|
Pulse Tube Refrigerator
The pulse tube refrigerator (PTR) or pulse tube cryocooler is a developing technology that emerged largely in the early 1980s with a series of other innovations in the broader field of thermoacoustics. In contrast with other cryocoolers (e.g. applications of the Stirling engine#Stirling cryocoolers, Stirling cryocooler and cryocooler#GM-refrigerators, GM-refrigerators), this cryocooler can be made without moving parts in the low temperature part of the device, making the cooler suitable for a wide variety of applications. Uses Pulse tube cryocoolers are used in niche industrial applications such as semiconductor fabrication and superconducting radio-frequency circuits. They are also used in military applications such as for the cooling of infrared sensors. In research, PTRs are often used as precoolers of dilution refrigerators. They are also being developed for cooling of astronomical detectors where liquid cryogens are typically used, such as the Atacama Cosmology Telescope or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoacoustics
Thermoacoustics is the interaction between temperature, density and pressure variations of Acoustic wave, acoustic waves. Thermoacoustic heat engines can readily be driven using solar energy or waste heat and they can be controlled using proportional control. They can use heat available at low temperatures which makes it ideal for heat recovery and low power applications. The components included in thermoacoustic engines are usually very simple compared to conventional Engine, engines. The device can easily be controlled and maintained. Thermoacoustic effects can be observed when partly molten glass tubes are connected to glass vessels. Sometimes spontaneously a loud and monotone sound is produced. A similar effect is observed if one side of a stainless steel tube is at room temperature (293 K) and the other side is in contact with liquid helium at 4.2 K. In this case, spontaneous Oscillation, oscillations are observed which are named "Taconis oscillations". The mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microphonics
Microphonics, microphony, or microphonism describes the phenomenon wherein certain components in electronic devices transform mechanical vibrations into an undesired electrical signal (noise). The term comes from analogy with a microphone, which is intentionally designed to convert vibrations to electrical signals. Description When electronic equipment was built using vacuum tubes, microphonics were often a serious design problem. The charged elements in the vacuum tubes can mechanically vibrate, changing the distance between the elements, producing charge flows in and out of the tube in a manner identical to a capacitor microphone. A system sufficiently susceptible to microphonics could experience audio feedback, and make noises if jarred or bumped. To minimize these effects, some vacuum tubes were made with thicker internal insulating plates and more supports, and tube-socket assemblies were sometimes shock-mounted by means of small rubber grommets placed in the screw hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SQUID
A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called ''squid'' despite not strictly fitting these criteria). Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, Symmetry (biology)#Bilateral symmetry, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle (mollusc), mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar Ecological niche, role to teleost fish as open-water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open-water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
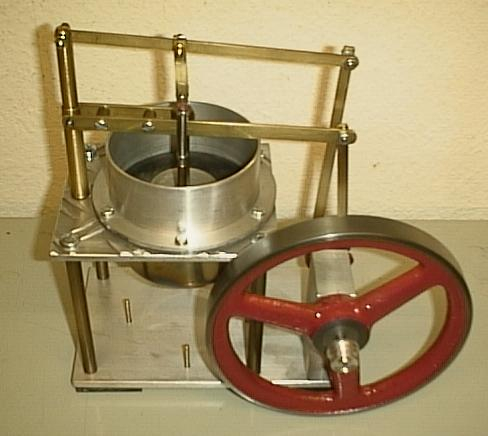
Stirling Engine
A Stirling engine is a heat engine that is operated by the cyclic expansion and contraction of air or other gas (the ''working fluid'') by exposing it to different temperatures, resulting in a net conversion of heat energy to mechanical Work (physics), work. More specifically, the Stirling engine is a closed-cycle regenerative heat engine, with a permanent gaseous working fluid. ''Closed-cycle'', in this context, means a thermodynamic system in which the working fluid is permanently contained within the system. ''Regenerative'' describes the use of a specific type of internal heat exchanger and thermal store, known as the Regenerative heat exchanger, ''regenerator''. Strictly speaking, the inclusion of the regenerator is what differentiates a Stirling engine from other closed-cycle hot air engines. In the Stirling engine, a working fluid (e.g. air) is heated by energy supplied from outside the engine's interior space (cylinder). As the fluid expands, mechanical work is extrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnot's Theorem (thermodynamics)
Carnot's theorem, also called Carnot's rule or Carnot's law, is a principle of thermodynamics developed by Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot in 1824 that specifies limits on the maximum efficiency that any heat engine can obtain. Carnot's theorem states that all heat engines operating between the same two thermal or heat reservoirs cannot have efficiencies greater than a reversible heat engine operating between the same reservoirs. A corollary of this theorem is that every reversible heat engine operating between a pair of heat reservoirs is equally efficient, regardless of the working substance employed or the operation details. Since a Carnot heat engine is also a reversible engine, the efficiency of all the reversible heat engines is determined as the efficiency of the Carnot heat engine that depends solely on the temperatures of its hot and cold reservoirs. The maximum efficiency (i.e., the Carnot heat engine efficiency) of a heat engine operating between hot and cold reservoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coefficient Of Performance
The coefficient of performance or COP (sometimes CP or CoP) of a heat pump, refrigerator or air conditioning system is a ratio of useful heating or cooling provided to work (energy) required. Higher COPs equate to higher efficiency, lower energy (power) consumption and thus lower operating costs. The COP is used in thermodynamics. The COP usually exceeds 1, especially in heat pumps, because instead of just converting work to heat (which, if 100% efficient, would be a COP of 1), it pumps additional heat from a heat source to where the heat is required. Most air conditioners have a COP of 3.5 to 5. Less work is required to move heat than for conversion into heat, and because of this, heat pumps, air conditioners and refrigeration systems can have a coefficient of performance greater than one. The COP is highly dependent on operating conditions, especially absolute temperature and relative temperature between sink and system, and is often graphed or averaged against expected conditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaxial Pulse Tube
In geometry, coaxial means that several three-dimensional linear or planar forms share a common axis. The two-dimensional analog is ''concentric''. Common examples: A coaxial cable has a wire conductor in the centre (D), a circumferential outer conductor (B), and an insulating medium called the dielectric (C) separating these two conductors. The outer conductor is usually sheathed in a protective PVC outer jacket (A). All these have a common axis. The dimension and material of the conductors and insulation determine the cable's characteristic impedance and attenuation at various frequencies. Coaxial rotors are a three-dimensional planar structure: a pair of helicopter rotors (wings) mounted one above the other on concentric shafts, with the same axis of rotation (but turning in opposite directions). In loudspeaker design, coaxial speakers are a loudspeaker system in which the individual drivers are mounted close to one another on the same axis, and thus radiate sound along th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, rock mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, Petrochemical, petrochemical plants, Oil refinery, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant. Flow arrangement There are three primary classifications of heat exchangers accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |