|
Puging
Puging is a village near Yingkiong in Upper Siang district of Arunachal Pradesh Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It share ... References Villages in Upper Siang district {{ArunachalPradesh-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
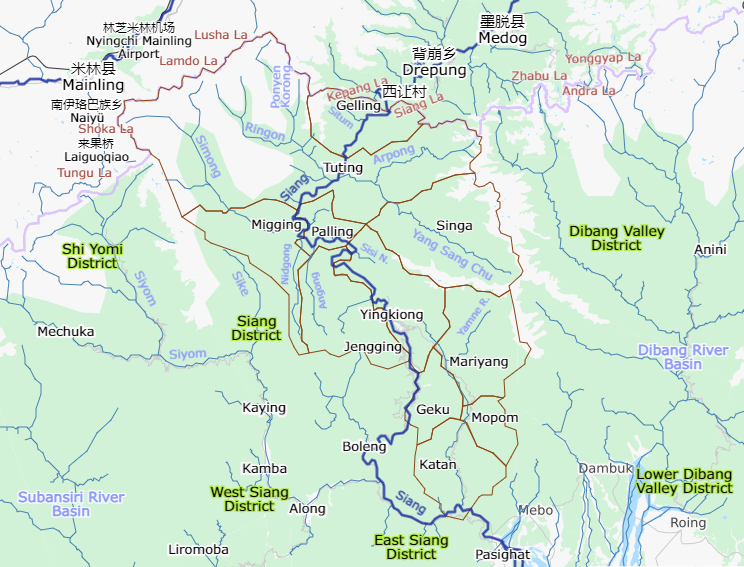
Yingkiong
Yingkiong is a town in and the administrative headquarters of Upper Siang district in the Northeast Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. It is located north of Itanagar, the capital of the state, and east of the River Siang. According to the 2011 Census, the town has a total population of 8,573. History In 1911, following the Anglo–Abor wars, the British gained administrative control of the Upper Siang region. It was put under the administrative control of the Assistant Political Officer stationed at Sadiya (in Assam) during the period. Some notable British civil servants who held the role of Assistant Political Officer included Jack Francis Needham, appointed in 1882, and Noel Williamson, who was assassinated by the villagers of Komsing in the present day East Siang district. After the independence of India, the region was part of the East Siang district until 1995, when it was separated for administrative convenience and made an independent district, northwest of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Siang District
Upper Siang (Pron:/ˈsjæŋ or ˈsɪæŋ/) is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in India. It is the fourth least populous district in the country (out of 640). History The majority of the people are of the Adi tribe while the Memba, Khamba tribe also exists there. Part of the area was controlled by the Tibetan Kingdom of Powo when streams of Tibetan pilgrims searching for one of the 'hidden lands' or beyul ( bo, sbas-yul) referred to in the prophecies of Guru Rinpoche in the East Himalayas from the mid-seventeenth century came south over the Doshong La pass, to seek the particular location of one of these earthly paradises called Padma bkod (written variously Pema köd, Pemakö and Pemako), literally 'Lotus Array' in the region. The region became administered by British India with the Simla Accord of 1914 and the demarcation of the McMahon Line, though China considers it part of South Tibet. The district was formed in 1999 when it was split from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed border with China in the north at the McMahon Line. Itanagar is the state capital of Arunachal Pradesh. Arunachal Pradesh is the largest of the Seven Sister States of Northeast India by area. Arunachal Pradesh shares a 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region. As of the 2011 Census of India, Arunachal Pradesh has a population of 1,382,611 and an area of . It is an ethnically diverse state, with predominantly Monpa people in the west, Tani people in the centre, Mishmi and Tai people in the east, and Naga people in the southeast of the state. About 26 major tribes and 100 sub-tribes live in the state. The main tribes of the state a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)