|
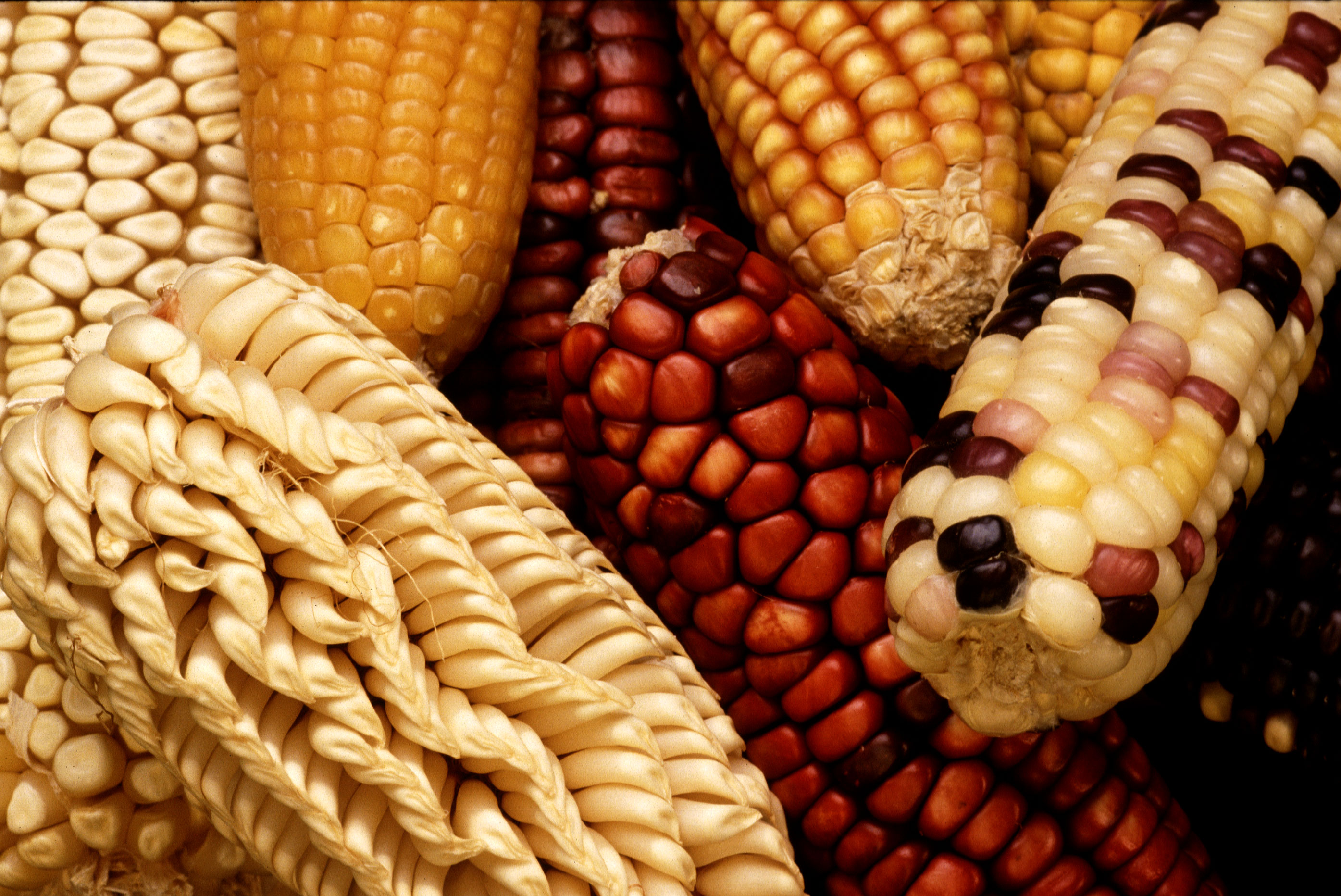
Purple Corn
Purple corn () or purple maize is group of flint maize varieties (Flint_corn, Zea mays indurata) originating in South America, descended from a common ancestral variety termed "kʼculli" in Quechuan languages, Quechua. It is most commonly grown in the Andes of Peru, Bolivia and Ecuador. Uses Common in Peru, purple corn is used in chicha morada, a drink made by boiling ground purple corn kernels with pineapple, cinnamon, clove, and sugar, and in mazamorra, a type of pudding". In Bolivia, purple corn "Kuli" is used in Api, a smoothie served hot. Color chemistry: anthocyanins The pigment giving purple corn its vivid color derives from an exceptional content of a class of polyphenols called anthocyanins. Cyanidin 3-O-glucoside, also called chrysanthemin, is the major anthocyanin in purple corn kernels, comprising about 73% of all anthocyanins present. Other anthocyanins identified are pelargonidin 3-O-β-D-glucoside, peonidin 3-O-β-D-glucoside, cyanidin 3-O-β-D-(6-malonyl-glucoside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthocyanins
Anthocyanins (), also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart named a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color, Anthokyan, in his treatise "''Die Farben der Blüthen''" (English: The Colors of Flowers). Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins. Anthocyanins belong to a parent class of molecules called flavonoids synthesized via the phenylpropanoid pathway. They can occur in all tissues of higher plants, including leaves, stems, roots, flowers, and fruits. Anthocyanins are derived from anthocyanidins by adding sugars. They are odorless and moderately astringent. Although approved as food and beverage colorant in the European Union, anthocyanins are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maize Varieties
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sweet corn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
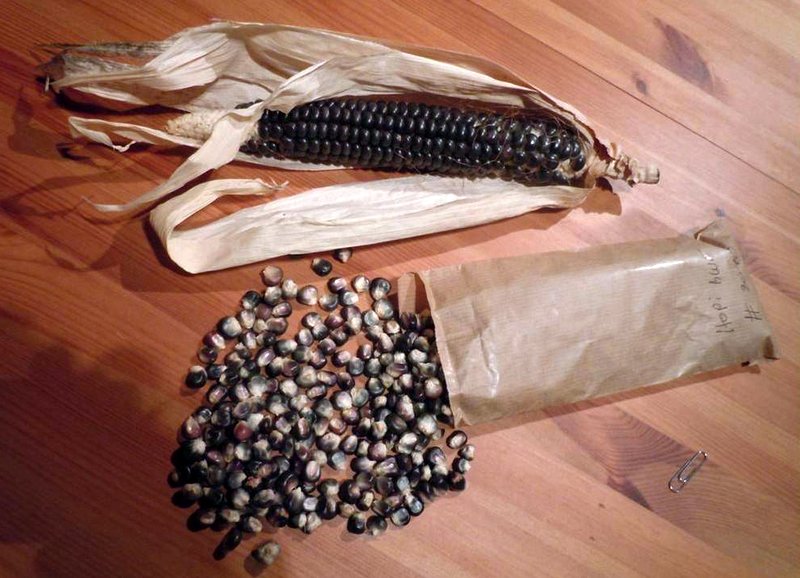
Blue Corn
Blue corn (also known as Hopi maize, Yoeme Blue, Tarahumara Maiz Azul, and Rio Grande Blue) is a group of several closely related varieties of flint corn grown in Mexico, the Southwestern United States, and the Southeastern United States. It is one of the main types of corn used for the traditional Southern and Central Mexican food known as tlacoyo. It was originally developed by the Hopi, the Pueblo Indians of the Rio Grande in Arizona, and several Southeastern tribes, including the Cherokee. It remains an essential part of Hopi dishes like piki bread. Blue corn meal is a corn meal that is ground from whole blue corn and has a sweet flavor. It is also a staple of New Mexican cuisine used commonly to make tortillas. Blue corn contains anthocyanins, which give the corn its blue color. Varieties Five Hopi blue corn cultivars identified in the 1950s showed significant differences for several traits, such as plant height, kernel weight, width of kernel, and thickness of kern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how biomass is defined, e.g., only from plants, from plants and algae, from plants and animals. The vast majority of biomass used for bioenergy does come from plants and fecal matter. Bioenergy is a type of renewable energy that the bioenergy industry claims has the potential to assist with climate change mitigation. Uses in different contexts Ecology * Biomass (ecology), the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. This can be the biomass of particular species or the biomass of a particular community or habitat. Energy * Biomass (energy), biomass used for energy production or in other words: biological mass used as a renewable energy source (usually produced through agriculture, forestry or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Husk
Husk (or hull) in botany is the outer shell or coating of a seed. In the United States, the term husk often refers to the leafy outer covering of an Ear (botany), ear of maize (corn) as it grows on the plant. Literally, a husk or hull includes the protective outer covering of a seed, fruit, or vegetable. It can also refer to the exuvia of insects or other small animals left behind after ecdysis, moulting. The term ''husk'' dates to c.14, it is probably based on Middle Dutch word ''huusken'' meaning 'little house', which is derived from ''hūs'' meaning house. In cooking, hull can also refer to other waste parts of fruits and vegetables, notably the cap or sepal of a strawberry. Grains such as wheat and barley have husks. The grains are the entire seed of a plant. The seed of a grain (which the grain industry calls a "Seed, kernel") is made up of three key edible parts – the bran, the wheat germ, germ, and the endosperm – which are all protected by an inedible husk that pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corncob
A corncob, also called corn cob or cob of corn, is the hard core of an ear of maize, bearing the kernels, made up of the chaff, woody ring, and pith. Corncobs contain mainly cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. However, during several instances of famine (especially in European countries throughout history), people have been known to eat the corncobs, especially the foamy middle part. The whole cob or just the middle used to be ground and mixed with whatever type of flour was available (usually wheat or corn flour). It served as a sort of peculiar "filler", to extend the quantity of the original flour and as such, it was used even in production of bread. The cob is not toxic to humans and can be digested, but the outside is rough and practically inedible in its original form. The foamy part has a peculiar texture when mature and is completely bland, which most people would find unappealing, due to the consistency similar to foam plastic. Corncobs are a particularly good source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash, the ashes of plants, from which its name derives. In the periodic table, potassium is one of the alkali metals, all of which have a single valence electron in the outer electron shell, which is easily removed to create cation, an ion with a positive charge (which combines with anions to form salts). In nature, potassium occurs only in ionic salts. Elemental potassium reacts vigorously with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite hydrogen emitted in the reaction, and burning with a lilac-flame color, colored flame. It is found dissolved in seawater (which is 0.04% potassium by weight), and occurs in many minerals such as orthoclase, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peonidin 3-O-β-D-(6-malonyl-glucoside)
Peonidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin derived from Cyanidin, and a primary plant pigment. Peonidin gives purplish-red hues to flowers such as the peony, from which it takes its name, and roses. It is also present in some blue flowers, such as the morning glory. Like most anthocyanidins Anthocyanidins are common plant pigments, the aglycones of anthocyanins. They are based on the flavylium cation, an oxonium ion, with various groups substituent, substituted for its hydrogen atoms. They generally change color from red through p ..., it is pH sensitive, and changes from red to blue as pH rises because anthocyanidins are highly conjugated chromophores. When the pH is changed, the extent of the conjugation (of the double bonds) is altered, which alters the wavelength of light energy absorbed by the molecule. (Natural anthocyanidins are most stable in a very low pH environment; at pH 8.0, most become colorless.) At pH 2.0, peonidin is cherry red; at 3.0 a strong yellowish pin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelargonidin 3-O-β-D-(6-malonyl-glucoside)
Pelargonidin is an anthocyanidin, a type of plant pigment producing a characteristic orange color used in food and industrial dyes. Natural occurrences Presence in flowers Pelargonidin can be found in red geraniums (Geraniaceae). It is the predominant pigment causing the red coloration in the spathes of ''Philodendron'' (Araceae). The orange-coloured flowers of blue pimpernel (''Anagallis monelli'', Myrsinaceae) have a higher concentration of pelargonidin pigment. Red and Pink Roses (Rosa) obtain their color from this phytochemical. Presence in food Pelargonidin can be found in berries such as ripe Raspberry, raspberries and Strawberry, strawberries, as well as Blueberry, blueberries, Blackberry, blackberries, Cranberry, cranberries but also in saskatoon berries and chokeberries. It is also found in plums and pomegranates. Pelargonidin gives red radish, radishes their color. It is present in large amounts in kidney beans. Glycosides In many plant systems, Pelargonidin c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanidin 3-O-β-D-(6-malonyl-glucoside)
Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin (glycoside version called anthocyanins). It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, chokeberry, cranberry, elderberry, hawthorn, loganberry, açai berry and raspberry. It can also be found in other fruits such as apples and plums, and in red cabbage and red onion. It has a characteristic reddish-purple color, though this can change with pH; solutions of the compound are red at pH 11. In certain fruits, the highest concentrations of cyanidin are found in the seeds and skin. Cyanidin has been found to be a potent sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) activator. List of cyanidin derivatives * Antirrhinin (cyanidin-3-rutinoside or 3-C-R), found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3-xylosylrutinoside, found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3,4′-di-''O''-β-glucopyranoside, found in red onion * Cyanidin-4′-''O''-β-glucoside, found in red onion * Chrysanthemin (cyan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peonidin 3-O-β-D-glucoside
Peonidin-3-''O''-glucoside is anthocyanin. It is found in fruits and berries, in red ''Vitis vinifera ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern ...'' grapes and red wine, in red onions and in purple corn.Anthocyanins isolated from purple corn (''Zea mays'' L.). Hiromitsu Aoki, Noriko Kuze and Yoshiaki Katoarticle) It is dark red to purple in colour. See also * Phenolic compounds in wine References O-methylated anthocyanins {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |