. However, the mission was aborted when cosmonauts Vladimir Kovalyonok and Valery Ryumin failed to engage the docking latches of the station despite five attempts. Lacking sufficient fuel to attempt a dock at the other end of the station and with battery power for only two days, they returned to Earth.The mission report is available here: http://www.spacefacts.de/mission/english/soyuz-25.htm The failure led to a new rule whereby every crew had to have at least one person aboard who had previously flown in space. Crew Backup crew Mission highlights Soyuz 25 was launched on 9 October 1977 with a crew of two cosmonauts to dock with the orbiting Salyut 6 space station, which had been launched 10 days earlier, on 29 September. The crew were to stay on board for about 90 days, which would break the Soviet space endurance reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz 27
Soyuz 27 (, ''Union 27'') was a 1978 Soviet crewed spacecraft which flew to the orbiting Salyut 6 space station, during the mission EP-1. It was the third crewed flight to the station, the second successful docking and the first visitation mission. Once docked, it marked the first time that three spacecraft were docked together. The main function of the EP-1 mission was to swap Soyuz craft with the orbiting crew, in so doing freeing a docking port for a forthcoming supply tanker. Cosmonauts Vladimir Dzhanibekov and Oleg Makarov returned to Earth in the Soyuz 26 spacecraft after spending five days on the station. The descent module is displayed at the Sergei Pavlovich Korolyov Museum of Cosmonautics in Zhytomyr, Ukraine Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor .... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Dzhanibekov
Vladimir Aleksandrovich Dzhanibekov (, born 13 May 1942) is a retired Soviet Air Force Major General and a cosmonaut veteran of five orbital missions. Biography Dzhanibekov was born Vladimir Aleksandrovich Krysin () in the remote area of Iskandar in what was then Bostanliq District, South Kazakhstan Region, Kazakh SSR (since 1956 – Tashkent Region, Uzbekistan) on 13 May 1942. His family moved to Tashkent soon after his birth. In 1964 he married Liliya Munirovna Dzhanibekova, who was a descendant of Janibeg, medieval ruler of the Golden Horde. As her father had no sons, Dzhanibekov took his wife's family name in order to honour her ancestry and continue her line of descent, an unusual step for a husband in the Soviet Union. In 1960 he entered Leningrad University to study physics, where he became involved in flying, something in which he had always been interested. In 1961 he decided to enroll in the V. M. Komarov Higher Military Flying School at Yeisk while simultaneousl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
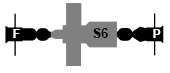
Salyut 6
Salyut 6 () was a Soviet orbital space station, the eighth station of the Salyut programme, and alternatively known DOS-5 as it was the fifth of the Durable Orbital Station series of civilian space stations. It was launched on 29 September 1977 by a Proton rocket. Salyut 6 was the first space station to receive large numbers of crewed and uncrewed spacecraft for human habitation, crew transfer, international participation and resupply, establishing precedents for station life and operations which were enhanced on Mir and the International Space Station. Salyut 6 was the first "second generation" space station, representing a major breakthrough in capabilities and operational success. In addition to a new propulsion system and its primary scientific instrument—the BST-1M multispectral telescope—the station had two docking ports, allowing two craft to visit simultaneously. This feature made it possible for humans to remain aboard for several months. Six long-term residen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Space Science Data Center
The NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive (NSSDCA) serves as the permanent archive for NASA space science mission data. "Space science" includes astronomy Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ... and astrophysics, solar and space plasma physics, and planetary and lunar science. As the permanent archive, NSSDCA teams with NASA's discipline-specific space science "active archives" which provide access to data to researchers and, in some cases, to the general public. NSSDCA also serves as NASA's permanent archive for space physics mission data. It provides access to several geophysical models and to data from some non-NASA mission data. NSSDCA was called the National Space Science Data Center (NSSDC) prior to March 2015. NSSDCA supports active space physics and ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |