|
Purbeck Monocline
The Purbeck Monocline is a geological fold in southern England. The term 'fold' is used in geology when one or more originally flat sedimentary strata surfaces are bent or curved as a result of plastic (i.e. permanent) deformation. A monocline is a step-like fold, in which one limb is roughly horizontal. The Purbeck Monocline was formed during the late Oligocene and early Miocene epochs, about 30 million years ago. It is the northernmost 'ripple' of the Alpine Orogeny. The Purbeck Monocline gives rise to the prominent ridge of steeply dipping Cretaceous chalk which now forms the Purbeck Hills. This chalk band runs from Swyre Head via Flower's Barrow to Old Harry Rocks. From here the fold continues under the sea to The Needles and forms the central spine of the Isle of Wight. Here it is also known as the Purbeck-Isle of Wight Disturbance. The monocline continues under the English Channel as the Wight-Bray Monocline. The Purbeck Hills run east–west through the small b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Strata, Durdle Door - Geograph
Rock most often refers to: * Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids * Rock music, a genre of popular music Rock or Rocks may also refer to: Places United Kingdom * Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales * Rock, Cornwall, a village in England * Rock, County Tyrone, a village in Northern Ireland * Rock, Devon, a location in England * Rock, Neath Port Talbot, a location in Wales * Rock, Northumberland, a village in England * Rock, Somerset, a location in England * Rock, West Sussex, a hamlet in Washington, England * Rock, Worcestershire, a village and civil parish in England United States * Rock, Kansas, an unincorporated community * Rock, Michigan, an unincorporated community * Rock, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Rock, Rock County, Wisconsin, a town in southern Wisconsin * Rock, Wood County, Wisconsin, a town in central Wisconsin Elsewhere * Corregidor, an island in the Philippines also known as "The Rock" * Jamaica, an is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
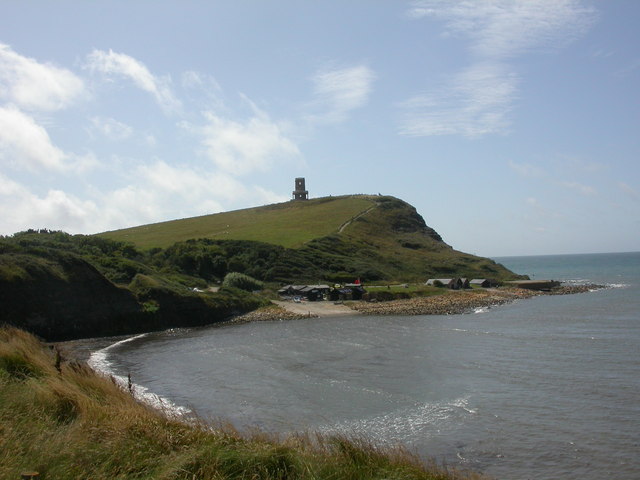
Old Harry Rocks
Old Harry Rocks are three chalk formations, including a stack and a stump, located at Handfast Point, on the Isle of Purbeck in Dorset, southern England. They mark the most eastern point of the Jurassic Coast, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Location Old Harry Rocks lie directly east of Studland, about north east of Swanage, and about south of the large towns of Poole and Bournemouth. To the south are the chalk cliffs of Ballard Down, much of which is owned by the National Trust. The rocks can be viewed from the Dorset section of the South West Coast Path. Formation The chalk of Old Harry Rocks used to be part of a long stretch of chalk between Purbeck and the Isle of Wight, but remained as a headland after large parts of this seam were eroded away. As the headland suffered hydraulic action (a process in which air and water are forced into small cracks by the force of the sea, resulting in enlarging cracks), first caves, then arches formed. The tops of the arches coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballard Down
Ballard Down is an area of chalk downland on the Purbeck Hills in the English county of Dorset. The hills meet the English Channel here, and Ballard Down forms a headland, Ballard Point, between Studland Bay to the north and Swanage Bay to the south. The chalk here forms part of a system of chalk downlands in southern England, and once formed a continuous ridge between what is now west Dorset and the present day Isle of Wight. Old Harry Rocks, just offshore from the dip slope of the down, and The Needles on the westernmost tip of the Isle of Wight, are remnants of this ridge. The scarp slope of the down faces south, over Swanage, meeting the sea as Ballard Cliff. The down was an area of calcareous grassland for up to 1000 years until World War II, when there was a sudden rise in the need for arable agricultural land. The down is now owned by the National Trust, and has largely been returned to grassland. The National Trust allows grazing on the down to prevent it becoming a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a Fracture (geology), planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of Rock (geology), rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust (geology), crust result from the action of Plate tectonics, plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction, subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the Plane (geometry), plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geological maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimmeridge Bay
Kimmeridge Bay () is a bay on the Isle of Purbeck, a peninsula on the English Channel coast in Dorset, England, close to and southeast of the village of Kimmeridge, on the Smedmore Estate. The area is renowned for its fossils, with The Etches Collection in the village of Kimmeridge displaying fossils found by Steve Etches in the area over a 30-year period. It is a popular place to access the coast for tourists. To the east are the Kimmeridge Ledges, where fossils can be found in the flat clay beds. Overview Kimmeridge Bay forms part of the Jurassic Coast, a World Heritage Site. The coast is also part of a Site of Special Scientific Interest, and the whole area is part of the Dorset National Landscape. Kimmeridge is the type locality for Kimmeridge clay, the geological formation that covers most of the area. Within the clay are bands of bituminous shale. An oil well has operated on the shore of Kimmeridge Bay since 1959. The bay is roughly semi-circular, facing southwest. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peveril Point
Peveril Point is a headland on the east-facing coast of the Isle of Purbeck in Dorset, England, and is part of the town of Swanage. It forms the southern end of Swanage Bay. It is located at OS Grid Ref: SZ 041 787. The rocks that make up Peveril Point are shale and Portland and Purbeck limestone in a syncline structure. This has resisted erosion more than the adjacent clay of Swanage Bay; whilst the clay has eroded away over time, the limestone has remained as a headland. On top of Peveril Point is a National Coastwatch Institution lookout. The point is also home to Swanage Lifeboat Station. Ward, Lock and Company, ltd, & Hammond, R. J. W. (1974). ''Complete England''. London: Ward Lock, p. 94. Peveril Point contains tunnels connecting disused gun emplacements which defended the entrance to Southampton Water from the west of the Isle of Wight during World War II World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arish Mell
Arish Mell is a small embayment and beach between Mupe Bay, Mupe and Worbarrow Bays in Dorset, England and is part of the Jurassic Coast and the South West Coast Path passes just to the north. It is about due south of Lulworth Castle and East Lulworth. The bay is relatively inaccessible because it is within the Lulworth Ranges, an Army tank firing range, and although the Range Walks are open at most weekends and public holidays, there is no public access to the beach and cliffs. History Arish Mell was the site of a series discharges pipes carrying effluent from the Winfrith Nuclear Power Station into the sea. Geology Arish Mell forms a break in the line of chalk hills that form the Purbeck Ridge. See also * List of Dorset beaches Gallery File:Arish Mell - geograph.org.uk - 161671.jpg, Arish Mell from the east. File:Behind Arish Mell - geograph.org.uk - 1521249.jpg, Behind Arish Mell Isle of Purbeck Bays of Dorset Jurassic Coast {{Dorset-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
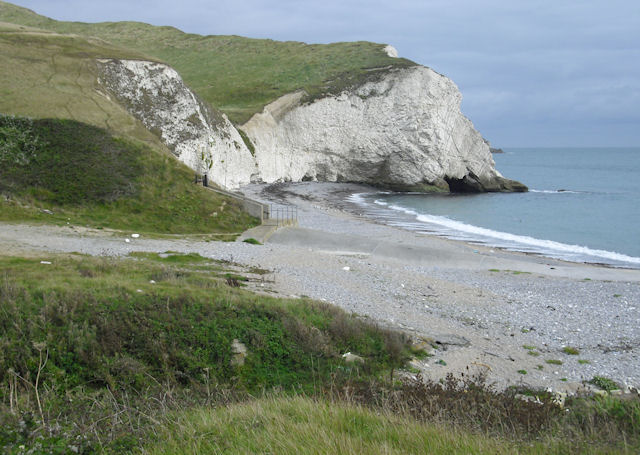
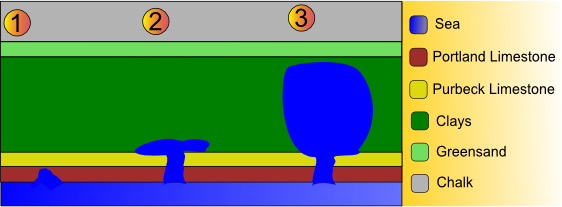
Lulworth Cove
Lulworth Cove is a cove near the village of West Lulworth, on the Jurassic Coast in Dorset, southern England. It is privately owned by the Weld family along with Durdle Door and the Lulworth Estate. The cove is one of the world's finest examples of such a landform, and is a World Heritage Site and tourist location with approximately 500,000 visitors every year, of whom about 30 per cent visit in July and August. It is close to the rock arch of Durdle Door and other Jurassic Coast sites. Geology The cove has formed as a result of bands of rock of alternating geological resistance running parallel to the coastline (a concordant coastline). On the seaward side the clays and sands have been eroded. A narrow (less than ) band of Portland limestone rocks forms the shoreline. Behind this is a narrow (less than ) band of slightly less-resistant Purbeck limestone. Behind this are of much less-resistant clays and greensands; Weald Clays, Gault and Upper Greensand. Forming t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stair Hole
Stair Hole is a small cove located just west of Lulworth Cove in Dorset, southern England. The Fold (geology), folded limestone stratum, strata known as the ''Lulworth crumple'' are particularly visible at Stair Hole. There are several caves visible from the seaward side of Stair Hole; Cathedral Cavern is supported by pillars of rock rising out of the water.Hammond, R. J. W., ''Dorset Coast'', Ward Lock Ltd, 1979, p149 The rock structure was created during the Alpine orogeny and exposed by subsequent erosion. Stair Hole featured in ''Nuts in May (Play for Today), Nuts in May'', a Play for Today directed by Mike Leigh, and in Five on a Treasure Island (film), ''Five on a Treasure Island'', a 1957 film serial by the Children's Film Foundation and was the background for the climactic sword fight between George Baker (British actor), George Baker and Peter Arne in ''The Moonraker'' (1957). Gallery File:E end of Stair Hole, Lulworth, England arp.jpg, East end of the Lulworth Crumpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wealden Group
The Wealden Group, occasionally also referred to as the Wealden Supergroup, is a group (stratigraphy), group (a sequence of rock strata) in the lithostratigraphy of southern England. The Wealden group consists of wiktionary:paralic, paralic to continental (freshwater) sedimentary facies, facies sedimentary rocks of Berriasian to Aptian age and thus forms part of the English Lower Cretaceous. It is composed of alternating sands and clays. The sandy units were deposited in a flood plain of braided rivers, the clays mostly in a lagoonal coastal plain.Jackson (2008) The Wealden Group can be found in almost all Early Cretaceous Sedimentary basin, basins of England: its outcrops curve from the Wessex Basin in the south to the Cleveland Basin in the northeast. It is not found in northwest England and Wales, areas which were at the time tectonic highs where no deposition took place. The same is true for the London Platform around London and Essex. Offshore, the Wealden Group can reach a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Purbeck
The Isle of Purbeck is a peninsula in Dorset, England. It is bordered by water on three sides: the English Channel to the south and east, where steep cliffs fall to the sea; and by the marshy lands of the River Frome, Dorset, River Frome and Poole Harbour to the north. Its western boundary is less well defined, with some medieval sources placing it at Flower's Barrow above Worbarrow Bay. John Hutchins (antiquary), John Hutchins, author of ''The History and Antiquities of the County of Dorset'', defined Purbeck's western boundary as the Luckford Lake stream, which runs south from the River Frome, Dorset, Frome. According to writer and broadcaster Ralph Wightman, Purbeck "is only an island if you accept the barren heaths between Arish Mell and Wareham, Dorset, Wareham as cutting off this corner of Dorset as effectively as the sea." The most southerly point is St Alban's Head (archaically St. Aldhelm's Head). From 1974 to 2019, the whole of the Isle of Purbeck lay within the local g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |