|
Pullalur
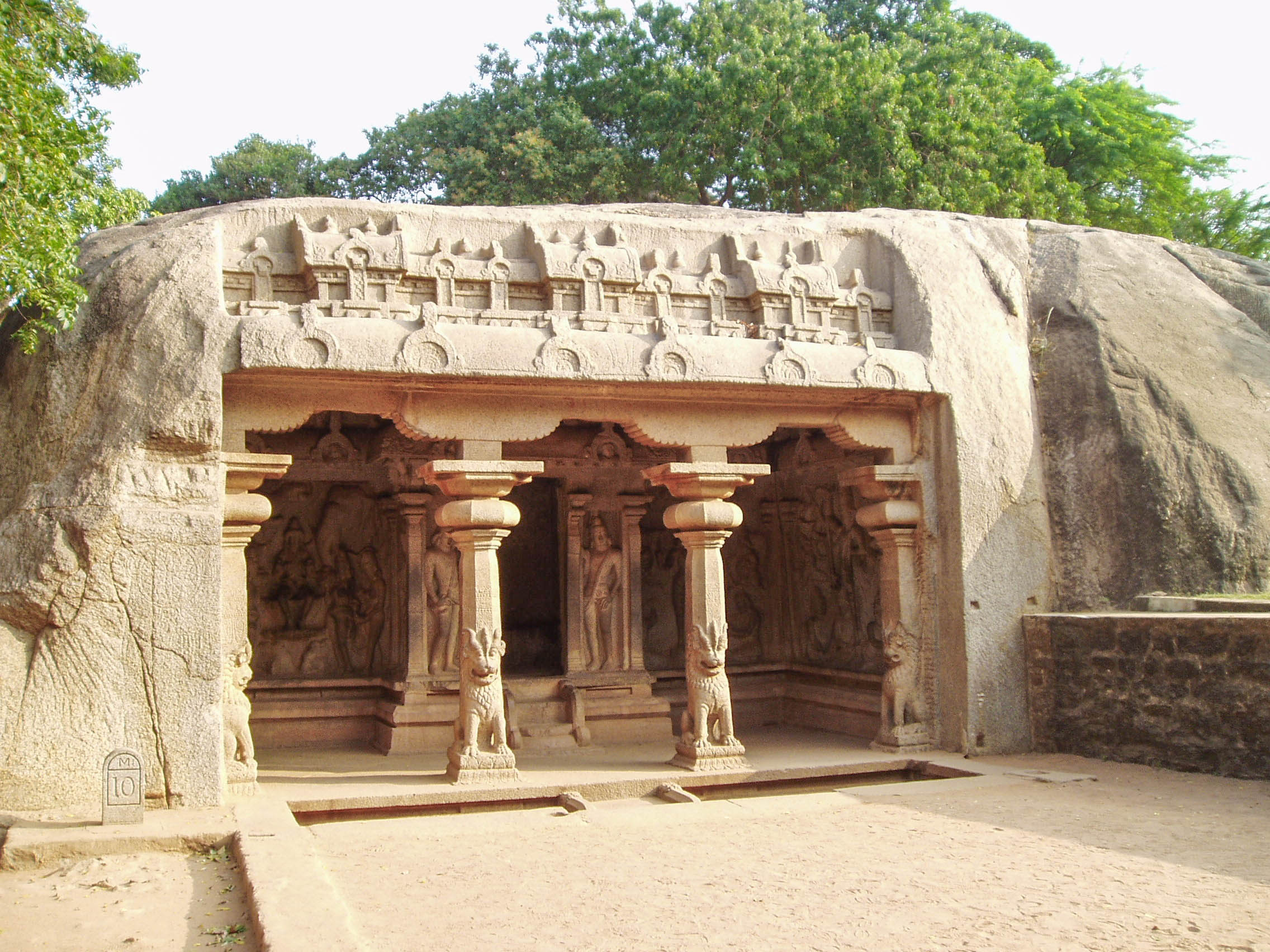
Pullalur or Pollilur is a village in the Kanchipuram taluk of Kanchipuram district in Tamil Nadu, India. The village has been the site of three historic battles - the Battle of Pullalur fought between the Chalukya king Pulakesin II and the Pallava king Mahendravarman I in 611-12, the Battle of Pollilur (1780) and Battle of Pollilur (1781) of the Second Anglo-Mysore War between Hyder Ali and the East India Company The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A .... Demographics As per the 2001 census, Pullalur had a population of 2,690 with 1,315 males and 1,375 females. The sex ratio was 1046 and the literacy rate, 63.52. References * {{coord, 12, 58, N, 79, 42, E, display=title, region:IN_type:city_source:GNS-enwiki Villages in Kanchipuram district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pullalur
The Battle of Pullalur was fought between the Chalukya king Pulakesin II and the Pallava king Mahendravarman I in the town of Pullalur (or Pollilur) in about 618–19. Causes The rapid expansion of the Chalukya Empire had resulted in the Chalukya annexation of the Vishnukundin kingdom. The Vishnukundins were allies of the Pallavas of Kanchi who were emerging as a major power in the 6th century AD. This embittered the Pallavas against them and a large number of battles were fought. Dikshit, p 93 Events In about 617–18, Pulakesin II invaded and annexed Vengi. Dikshit, p 94 After his success against Vengi, he proceeded southwards and confining the Pallavas to the area around Kanchi. The Pallava king Mahendravarman I met Pulakesin at the town of Pullalur or Pollilur, about nine miles north of Kanchi. In the ensuing battle, Mahendravarman is believed to have given Pulikesin II a devastating defeat. The Aihole inscription of Pulakesin II gives a detailed description of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
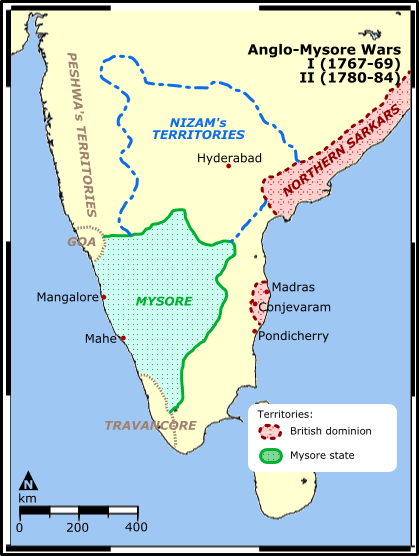
Battle Of Pollilur (1780)
The Battle of Pollilur (a.k.a. Pullalur), also known as the Battle of Polilore or Battle of Perambakam, took place on 10 September 1780 at Pollilur near Conjeevaram, the city of Kanchipuram in present-day Tamil Nadu state, India, as part of the Second Anglo-Mysore War. It was fought between an army commanded by King Tipu Sultan of the Kingdom of Mysore, and a British East India Company force led by William Baillie. The EIC force suffered a high number of casualties before surrendering. It was fought between a Brigade Column of the East India Company, led by Colonel William Baillie, and the Mysore Army, under the command of Haidar Ali and Tipu Sultan. It was the worst loss the East India Company suffered on the subcontinent until Chillianwala. Benoît de Boigne, a French officer in the service of 6th Regiment of Madras Native Infantry, wrote, "There is not in India an example of a similar defeat". Background King Tipu prevented Baillie from joining another force, consisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulakesin II
Pulakeshin II (IAST: Pulakeśin r. –642 CE) popularly known as Immaḍi Pulakeśi, was the greatest Chalukyan Emperor who reigned from Vatapi (present-day Badami in Karnataka, India). During his reign, the Chalukya empire expanded to cover most of the Deccan region in peninsular India. A son of the Chalukya monarch Kirttivarman I, Pulakeshin overthrew his uncle Mangalesha to gain control of the throne. He suppressed a rebellion by Appayika and Govinda, and decisively defeated the Kadambas of Banavasi in the south. The Alupas and the Gangas of Talakadu recognized his suzerainty. He consolidated the Chalukya control over the western coast by subjugating the Mauryas of Konkana. His Aihole inscription also credits him with subjugating the Latas, the Malavas, and the Gurjaras in the north. The most notable military achievement of Pulakeshin was his victory over the powerful northern emperor Harshavardhana, whose failure to conquer the Chalukyan territories to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pollilur (1781)
The Battle of Pollilur was fought on 27 August 1781, between forces of the Kingdom of Mysore under Hyder Ali and British East India Company The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ... forces led by General Eyre Coote. The battle was fought on the site of a 1780 encounter in which a Company force was almost completely routed or captured. In the 1781 battle, the company's army was organized into two lines. One line fought against the troops under Tipu Sultan. But Hyder Ali's army faced severe casualties and retreated to Kanchipuram. After the battle, a shortage of provisions led Coote to move his forces toward Tripassore.Roy p.85 Both the sides retreated in a drawn battle and both claimed victory by firing a salute though the British claimed "dubious victory". Battlefiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahendravarman I
Mahendravarman I (600–630 CE) was a Pallava emperor who ruled over realm covering the southern portions of present-day Andhra region and northern regions of what forms present-day Tamil Nadu in India, in the early 7th century. He was a scholar, a painter, an architect and a musician. He was the son of Simhavishnu, who defeated the Kalabhras and re-established the Pallava kingdom. During his reign, the Chalukya monarch Pulakeshin II attacked the Pallava realm. The Pallavas fought a series of wars in the northern Vengi region, before Mahendra-varman decimated his chief enemies at Pullalur (according to Pallava grants at Kuram, Kasakudi and Tadantottam). Although Mahendra-varman saved his capital, he lost the northern provinces to Pulakeshin. Tamil literature flourished under his rule, with the rise in popularity of ''Tevaram'' written by Appar and Sambandhar. Mahendravarman I was the author of the play '' Mattavilasa Prahasana'' which is a Sanskrit satire. During his perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federalism, federal union comprising 28 federated state, states and 8 union territory, union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 List of districts in India, districts and smaller administrative divisions of India, administrative divisions by the respective subnational government. The states of India are self-governing administrative divisions, each having a State governments of India, state government. The governing powers of the states are shared between the state government and the Government of India, union government. On the other hand, the union territories are directly governed by the union government. History 1876–1919 The British Raj was a very complex political entity consisting of various imperial divisions and states and territories of varying autonomy. At the time of its establishment in 1876, it was made up of 584 princely state, constituent states and the prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali (''Haidar'alī''; ; 1720 – 7 December 1782) was the Sultan and ''de facto'' ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born as Hyder Ali, he distinguished himself as a soldier, eventually drawing the attention of Mysore's rulers. Rising to the post of Dalavayi ( commander-in-chief) to Krishnaraja Wodeyar II, he came to dominate the titular monarch and the Mysore government. He became the ''de facto'' ruler, King of Mysore as Sarvadhikari (Chief Minister) by 1761. During intermittent conflicts against the East India Company during the First and Second Anglo–Mysore Wars, Hyder Ali was the military leader. Though illiterate, Hyder Ali concluded an alliance with the French, and used the services of French workmen in raising his artillery and arsenal. His rule of Mysore was characterised by frequent warfare with his neighbours and rebellion within his territories. This was not unusual for the time as much of the Indian subcontinent was then in turmoil. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Anglo-Mysore War
The Second Anglo-Mysore War was a conflict between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company from 1780 to 1784. At the time, Mysore was a key French ally in India, and the conflict between Britain against the French and Dutch in the American Revolutionary War influenced Anglo-Mysorean hostilities in India. The great majority of soldiers on the company side were raised, trained, paid and commanded by the company, not the British government. However, the company's operations were also bolstered by Crown troops sent from Great Britain, and by troops from Hanover, which was also ruled by Great Britain's King George III. Following the British seizure of the French port of Mahé in 1779, Mysorean ruler Hyder Ali opened hostilities against the British in 1780, with significant success in early campaigns. As the war progressed, the British recovered some territorial losses. Both France and Britain sent troops and naval squadrons from Europe to assist in the war effort, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallava
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of South India, the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The Pallavas played a crucial role in shaping in particular southern Indian history and heritage. The dynasty rose to prominence after the downfall of the Satavahanas, Satavahana Empire, whom they had formerly served as feudatories. The Pallavas became a major South India, southern Indian power during the reign of Mahendravarman I (600–630 CE) and Narasimhavarman I (630–668 CE), and dominated the southern Andhra Pradesh, Telugu region and the northern parts of the Ancient Tamil country, Tamil region for about 600 years, until the end of the 9th century. Throughout their reign, they remained in constant conflict with both the Chalukyas of Badami, Vatapi to the north, and the Tamil kingdoms of Chola Dynasty, Chola and Pandyas to their south. The Pallavas were finally defeated by the Chola ruler Aditya I in the 9th century CE. The Pallav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalukya
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi (modern Badami) from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakeshin II. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century. These Western Chalukyas ruled from Kalyani (modern Basavakalyan) until the end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India by population, sixth largest by population, Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, who speak the Tamil language—the state's official language and one of the longest surviving Classical languages of India, classical languages of the world. The capital and largest city is Chennai. Located on the south-eastern coast of the Indian peninsula, Tamil Nadu is straddled by the Western Ghats and Deccan Plateau in the west, the Eastern Ghats in the north, the Eastern Coastal Plains lining the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait to the south-east, the Laccadive Sea at the southern Cape (geography), cape of the peninsula, with the river Kaveri bisecting the state. Politically, Tamil Nadu is bound by the Indian sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanchipuram Taluk
Kancheepuram taluk is a taluk of Kancheepuram district of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. The headquarters of the taluk is the town of Kanchipuram Kanchipuram (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: '; ), also known as Kanjeevaram, is a stand alone city corporation, satellite nodal city of Chennai in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu in the Tondaimandalam region, from .... References Taluks of Kanchipuram district {{Kanchipuram-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |