|
Purgaz
Purgaz or Inäzor Purgaz (, , ''Purgas'') was an Erzän leader in the first half of the 13th century. He was a Grand Duke (''inäzor'') of the Erzän Principality of Purgaz. Being an ally of Volga Bulgaria, he resisted easterly Slavic expansion of Suzdalian Rus forces into the region. In later times, he became a symbol of Erzän independence and a figure of legend. Life Purgaz was named in the Russian chronicles several times. In January, 1229 his army repulsed a raid of the Russian princes Yaroslav Vsevolodovich, Vasily Konstantinovich and Vsevolod Konstantinovich. Then Purgaz defeated the Mokshan prince, Puresh In April, 1229 he tried to regain Nizhny Novgorod from the hands of Zalesyean Rus', which was formerly the Erzyan settlement of Obran Osh. His troops burned down the settlement, but the citadel stayed safe. Several months later he was defeated by Puresh. During Purgaz's reign his land noted an influx of Ruthenian Slavic peasants into it. In the summer of 123 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Purgaz
The Principality of Purgaz (; ), also referred to as the Purgas Volost, was a "Mordvin" principality located between the Oka and Sura rivers. The principality is an important part of Mordvin history and is notable for marking the first time the Erzyas and Mokshas united under a single polity. Background The Mordvin peoples, comprising the Erzya and Moksha ethnic groups, began to unify at the start of the 2nd millennium as a result of upheavals in the social structure of Mordvin tribes and the establishment of early class relations. Further assisting the political unification of the Mordvins was a series of military campaigns by the Khazars and Kievan Rus', which brought the Mordvin tribes together in a successful effort to defeat foreign militaries. According to the ''Primary Chronicle'', a March 1103 invasion of the Mordvins by the Kievan Rus' ended in a Mordvin victory. History Attempts to conquer the Mordvins escalated in 1184, with a violent process of colonisation by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Mordovia
Mordovia ( ),; Moksha language, Moksha and officially the Republic of Mordovia,; ; is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia, situated in Eastern Europe. Its capital city, capital is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Saransk. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, the population of the republic was 834,755. Ethnic Russians (53.1%) and Mordvins (39.8%) account for the majority of the population. History Early history The earliest archaeological signs of modern humans in the area of Mordovia are from the Neolithic, Neolithic era. Mordvins are mentioned in written sources from the 6th century. Later, Mordvins were under the influence of both Volga Bulgaria and the Kievan Rus. Mordvin princes sometimes raided Muroma and Volga Bulgaria and often despoiled each other's holdings. Mordovia was briefly united under the Principality of Purgaz, led by Erzya prince Purgaz, who fought against the colonisation of the region by Vladimir-Suzdal. The Mordvin t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mokshas
The Mokshas (also ''Mokshans'', ''Moksha people''; ) comprise a Mordvins, Mordvinian ethnic group belonging to the Volga Finns, Volgaic branch of the Finno-Ugric peoples. They live in Russia, mostly near the Volga and Moksha (river), Moksha rivers, a tributary of the Oka (river), Oka River. Their native language is Moksha language, Mokshan, one of the two surviving members of the Mordvinic languages, Mordvinic branch of the Uralic language family. According to a List of Russian censuses, 1994 Russian census, 49% of the autochthonal Volga Finns, Finnic population in Mordovia identified themselves as Mokshas, totaling more than 180,000 people. Most Mokshas belong to the Russian Orthodox Church; other religions practised by Mokshas include Lutheranism and paganism. Name William of Rubruck, the Franciscan friar whom King Louis IX of France sent as an ambassador to the Mongols in the 1250s, called them "Moxel". The same term appears in the Persian/Arabic 14th-century Jami' al-tawar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puresh
Puresh () was a Moksha ruler of Mukhsha Ulus in Middle Volga. History In the 1230s, the Erzyan King Purgaz and the Mokshan King Puresh were at war and while Purgaz was allied with Volga Bulgaria, Puresh was an ally of Grand Prince Yuri II of Vladimir. Legend See also * Mongol invasion of Rus' * Mongol invasion of Europe From the 1220s to the 1240s, the Mongol Empire, Mongols conquered the Turkic peoples, Turkic states of Volga Bulgaria, Cumania and Iranian peoples, Iranian state of Alania, and various principalities in Eastern Europe. Following this, they began ... References 1241 deaths Assassinated nobility 13th-century soldiers Military strategists 13th-century monarchs in Europe People murdered in Poland Moksha people {{europe-noble-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət, t=Lower Newtown; colloquially shortened to Nizhny) is a city and the administrative centre of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast and the Volga Federal District in Russia. The city is located at the confluence of the Oka (river), Oka and the Volga rivers in Central Russia, with a population of over 1.2 million residents, up to roughly 1.7 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Nizhny Novgorod is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, sixth-largest city in Russia, the Volga#Biggest cities on the shores of the Volga, second-most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. The city is located 420 kilometers (260 mi) east of Moscow. It is an important economic, transportation, scientific, educational and cultural centre in Russia and the vast Volga-Vyatka economic region, and the main centre of river tourism in Russia. In the his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erzyas
The Erzyas (also ''Erzyans'', ''Erzya people''; , ) are one of the Mordvin peoples. Famous people of Erzya descent * Purgaz * Syreś Boläeń, public figure, poet and translator, half-Erzya * Stepan Erzia, Russian sculptor * Nadezhda Kadysheva, Russian singer * Vasily Chapayev, Bolshevik The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, ... commander See also * Shoksha References {{Finno-Ugric peoples Volga Finns Paganism in Europe Lutheranism in Russia Indigenous peoples of Europe Ethnic groups in Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga Finns
The Volga Finns are a historical group of peoples living in the vicinity of the Volga, who speak Uralic languages. Their modern representatives are the Mari people, the Erzya and the Moksha (commonly grouped together as Mordvins) as well as speakers of the extinct Merya, Muromian and Meshchera languages. The modern representatives of Volga Finns live in the basins of the Sura and Moksha rivers, as well as (in smaller numbers) in the interfluve between the Volga and the Belaya rivers. The Mari language has two dialects, the Meadow Mari and the Hill Mari. Traditionally the Mari and the Mordvinic languages ( Erzya and Moksha) were considered to form a ''Volga-Finnic'' or ''Volgaic'' group within the Uralic language family, accepted by linguists like Robert Austerlitz (1968), Aurélien Sauvageot & Karl Heinrich Menges (1973) and Harald Haarmann (1974), but rejected by others like Björn Collinder (1965) and Robert Thomas Harms (1974). This grouping has also been cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erzya Language
The Erzya language (, , ), also Erzian or historically Arisa, is spoken by approximately 300,000 people in the northern, eastern and north-western parts of the Republic of Mordovia and adjacent regions of Nizhny Novgorod, Chuvashia, Penza, Samara, Saratov, Orenburg, Ulyanovsk, Tatarstan and Bashkortostan in Russia. A diaspora can also be found in Armenia and Estonia, as well as in Kazakhstan and other states of Central Asia. Erzya is currently written using Cyrillic with no modifications to the variant used by the Russian language. In Mordovia, Erzya is co-official with Moksha and Russian. The language belongs to the Mordvinic branch of the Uralic languages. Erzya is a language that is closely related to Moksha but has distinct phonetics, morphology and vocabulary. Phonology Consonants The following table lists the consonant phonemes of Erzya together with their Cyrillic equivalents. Palatalization is widespread in Erzya, but is contrastive only for the alveolar cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats and the Buryats are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or as subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity, descending from the Proto-Mongols. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The contiguous geographical area in which the Mongols primarily live is referred to as the Mongol heartland, especially in discussions of the Mongols' history under the Mongol Empire. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyks and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Arkhorchin, Asud, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
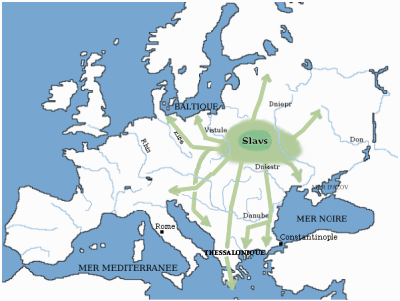
Slavic Peoples
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe, and North Asia, Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianization of the Slavs, Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the First Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenia
''Ruthenia'' is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin, as one of several terms for Rus'. Originally, the term ''Rus' land'' referred to a triangular area, which mainly corresponds to the tribe of Polans in Dnieper Ukraine. ''Ruthenia'' was used to refer to the East Slavic and Eastern Orthodox people of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland, and later the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Austria-Hungary, mainly to Ukrainians and sometimes Belarusians, corresponding to the territories of modern Belarus, Ukraine, Eastern Poland and some of western Russia. Historically, in a broader sense, the term was used to refer to all the territories under Kievan dominion (mostly East Slavs). The Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria (1772–1918), corresponding to parts of Western Ukraine, was referred to as ''Ruthenia'' and its people as ''Ruthenians''. As a result of a Ukrainian national identity gradually dominating over much of present-day Ukraine in the 19t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rus' People
The Rus, also known as Russes, were a people in early medieval Eastern Europe. The scholarly consensus holds that they were originally Norsemen, mainly originating from present-day Sweden, who settled and ruled along the river-routes between the Baltic and the Black Seas from around the 8th to 11th centuries AD. The two original centres of the Rus' were Ladoga (''Aldeigja''), founded in the mid-8th century, and Rurikovo Gorodische (''Holmr''), founded in the mid-9th century. The two settlements were situated at opposite ends of the Volkhov River, between Lake Ilmen and Lake Ladoga, and the Norsemen likely called this territory ''Gardar''. From there, the name of the Rus' was transferred to the Middle Dnieper, and the Rus' then moved eastward to where the Finnic tribes lived and southward to where the Slavs lived. The name '' Garðaríki'' was applied to the newly formed state of Kievan Rus', and the ruling Norsemen along with local Finnic tribes gradually assimilated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |