|
PyMC Labs
PyMC (formerly known as PyMC3) is a probabilistic programming language written in Python. It can be used for Bayesian statistical modeling and probabilistic machine learning. PyMC performs inference based on advanced Markov chain Monte Carlo and/or variational fitting algorithms. It is a rewrite from scratch of the previous version of the PyMC software. Unlike PyMC2, which had used Fortran extensions for performing computations, PyMC relies on PyTensor, a Python library that allows defining, optimizing, and efficiently evaluating mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays. From version 3.8 PyMC relies on ArviZ to handle plotting, diagnostics, and statistical checks. PyMC and Stan are the two most popular probabilistic programming tools. PyMC is an open source project, developed by the community and has been fiscally sponsored by NumFOCUS. PyMC has been used to solve inference problems in several scientific domains, including astronomy, epidemiology, molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular and cellular studies of individual neurons to imaging of sensory, motor and cognitive tasks in the brain. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
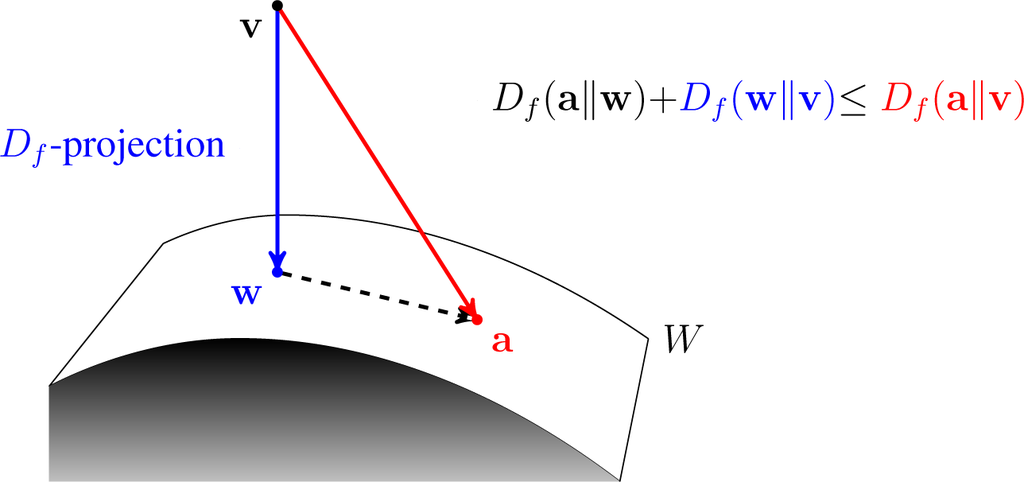
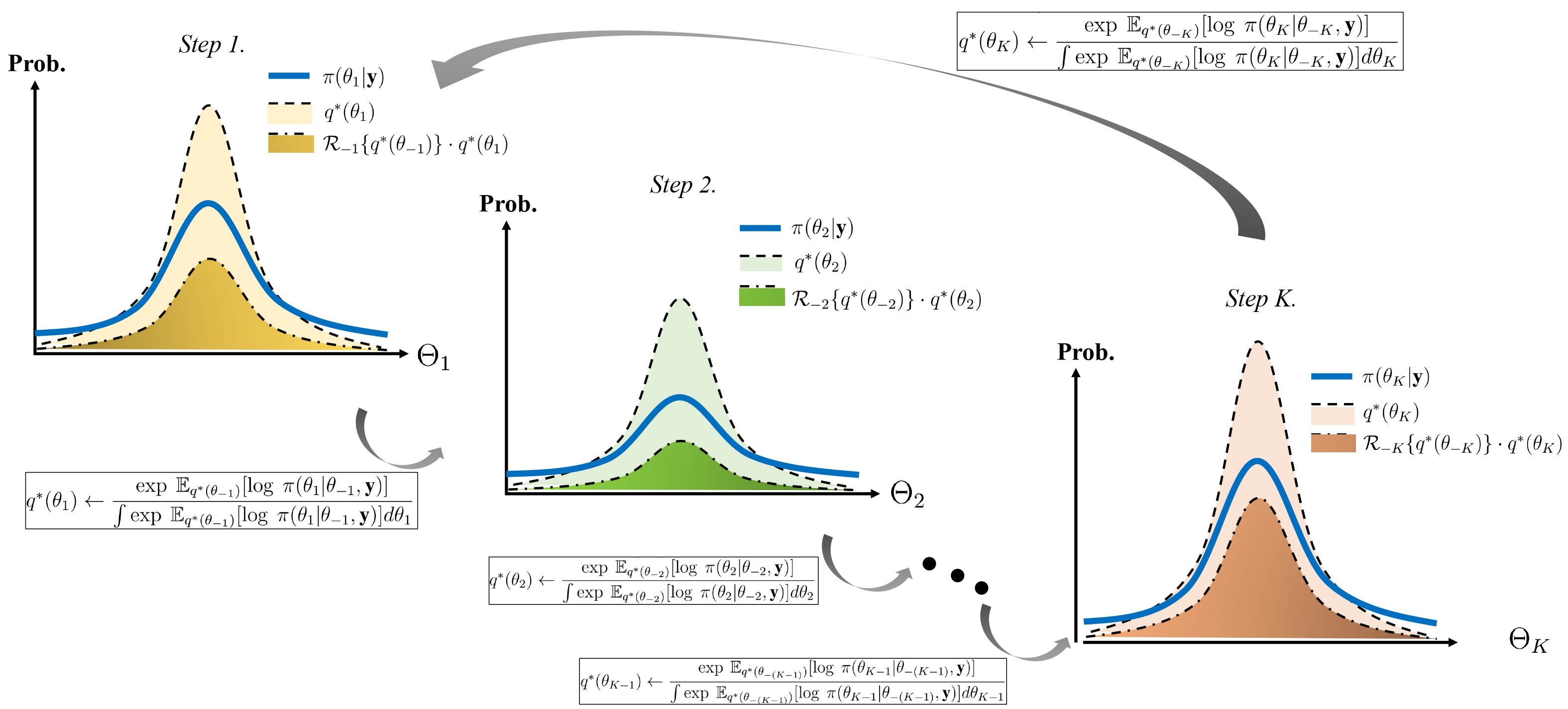
Variational Inference
Variational Bayesian methods are a family of techniques for approximating intractable integrals arising in Bayesian inference and machine learning. They are typically used in complex statistical models consisting of observed variables (usually termed "data") as well as unknown parameters and latent variables, with various sorts of relationships among the three types of random variables, as might be described by a graphical model. As typical in Bayesian inference, the parameters and latent variables are grouped together as "unobserved variables". Variational Bayesian methods are primarily used for two purposes: # To provide an analytical approximation to the posterior probability of the unobserved variables, in order to do statistical inference over these variables. # To derive a lower bound for the marginal likelihood (sometimes called the ''evidence'') of the observed data (i.e. the marginal probability of the data given the model, with marginalization performed over unobserved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approximate Bayesian Computation
Approximate Bayesian computation (ABC) constitutes a class of computational methods rooted in Bayesian statistics that can be used to estimate the posterior distributions of model parameters. In all model-based statistical inference, the likelihood function is of central importance, since it expresses the probability of the observed data under a particular statistical model, and thus quantifies the support data lend to particular values of parameters and to choices among different models. For simple models, an analytical formula for the likelihood function can typically be derived. However, for more complex models, an analytical formula might be elusive or the likelihood function might be computationally very costly to evaluate. ABC methods bypass the evaluation of the likelihood function. In this way, ABC methods widen the realm of models for which statistical inference can be considered. ABC methods are mathematically well-founded, but they inevitably make assumptions and app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolis–Hastings Algorithm
In statistics and statistical physics, the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm is a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method for obtaining a sequence of random samples from a probability distribution from which direct sampling is difficult. New samples are added to the sequence in two steps: first a new sample is proposed based on the previous sample, then the proposed sample is either added to the sequence or rejected depending on the value of the probability distribution at that point. The resulting sequence can be used to approximate the distribution (e.g. to generate a histogram) or to compute an integral (e.g. an expected value). Metropolis–Hastings and other MCMC algorithms are generally used for sampling from multi-dimensional distributions, especially when the number of dimensions is high. For single-dimensional distributions, there are usually other methods (e.g. adaptive rejection sampling) that can directly return independent samples from the distribution, and these are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Monte Carlo
The Hamiltonian Monte Carlo algorithm (originally known as hybrid Monte Carlo) is a Markov chain Monte Carlo method for obtaining a sequence of random samples whose distribution converges to a target probability distribution that is difficult to sample directly. This sequence can be used to estimate integrals of the target distribution, such as expected values and moments. Hamiltonian Monte Carlo corresponds to an instance of the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm, with a Hamiltonian dynamics evolution simulated using a time-reversible and volume-preserving numerical integrator (typically the leapfrog integrator) to propose a move to a new point in the state space. Compared to using a Gaussian random walk proposal distribution in the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm, Hamiltonian Monte Carlo reduces the correlation between successive sampled states by proposing moves to distant states which maintain a high probability of acceptance due to the approximate energy conserving propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Machine Learning Research
The ''Journal of Machine Learning Research'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering machine learning. It was established in 2000 and the first editor-in-chief was Leslie Kaelbling. The current editors-in-chief are Francis Bach (Inria) and David Blei (Columbia University). History The journal was established as an open-access alternative to the journal ''Machine Learning''. In 2001, forty editorial board members of ''Machine Learning'' resigned, saying that in the era of the Internet, it was detrimental for researchers to continue publishing their papers in expensive journals with pay-access archives. The open access model employed by the ''Journal of Machine Learning Research'' allows authors to publish articles for free and retain copyright, while archives are freely available online. Print editions of the journal were published by MIT Press until 2004 and by Microtome Publishing thereafter. From its inception, the journal received no revenue from the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variational Bayesian Methods
Variational Bayesian methods are a family of techniques for approximating intractable integrals arising in Bayesian inference and machine learning. They are typically used in complex statistical models consisting of observed variables (usually termed "data") as well as unknown parameters and latent variables, with various sorts of relationships among the three types of random variables, as might be described by a graphical model. As typical in Bayesian inference, the parameters and latent variables are grouped together as "unobserved variables". Variational Bayesian methods are primarily used for two purposes: # To provide an analytical approximation to the posterior probability of the unobserved variables, in order to do statistical inference over these variables. # To derive a lower bound for the marginal likelihood (sometimes called the ''evidence'') of the observed data (i.e. the marginal probability of the data given the model, with marginalization performed over unobserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markov Chain Monte Carlo
In statistics, Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) is a class of algorithms used to draw samples from a probability distribution. Given a probability distribution, one can construct a Markov chain whose elements' distribution approximates it – that is, the Markov chain's Discrete-time Markov chain#Stationary distributions, equilibrium distribution matches the target distribution. The more steps that are included, the more closely the distribution of the sample matches the actual desired distribution. Markov chain Monte Carlo methods are used to study probability distributions that are too complex or too highly N-dimensional space, dimensional to study with analytic techniques alone. Various algorithms exist for constructing such Markov chains, including the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm. General explanation Markov chain Monte Carlo methods create samples from a continuous random variable, with probability density proportional to a known function. These samples can be used to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numba
Numba is an open-source JIT compiler that translates a subset of Python and NumPy into fast machine code using LLVM, via the llvmlite Python package. It offers a range of options for parallelising Python code for CPUs and GPUs, often with only minor code changes. Numba was started by Travis Oliphant in 2012 and has since been under active development aits repository in GitHubwith frequent releases. The project is driven by developers at Anaconda, Inc., with support by DARPA, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, Intel, Nvidia and AMD, and a community of contributors on GitHub. Example Numba can be used by simply applying the numba.jit decorator to a Python function that does numerical computations: import numba import random @numba.jit def monte_carlo_pi(n_samples: int) -> float: """Monte Carlo""" acc = 0 for i in range(n_samples): x = random.random() y = random.random() if (x**2 + y**2) >> monte_carlo_pi(1000000) 3.14 Numba's webs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google JAX
JAX is a Python library for accelerator-oriented array computation and program transformation, designed for high-performance numerical computing and large-scale machine learning. It is developed by Google with contributions from Nvidia and other community contributors. It is described as bringing together a modified version oautograd(automatic obtaining of the gradient function through differentiation of a function) and OpenXLA's XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra). It is designed to follow the structure and workflow of NumPy as closely as possible and works with various existing frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch. The primary features of JAX are: # Providing a unified NumPy-like interface to computations that run on CPU, GPU, or TPU, in local or distributed settings. # Built-in Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation via Open XLA, an open-source machine learning compiler ecosystem. # Efficient evaluation of gradients via its automatic differentiation transformations. # Automatically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |