|
Pulsatile Secretion
Pulsatile secretion is a biochemical phenomenon observed in a wide variety of cell and tissue types, in which chemical products are secreted in a regular temporal pattern. The most common cellular products observed to be released in this manner are intercellular signaling molecules such as hormones or neurotransmitters. Examples of hormones that are secreted pulsatilely include insulin, thyrotropin, TRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and growth hormone (GH). In the nervous system, pulsatility is observed in oscillatory activity from central pattern generators. In the heart, pacemakers are able to work and secrete in a pulsatile manner. A pulsatile secretion pattern is critical to the function of many hormones in order to maintain the delicate homeostatic balance necessary for essential life processes, such as development and reproduction. Variations of the concentration in a certain frequency can be critical to hormone function, as evidenced by the case of GnRH agonist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, and metabolism. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become successful at explaining living processes through these three disciplines. Almost all List of life sciences, areas of the life sciences are being uncovered and developed through biochemical methodology and research.#Voet, Voet (2005), p. 3. Biochemistry focuses on understanding the chemical basis that allows biomolecule, biological molecules to give rise to the processes that occur within living Cell (biology), cells and between cells,#Karp, Karp (2009), p. 2. in turn relating greatly to the understanding of tissue (biology), tissues and organ (anatomy), organs as well as organism structure and function.#Miller, Miller (2012). p. 62. Biochemistry is closely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downregulation And Upregulation
In biochemistry, in the biological context of organisms' regulation of gene expression and production of gene products, downregulation is the process by which a cell decreases the production and quantities of its cellular components, such as RNA and proteins, in response to an external stimulus. The complementary process that involves increase in quantities of cellular components is called upregulation. An example of downregulation is the cellular decrease in the expression of a specific receptor in response to its increased activation by a molecule, such as a hormone or neurotransmitter, which reduces the cell's sensitivity to the molecule. This is an example of a locally acting (negative feedback) mechanism. An example of upregulation is the response of liver cells exposed to such xenobiotic molecules as dioxin. In this situation, the cells increase their production of cytochrome P450 enzymes, which in turn increases degradation of these dioxin molecules. Downregulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation. By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. However, when a medication is administered via routes other than intravenous, its bioavailability is lower due to intestinal epithelium absorption and first-pass metabolism. Thereby, mathematically, bioavailability equals the ratio of comparing the area under the plasma drug concentration curve versus time (AUC) for the extravascular formulation to the AUC for the intravascular formulation. AUC is used because AUC is proportional to the dose that has entered the systemic circulation. Bioavailability of a drug is an average value; to take population variability into account, deviation range is shown as ±. To ensure that the drug taker who has poor absorption is dosed appropriately, the bottom value of the deviation range is employed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
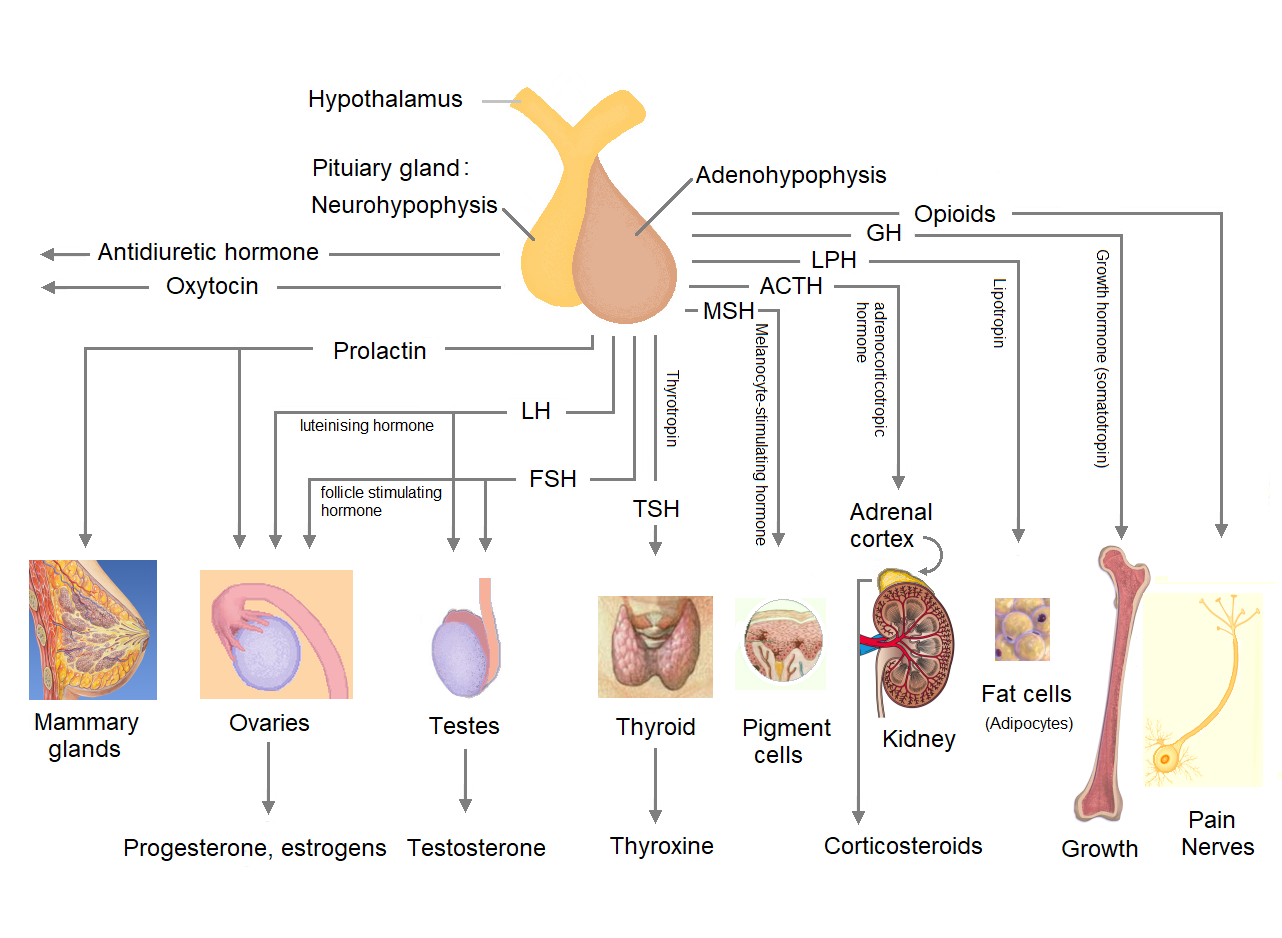
Follicle-stimulating Hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, puberty, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) work together in the reproductive system. Structure FSH is a 35.5 kDa glycoprotein protein dimer, heterodimer, consisting of two polypeptide units, alpha and beta. Its structure is similar to those of luteinizing hormone (LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The chorionic gonadotropin alpha, alpha subunits of the glycoproteins LH, FSH, TSH, and hCG are identical and consist of 96 amino acids, while the beta subunits vary. Both subunits are required for biological activity. FSH has a beta subunit of 111 amino acids (FSH β), which confers its specific biologic action, and is responsible for interaction with the follicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luteinizing Hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH, also known as luteinising hormone, lutropin and sometimes lutrophin) is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus. In females, an acute rise of LH known as an LH surge, triggers ovulation and development of the corpus luteum. In males, where LH had also been called interstitial cell–stimulating hormone (ICSH), it stimulates Leydig cell production of testosterone. It acts synergistically with follicle-stimulating hormone ( FSH). Etymology The term luteinizing comes from the Latin "luteus", meaning "yellow". This is in reference to the corpus luteum, which is a mass of cells that forms in an ovary after an ovum (egg) has been discharged. The corpus luteum is so named because it often has a distinctive yellow color. The process of forming the corpus luteum is known as " luteinization", and thus the hormone that triggers th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
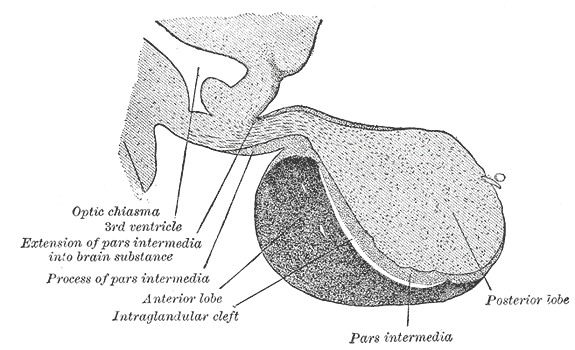
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control much of the body's endocrine system. It is seated in part of the sella turcica a fossa (anatomy), depression in the sphenoid bone, known as the hypophyseal fossa. The human pituitary gland is ovoid, oval shaped, about 1 cm in diameter, in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean. Digital version. There are two main lobes of the pituitary, an anterior pituitary, anterior lobe, and a posterior pituitary, posterior lobe joined and separated by a small intermediate lobe. The anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) is the glandular part that produces and secretes several hormones. The posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) secretes neurohypophysial hormones produced in the hypothalamus. Both lobes have different origins and they are both co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophyseal Portal System
The hypophyseal portal system is a system of blood vessels in the microcirculation at the base of the brain, connecting the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary. Its main function is to quickly transport and exchange hormones between the hypothalamus arcuate nucleus and anterior pituitary gland. The capillaries in the portal system are fenestrated (have many small channels with high vascular permeability) which allows a rapid exchange between the hypothalamus and the pituitary. The main hormones transported by the system include gonadotropin-releasing hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone, growth hormone–releasing hormone, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Structure The blood supply and direction of flow in the hypophyseal portal system has been studied over many years on laboratory animals and human cadaver specimens with injection and vascular corrosion casting methods. Short portal vessels between the neural and anterior pituitary lobes provide an avenue for rap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuate Nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARH), or ARC, is also known as the infundibular nucleus to distinguish it from the arcuate nucleus of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. The arcuate nucleus is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraventricular Nucleus Of Hypothalamus
The paraventricular nucleus (PVN) is a nucleus in the hypothalamus, located next to the third ventricle. Many of its neurons project to the posterior pituitary where they secrete oxytocin, and a smaller amount of vasopressin. Other secretions are corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). CRH and TRH are secreted into the hypophyseal portal system, and target different neurons in the anterior pituitary. Dysfunctions of the PVN can cause hypersomnia in mice. In humans, the dysfunction of the PVN and the other nuclei around it can lead to drowsiness for up to 20 hours per day. The PVN is thought to mediate many diverse functions through different hormones, including osmoregulation, appetite, wakefulness, and the response of the body to stress. Location The paraventricular nucleus lies adjacent to the third ventricle. It lies within the periventricular zone and is not to be confused with the periventricular nucleus, which occupies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. It forms the Basal (anatomy), basal part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is about the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus has the function of regulating certain metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls thermoregulation, body temperature, hunger (physiology), hunger, important aspects o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parathyroid Hormone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates serum calcium and phosphate through its actions on the bone, kidneys, and small intestine. PTH increases serum calcium levels and is counteracted by calcitonin. Additionally, it promotes the synthesis of calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D. PTH influences bone remodeling, which is an ongoing process in which bone tissue is alternately resorbed and rebuilt over time. PTH is secreted in response to low blood serum calcium (Ca2+) levels. PTH indirectly stimulates osteoclast activity within the bone matrix ( osteon), in an effort to release more ionic calcium (Ca2+) into the blood to elevate a low serum calcium level. The bones store calcium from which the body can release into the blood as needed as needed to keep the amount of calcium in the blood at appropriate levels despite the ever-present challenges of metabolism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
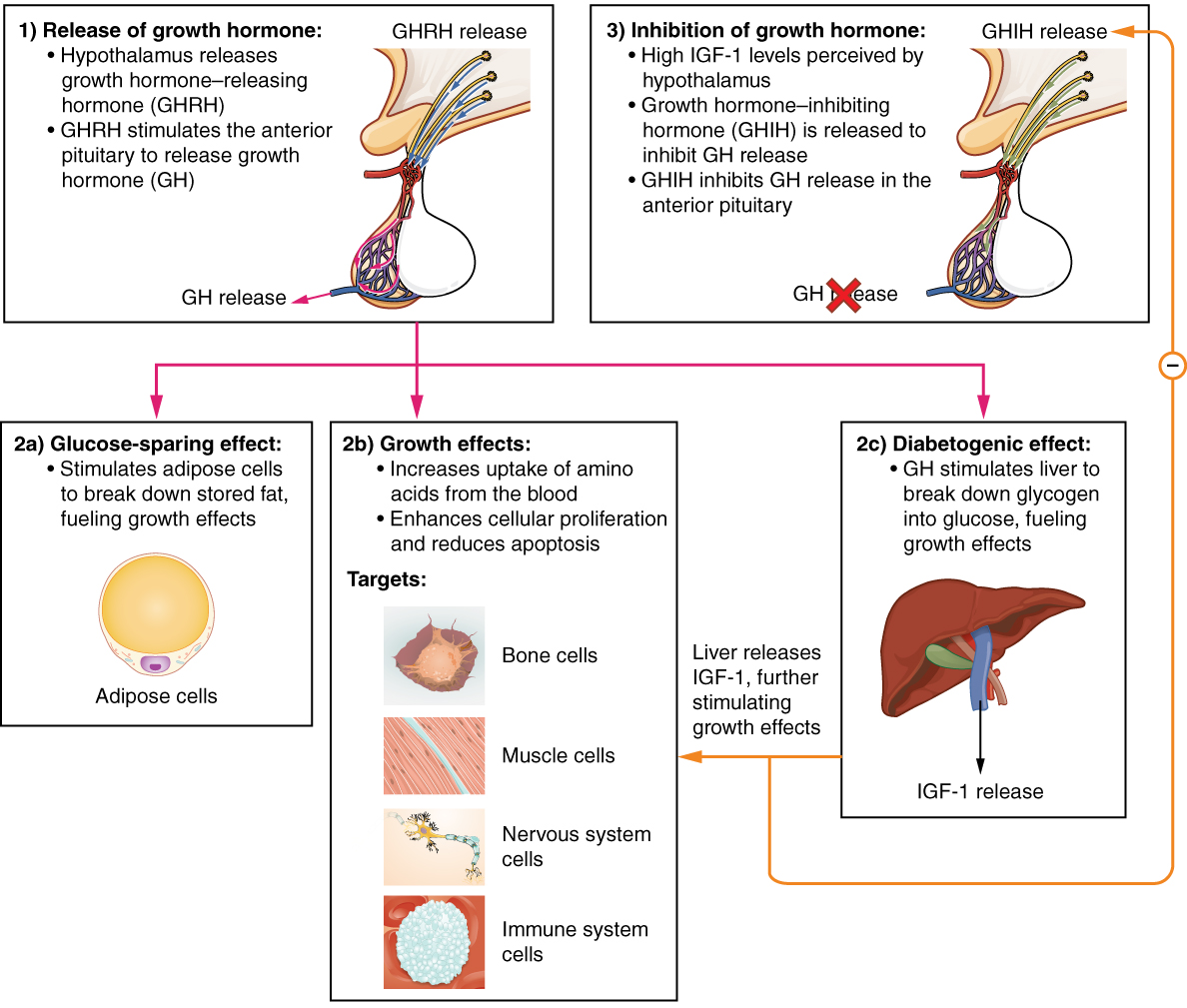
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of HGH called somatropin ( INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |