|
Purine
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature. Dietary sources Purines are found in high concentration in meat and meat products, especially internal organs, such as liver and kidney, and in various seafoods, high-fructose beverages, alcohol, and yeast products. Examples of high-purine food sources include anchovies, sardines, liver, beef, kidneys, brains, monkfish, dried mackerel, and shrimp. Foods particularly rich in hypoxanthine, adenine, and guanine lead to higher blood levels of uric acid. Foods having more than 200 mg of hypoxanthine per 100 g, particularly animal and fish meats containing hypoxanthine as more than 50% of total purines, are more likely to increase uri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogenous Base
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. The ability of nucleobases to form base pairs and to stack one upon another leads directly to long-chain helical structures such as ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Five nucleobases—adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T), and uracil (U)—are called ''primary'' or ''canonical''. They function as the fundamental units of the genetic code, with the bases A, G, C, and T being found in DNA while A, G, C, and U are found in RNA. Thymine and uracil are distinguished by merely the presence or absence of a methyl group on the fifth carbon (C5) of these heterocyclic six-membered rings. In addition, some viruses have aminoadenine (Z) instead of adenine. It differs in having an extra amine group, cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperuricemia
Hyperuricaemia or hyperuricemia is an abnormally high level of uric acid in the blood. In the pH conditions of body fluid, uric acid exists largely as urate, the ion form. Serum uric acid concentrations greater than 6 mg/dL for females, 7 mg/dL for males, and 5.5 mg/dL for youth (under 18 years old) are defined as hyperuricemia. The amount of urate in the body depends on the balance between the amount of purines eaten in food, the amount of urate synthesised within the body (e.g., through cell turnover), and the amount of urate that is excreted in urine or through the gastrointestinal tract. Hyperuricemia may be the result of increased production of uric acid, decreased excretion of uric acid, or both increased production and reduced excretion. Signs and symptoms Unless high blood levels of uric acid are determined in a clinical laboratory, hyperuricemia may not cause noticeable symptoms in most people. Development of gout which is a painful, short-term d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of pain in a red, tender, hot, and Joint effusion, swollen joint, caused by the deposition of needle-like crystals of uric acid known as monosodium urate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensity in less than 12 hours. The Metatarsophalangeal joint, joint at the base of the Hallux, big toe is affected (''Podagra'') in about half of cases. It may also result in Tophus, tophi, kidney stones, or Urate nephropathy, kidney damage. Gout is due to persistently elevated levels of uric acid (urate) in the blood (hyperuricemia). This occurs from a combination of diet, other health problems, and genetic factors. At high levels, uric acid crystallizes and the crystals deposit in joints, tendons, and surrounding tissues, resulting in an attack of gout. Gout occurs more commonly in those who regularly drink beer or sugar-sweetened beverages; eat foods that are high in purines such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux repor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is called guanosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine- imidazole ring system with conjugated double bonds. This unsaturated arrangement means the bicyclic molecule is planar. Properties Guanine, along with adenine and cytosine, is present in both DNA and RNA, whereas thymine is usually seen only in DNA, and uracil only in RNA. Guanine has multiple tautomeric forms. For the imidazole ring, the proton can reside on either nitrogen. For the pyrimidine ring, the ring N-H can center can reside on either of the ring nitrogens. The latter tautomer does not apply to nucleoside or nucleotide versions of guanine. It binds to cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. In cytosine, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is complementary and pairs to either thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA. In cells adenine, as an independent molecule, is rare. It is almost always covalent bond, covalently bound to become a part of a larger biomolecule. Adenine has a central role in cellular respiration. It is part of adenosine triphosphate which provides the energy that drives and supports most activities in living cell (biology), cells, such as Protein biosynthesis, protein synthesis, chemical synthesis, muscle contraction, and nerve impulse propagation. In respiration it also participates as part of the cofactor (biochemistry), cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, flavin adenine dinucleotide, and Coenzyme A. It is also part of adenosine, adenosine monophosphate, cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxanthine
Hypoxanthine is a naturally occurring purine derivative. It is occasionally found as a constituent of nucleic acids, where it is present in the anticodon of tRNA in the form of its nucleoside inosine. It has a tautomer known as 6-hydroxypurine. Hypoxanthine is a necessary additive in certain cells, bacteria, and parasite cultures as a substrate and nitrogen source. For example, it is commonly a required reagent in malaria culture, malaria parasite cultures, since ''Plasmodium falciparum'' requires a source of hypoxanthine for nucleic acid synthesis and energy metabolism. In August 2011, a report, based on NASA studies with meteorites found on Earth, was published suggesting hypoxanthine and related organic molecules, including the DNA and RNA components adenine and guanine, may have been formed extraterrestrially in outer space. The ''Pheretima, Pheretima aspergillum'' worm, used in Chinese medicine preparations, contains hypoxanthine. Reactions It is one of the products of the ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imidazole
Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula . It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. It can be classified as a heterocycle, specifically as a diazole. Many natural products, especially alkaloids, contain the imidazole ring. These imidazoles share the 1,3-C3N2 ring but feature varied substituents. This ring system is present in important biological building blocks, such as histidine and the related hormone histamine. Many drugs contain an imidazole ring, such as certain antifungal drugs, the nitroimidazole series of antibiotics, and the sedative midazolam. When fused to a pyrimidine ring, it forms a purine, which is the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing Heterocyclic compound, heterocycle in nature. The name "imidazole" was coined in 1887 by the German chemist Arthur Rudolf Hantzsch (1857–1935). Structure and properties Imidazole is a planar 5-membered ring, that exists in two equivalent tautomeric f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
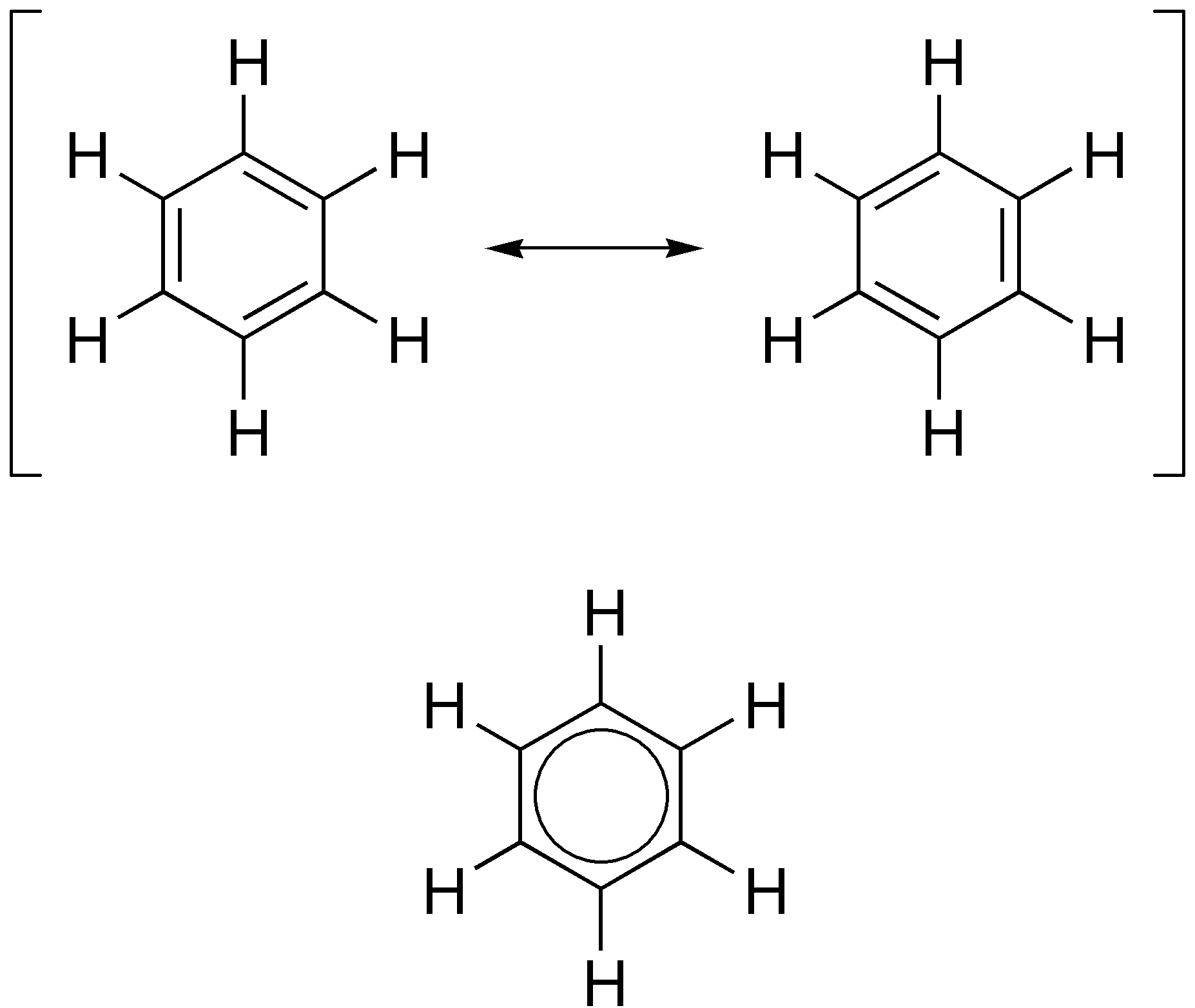
Aromatic
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated system, conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfaction, olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of Resonance (chemistry), resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double-covalent bond, bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Friedrich August Kekulé ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compound
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of py ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tautomer
In chemistry, tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydrogen atom within the compound. The phenomenon of tautomerization is called tautomerism, also called desmotropism. Tautomerism is for example relevant to the behavior of amino acids and nucleic acids, two of the fundamental building blocks of life. Care should be taken not to confuse tautomers with depictions of "contributing structures" in chemical resonance. Tautomers are distinct chemical species that can be distinguished by their differing atomic connectivities, molecular geometries, and physicochemical and spectroscopic properties, whereas resonance forms are merely alternative Lewis structure (valence bond theory) depictions of a single chemical species, whose true structure is a quantum superposition, essentially the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal artery, renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the urinary bladder, bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, Acid-base homeostasis, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |