|
Pulses Per Quarter Note
MIDI beat clock, or simply MIDI clock, is a clock signal that is broadcast via MIDI to ensure that several MIDI-enabled devices such as a synthesizer or music sequencer stay in synchronization. Clock events are sent at a rate of 24 pulses per quarter note. Those pulses are used to maintain a synchronized tempo for synthesizers that have Beats per minute, beats-per-minute-dependent voices and also for arpeggiator synchronization. The clock is presented as a stream of single-byte MIDI messages. Playback at the tempo presented by the beat clock can be started, stopped and resumed with other single-byte MIDI messages. Location information can be specified using Song Position Pointer messages. MIDI beat clock differs from MIDI timecode in that MIDI beat clock is tempo-dependent. Messages MIDI beat clock defines the following real-time messages: * clock (decimal 248, hex 0xF8) * start (decimal 250, hex 0xFA) * continue (decimal 251, hex 0xFB) * stop (decimal 252, hex 0xFC) MIDI also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIDI
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (; MIDI) is an American-Japanese technical standard that describes a communication protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing, and recording music. A single MIDI cable can carry up to sixteen channels of MIDI data, each of which can be routed to a separate device. Each interaction with a key, button, knob or slider is converted into a MIDI event, which specifies musical instructions, such as a note's pitch, timing and velocity. One common MIDI application is to play a MIDI keyboard or other controller and use it to trigger a digital sound module (which contains synthesized musical sounds) to generate sounds, which the audience hears produced by a keyboard amplifier. MIDI data can be transferred via MIDI or USB cable, or recorded to a sequencer or digital audio workstation to be edited or played back. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
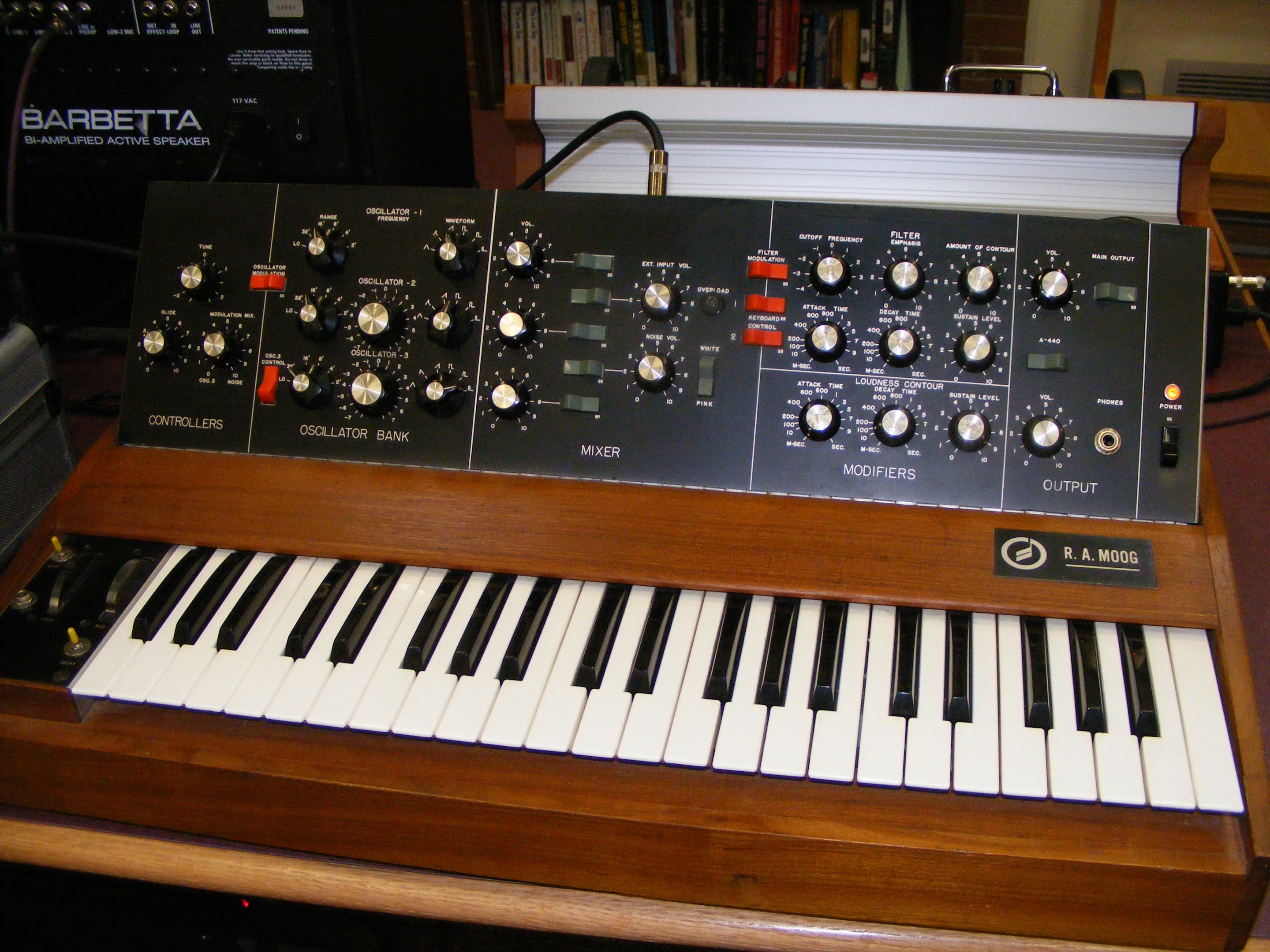
Synthesizer
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and frequency modulation synthesis. These sounds may be altered by components such as filters, which cut or boost frequencies; envelopes, which control articulation, or how notes begin and end; and low-frequency oscillators, which modulate parameters such as pitch, volume, or filter characteristics affecting timbre. Synthesizers are typically played with keyboards or controlled by sequencers, software or other instruments, and may be synchronized to other equipment via MIDI. Synthesizer-like instruments emerged in the United States in the mid-20th century with instruments such as the RCA Mark II, which was controlled with punch cards and used hundreds of vacuum tubes. The Moog synthesizer, developed by Robert Moog and first so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Sequencer
A music sequencer (or audio sequencer or simply sequencer) is a device or application software that can record, edit, or play back music, by handling Musical note, note and performance information in several forms, typically CV/Gate, MIDI, or Open Sound Control, and possibly audio signal, audio and automation data for digital audio workstations (DAWs) and Audio plugin, plug-ins. Overview Modern sequencers The advent of Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) in the 1980s gave programmers the opportunity to design software that could more easily record and play back sequences of notes played or programmed by a musician. As the technology matured, sequencers gained more features, such as the ability to record multitrack audio. Sequencers used for audio recording are called digital audio workstations (DAWs). Many modern sequencers can be used to control Software synthesizer, virtual instruments implemented as software Audio plug-in, plug-ins. This allows musicians to repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beats Per Minute
Beat, beats, or beating may refer to: Common uses * Assault, inflicting physical harm or unwanted physical contact * Battery (crime), a criminal offense involving unlawful physical contact * Battery (tort), a civil wrong in common law of intentional harmful or offensive contact * Corporal punishment, punishment intended to cause physical pain * Patrol, or beat, a group of personnel assigned to monitor a specific area ** Beat (police), the territory that a police officer patrols ** Gay beat, an area frequented by gay men * Strike (attack), repeatedly and violently striking a person or object * Victory, success achieved in personal combat, military operations or in any competition * Beating (hunt), driving game out of areas of cover during a hunt Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters * Beat, an anthro fox in the animated series " Motto! Majime ni Fumajime Kaiketsu Zorori" * Beat, in the video game '' Eternal Sonata'' * Beat, in the video game '' Jet Set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arpeggiator
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and frequency modulation synthesis. These sounds may be altered by components such as filters, which cut or boost frequencies; envelopes, which control articulation, or how notes begin and end; and low-frequency oscillators, which modulate parameters such as pitch, volume, or filter characteristics affecting timbre. Synthesizers are typically played with keyboards or controlled by sequencers, software or other instruments, and may be synchronized to other equipment via MIDI. Synthesizer-like instruments emerged in the United States in the mid-20th century with instruments such as the RCA Mark II, which was controlled with punch cards and used hundreds of vacuum tubes. The Moog synthesizer, developed by Robert Moog and first sold in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIDI Timecode
MIDI time code (MTC) embeds the same timing information as standard SMPTE timecode as a series of small 'quarter-frame' MIDI messages. There is no provision for the user bits in the standard MIDI time code messages, and SysEx messages are used to carry this information instead. The quarter-frame messages are transmitted in a sequence of eight messages, thus a complete timecode value is specified every two frames. If the MIDI data stream is running close to capacity, the MTC data may arrive a little behind schedule which has the effect of introducing a small amount of jitter. In order to avoid this it is ideal to use a completely separate MIDI port for MTC data. Larger full-frame messages, which encapsulate a frame worth of timecode in a single message, are used to locate to a time while timecode is not running. Unlike standard SMPTE timecode, MIDI timecode's quarter-frame, and full-frame messages carry a two-bit flag value that identifies the rate of the timecode, specifying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian for 'time'; plural 'tempos', or from the Italian plural), measured in beats per minute, is the speed or pace of a given musical composition, composition, and is often also an indication of the composition's character or atmosphere. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (often using conventional Italian terms) and, if a specific metrical pace is desired, is usually measured in beat (music), beats per minute (bpm or BPM). In modern classical compositions, a "metronome mark" in beats per minute, indicating only measured speed and not any form of expression, may supplement or replace the normal tempo marking, while in modern genres like electronic dance music, tempo will typically simply be stated in bpm. Tempo (the underlying pulse of the music) is one of the three factors that give a piece of music its texture (music), texture. The others are meter (music), meter, which is indicated by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sync24
DIN sync, also called Sync24, is a synchronization interface for electronic musical instruments. It was introduced in 1980 by Roland Corporation and has been superseded by MIDI. Definition and history DIN sync was introduced in 1980 by Roland Corporation with the release of the TR-808 drum machine. The intended use was the synchronization of music sequencers, drum machines, arpeggiators and similar devices. It was superseded by MIDI in the mid-to-late 1980s. DIN sync consists of two signals, clock (tempo) and run/stop. Both signals are TTL compatible, meaning the low state is 0 V and the high state is about +5 V. The clock signal is a low-frequency pulse wave suggesting the tempo. Instead of measuring the waveform's frequency, the machine receiving the signal merely has to count the number of pulses to work out when to increment its position in the music. Roland equipment uses 24 pulses per quarter note, known as Sync24. Therefore, a Roland-compatible device ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Note
A quarter note ( AmE) or crotchet ( BrE) () is a musical note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note (or semibreve). Quarter notes are notated with a filled-in oval note head and a straight, flagless stem. The stem usually points upwards if it is below the middle line of the staff, and downwards if it is on or above the middle line. An upward stem is placed on the right side of the notehead, a downward stem is placed on the left (see image). The Unicode symbol is U+2669 (). A quarter rest (or crotchet rest) denotes a silence of the same duration as a quarter note or crotchet. It is notated with the symbol . In some older music it was notated with symbol .''Rudiments and Theory of Music'' Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music, London 1958. I,33 and III,25. The former section shows both forms without distinction, the latter the "old" form only. The book was the Official ABRSM theory manual in the UK up until at least 1975. The "old" form was taugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIN Sync
DIN sync, also called Sync24, is a synchronization interface for electronic musical instruments. It was introduced in 1980 by Roland Corporation and has been superseded by MIDI. Definition and history DIN sync was introduced in 1980 by Roland Corporation with the release of the TR-808 drum machine. The intended use was the synchronization of music sequencers, drum machines, arpeggiators and similar devices. It was superseded by MIDI in the mid-to-late 1980s. DIN sync consists of two signals, clock (tempo) and run/stop. Both signals are TTL compatible, meaning the low state is 0 V and the high state is about +5 V. The clock signal is a low-frequency pulse wave suggesting the tempo. Instead of measuring the waveform's frequency, the machine receiving the signal merely has to count the number of pulses to work out when to increment its position in the music. Roland equipment uses 24 pulses per quarter note, known as Sync24. Therefore, a Roland-compatible dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Clock
In digital audio electronics, a word clock or wordclock (sometimes sample clock, which can have a broader meaning) is a clock signal used to synchronise other devices, such as digital audio tape machines and compact disc players, which interconnect via digital audio signals. Word clock is so named because it clocks each audio sample. Samples are represented in data words. S/PDIF, AES/EBU, MADI, ADAT, and TDIF are some of the formats that use a word clock. Various audio over Ethernet systems use communication protocol A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics (computer science), sem ...s to distribute word clock. The device which generates the word clock is the clock source for all the other audio devices. The signal is used for synchronizing digital audio signals between devices, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |