|
Purpuric
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not Blanch (medical), blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, or other causes. They measure 3–10 mm, whereas petechiae measure less than 3 mm, and Ecchymosis, ecchymoses greater than 1 cm. Purpura is common with typhus and can be present with meningitis caused by meningococci or Sepsis, septicaemia. In particular, meningococcus (''Neisseria meningitidis''), a Gram-negative diplococcus organism, releases endotoxin when it lysis, lyses. Endotoxin activates the Hageman factor (clotting factor XII), which causes disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). The DIC is what appears as a rash on the affected individual. Classification Purpura are a common and nonspecific medical sign; however, the underlying mechanism commonly involves one of: *Platelet, Platelet disor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both artery, arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily caused by white blood cell, leukocyte migration and resultant damage. Although both occur in vasculitis, inflammation of veins (phlebitis) or arteries (arteritis) on their own are separate entities. Signs and symptoms The clinical presentation of the various vasculitides on the skin and internal organs is mostly determined by the diameter or size of the vessels mainly affected. Non-specific symptoms are common and include fever, headache, fatigue, myalgia, weight loss, and arthralgia. All forms of vasculitis, even large vessel vasculitides, may cause skin manifestations. The most common skin manifestations include purpura, Nodule (dermatology), nodules, livedo reticularis, Ulcer (dermatology), skin ulcers, and purpuric Hives, urticaria. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
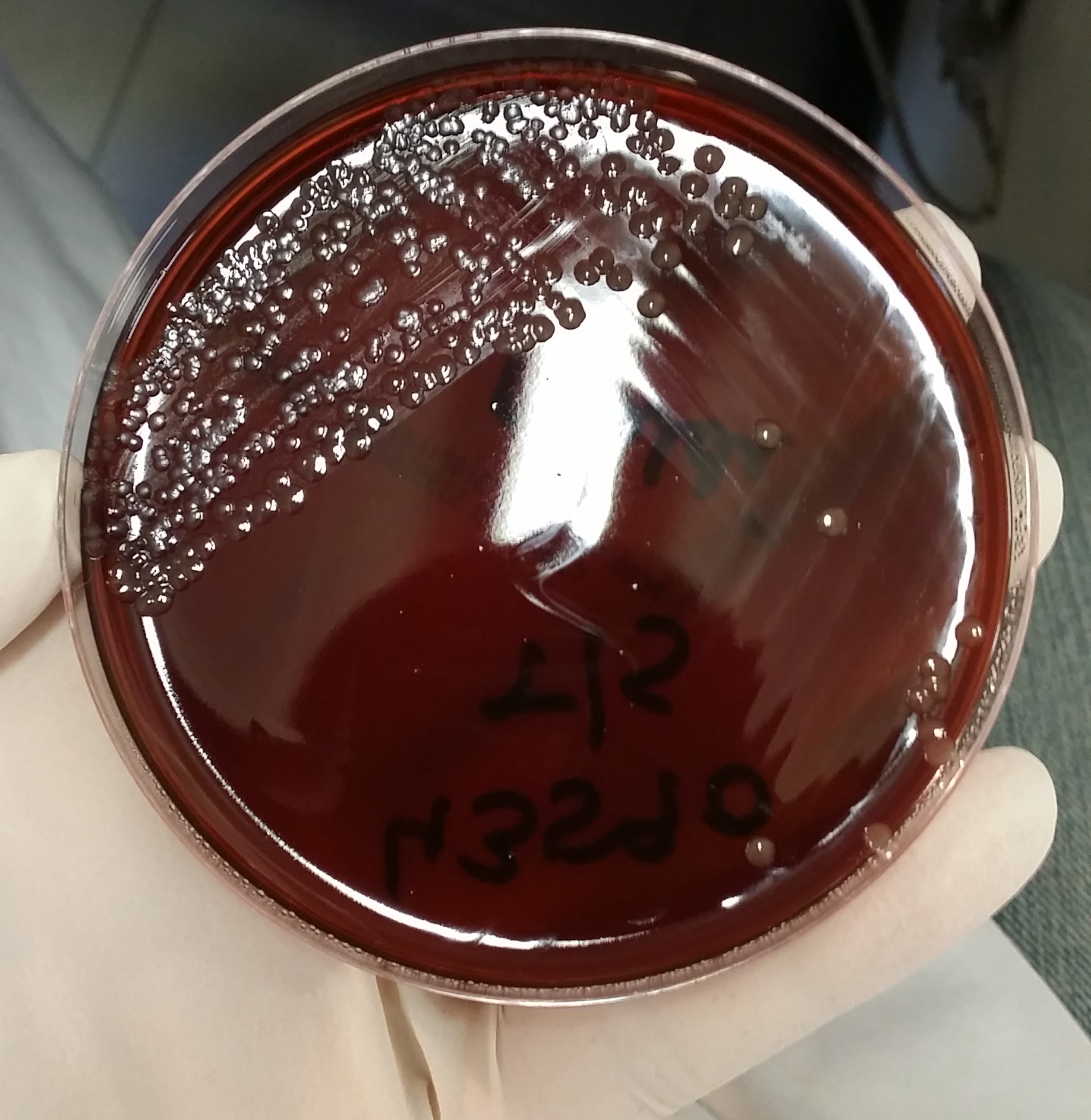
Neisseria Meningitidis
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as the meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a coccus because it is round, and more specifically a diplococcus because of its tendency to form pairs. About 10% of adults are carriers of the bacteria in their nasopharynx. As an exclusively human pathogen, it causes developmental impairment and death in about 10% of cases. It causes the only form of bacterial meningitis known to occur epidemically, mainly in Africa and Asia. It occurs worldwide in both epidemic and endemic form. ''N. meningitidis'' is spread through saliva and respiratory secretions during coughing, sneezing, kissing, chewing on toys and through sharing a source of fresh water. It has also been reported to be Sexually transmitted infection, transmitted through oral sex and cause urethritis in men. It infects its hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petechiae
A petechia (; : petechiae) is a small red or purple spot ( 1 cm in diameter) and purpura (3 to 10 mm in diameter). The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant. Causes Physical trauma The most common cause of petechiae is through physical trauma such as a hard bout of coughing, holding breath, vomiting, or crying, which can result in facial petechiae, especially around the eyes. Excessive scratching and friction, especially on thin and poorly circulated parts of the body may also cause petechiae. Such instances are generally considered harmless and usually disappear within a few days, but depending on severity and frequency may be indicative of an underlying medical condition. * Constriction, asphyxiation – petechiae, especially in the eyes, may also occur when excessive pressure is applied to tissue (e.g., when a tourniquet is applied to an extremity or with excessive coughing or vomiting). * Sunburn, childbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, build up in tissue. There are several non-specific and vague signs and symptoms associated with amyloidosis. These include fatigue, peripheral edema, weight loss, shortness of breath, palpitations, and Orthostatic hypotension, feeling faint with standing. In AL amyloidosis, specific indicators can include enlargement of the tongue and periorbital purpura. In wild-type ATTR amyloidosis, non-cardiac symptoms include: bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome, lumbar spinal stenosis, biceps tendon rupture, Small fiber peripheral neuropathy, small fiber neuropathy, and autonomic dysfunction. There are about 36 different types of amyloidosis, each due to a specific Proteopathy, protein misfolding. Within these 36 proteins, 19 are grouped into Organ-limited amyloidosis, localized forms, 14 are grouped as Systemic disease, systemic forms, and three proteins can identify as either. These proteins can become ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibril
Fibrils () are structural biological materials found in nearly all living organisms. Not to be confused with fibers or protein filament, filaments, fibrils tend to have diameters ranging from 10 to 100 nanometers (whereas fibers are micro to milli-scale structures and filaments have diameters approximately 10–50 nanometers in size). Fibrils are not usually found alone but rather are parts of greater hierarchical structures commonly found in biological systems. Due to the prevalence of fibrils in biological systems, their study is of great importance in the fields of microbiology, biomechanics, and materials science. Structure and mechanics Fibrils are composed of linear biopolymers, and are characterized by rod-like structures with high length-to-diameter ratios. They often spontaneously arrange into helical structures. In biomechanics problems, fibrils can be characterized as classical beams with a roughly circular cross-sectional area on the nanometer scale. As such, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningococcal Disease
Meningococcal disease is a serious infection caused by ''Neisseria meningitidis'', also known as meningococcus, a gram negative diplococcus. Meningococcal disease includes meningitis, meningococcal septicemia, or a combination of both, which can be life-threatening and rapidly progressive. If left untreated, the disease has a high mortality rate; however, it is preventable through vaccination. Meningitis and meningococcal sepsis are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both Developed countries, developed and Underdeveloped countries, under-developed countries. Meningococcal disease can be transmitted to others through saliva, close contact with an infected individual by inhaling respiratory air droplets. Initial symptoms may be subtle and similar to other bacterial infection, but can quickly progress to include fever, rash, body aches, photophobia and other complications. ''Neisseria meningitidis'' colonizes a substantial proportion of the general population withou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription dietary supplement. As a therapy, it is used to prevent and treat scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Vitamin C may be taken by mouth or by intramuscular, subcutaneous or intravenous injection. Various health claims exist on the basis that moderate vitamin C deficiency increases disease risk, such as for the common cold, cancer or COVID-19. There are also claims of benefits from vitamin C supplementation in excess of the recommended d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease (state of malnutrition) resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, fatigue, and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding from the skin may occur. As scurvy worsens, there can be poor wound healing, personality changes, and finally death from infection or bleeding. It takes at least a month of little to no vitamin C in the diet before symptoms occur. In modern times, scurvy occurs most commonly in people with mental disorders, unusual eating habits, alcoholism, and older people who live alone. Other risk factors include intestinal malabsorption and Kidney dialysis, dialysis. While many animals produce their vitamin C, humans and a few others do not. Vitamin C, an antioxidant, is required to make the building blocks for collagen, carnitine, and catecholamines, and assists the intestines in the absorption of iron from foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
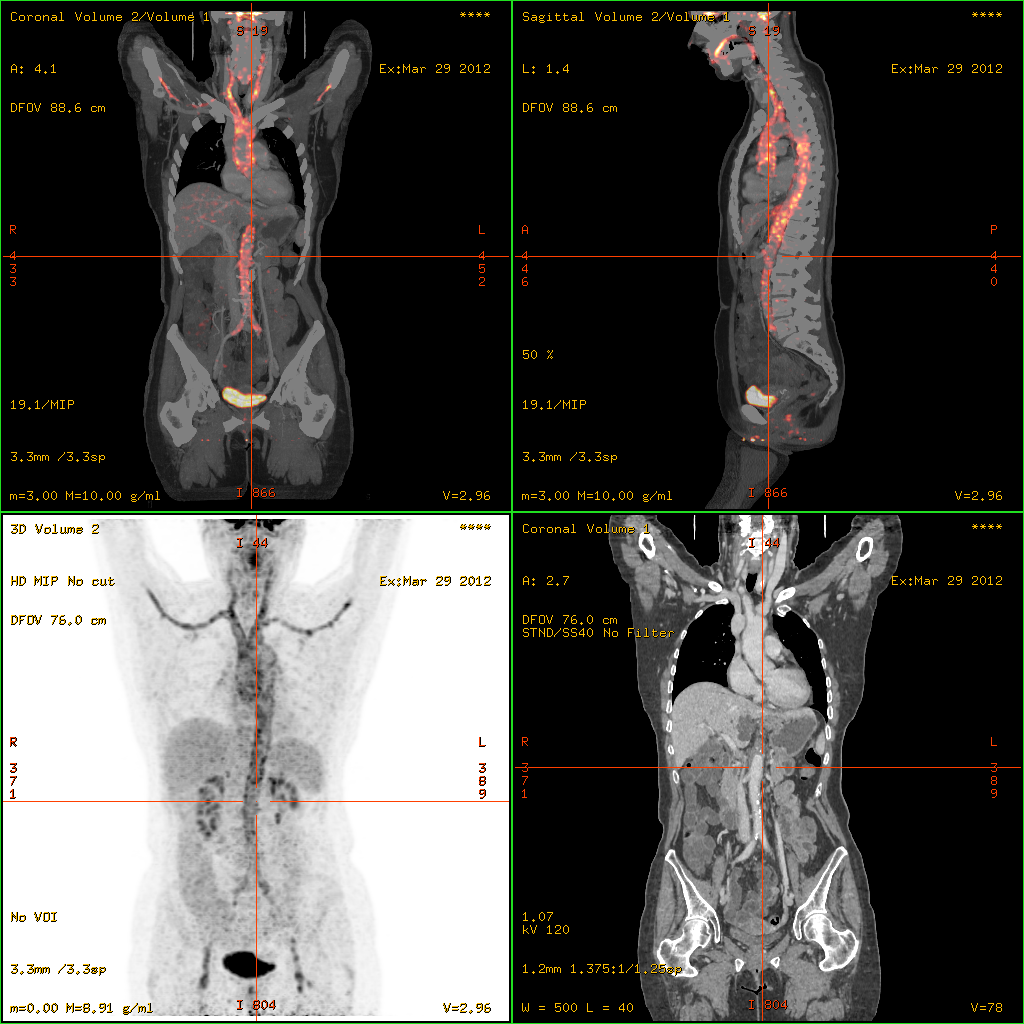
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking Microvessel, small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems moving parts of the body. As clotting factors and platelets are used up, bleeding may occur. This may include hematuria, blood in the urine, GI bleed, blood in the stool, or bleeding into the skin. Complications may include organ failure. Relatively common causes include sepsis, surgery, major trauma, cancer, and complications of pregnancy. Less common causes include snake bites, frostbite, and burns. There are two main types: acute (rapid onset) and chronic (slow onset). Diagnosis is typically based on blood tests. Findings may include thrombocytopenia, low platelets, low fibrinogen, high International normalized ratio, INR, or high D-dimer. Treatment is mainly directed towards the underlying condition. Other measures may include givin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coagulopathy
Coagulopathy (also called a bleeding disorder) is a condition in which the blood's ability to coagulate (form clots) is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding ( bleeding diathesis), which may occur spontaneously or following an injury or medical and dental procedures. Coagulopathies are sometimes erroneously referred to as "clotting disorders", but a clotting disorder is the opposite, defined as a predisposition to excessive clot formation (thrombus), also known as a hypercoagulable state or thrombophilia. Signs and symptoms Coagulopathy may cause uncontrolled internal or external bleeding. Left untreated, uncontrolled bleeding may cause damage to joints, muscles, or internal organs and may be life-threatening. People should seek immediate medical care for serious symptoms, including heavy external bleeding, blood in the urine or stool, double vision, severe head or neck pain, repeated vomiting, difficulty walking, convulsions, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henoch–Schönlein Purpura
IgA vasculitis (HSP), previously known as Henoch–Schönlein purpura, is an autoimmune disease that most commonly affects children. In the skin, the disease causes palpable purpura (small, raised areas of bleeding underneath the skin), often with arthralgia, joint pain and abdominal pain. With kidney involvement, there may be a loss of small amounts of blood and protein in the urine (hematuria and proteinuria), but this usually goes unnoticed; in a small proportion of cases, the kidney involvement proceeds to chronic kidney disease. HSP is often preceded by an infection, such as a pharyngitis, throat infection. HSP is a systemic vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels) and is characterized by deposition of immune complexes containing the antibody immunoglobulin A (IgA); the exact cause for this phenomenon is unknown. In children, it usually resolves within several weeks and requires no treatment apart from symptom control but may relapse in a third of cases and cause irreversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |