|
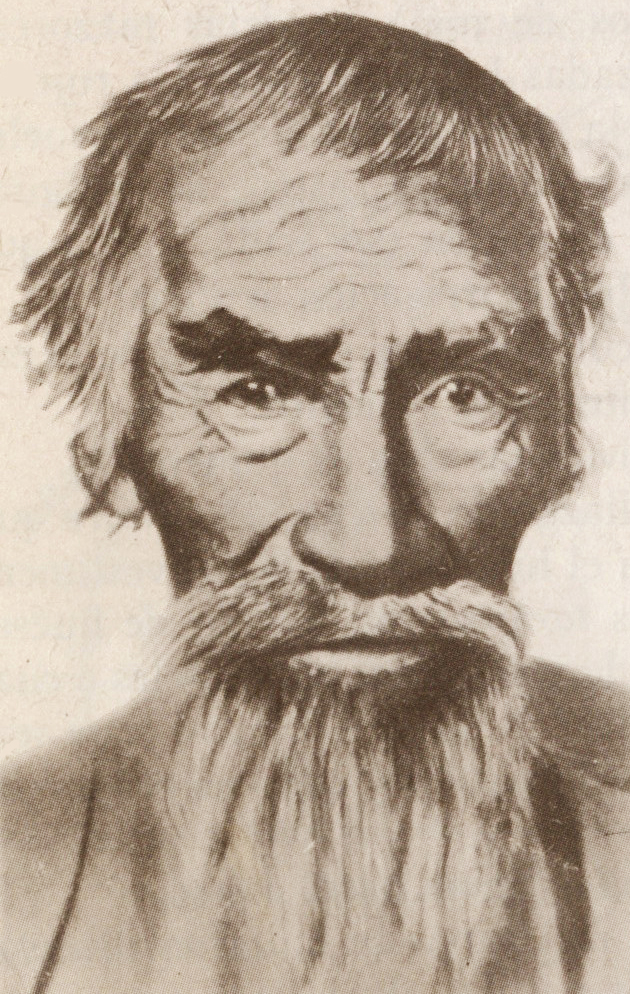
Puelche People
The Gününa küna (Guennakin), or sometimes Puelche (Mapudungun: ''pwelche'', "people of the east") were Indigenous peoples living east of the Andes Mountains in Chile and Southwest Argentina. They were annihilated by Plague (disease), plagues and epidemics in the late 18th century, with survivors merging into other groups such as the Mapuche, Het people, Het, and Tehuelche people, Tehuelche. Language and name They spoke the Puelche language, which went extinct around the 1970s. Currently, there are efforts to revitalize the language. The name "Puelche" was not an autonym but was given to them by the Mapuche. Lifeways The Puelches, like the Pehuenches, were hunters, gatherers, and fishermen. They used bows, arrows, and — after the arrival of the Mapuche — spears. They were tall and stout and dressed in fur ''quillangos'' (cloaks) and turbans of rolled threads with nets that covered their heads and on which they attached feather ornaments. They build their houses wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the List of countries and dependencies by area, eighth-largest country in the world. Argentina shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a Federation, federal state subdivided into twenty-three Provinces of Argentina, provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and List of cities in Argentina by population, largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a Federalism, federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
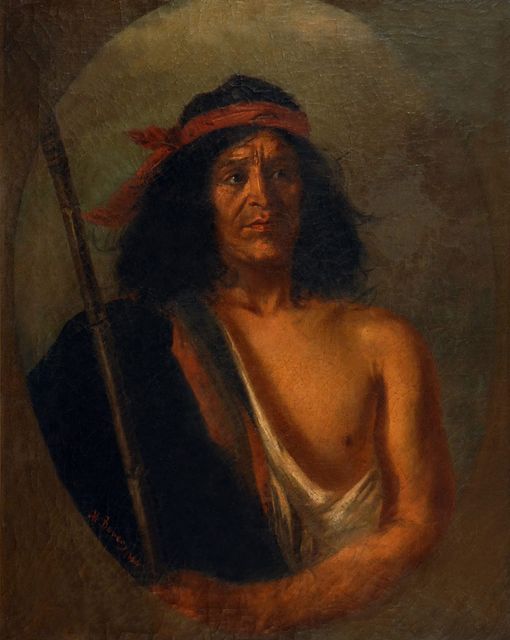
Mapuche
The Mapuche ( , ) also known as Araucanians are a group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who share a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their homelands once extended from Choapa River, Choapa Valley to the Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land comprising part of the Pampas, Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the Indigenous peoples in Chile and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are concentrated in the Araucanía (historic region), Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities, more than 92% of the Mapuches are from Chile. The Mapuche traditional e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huarpe
The Huarpes or Warpes are an Indigenous people of Argentina, living in the Cuyo region. Some scholars assume that in the Huarpe language, this word means "sandy ground," but according to ''Arte y Vocabulario de la lengua general del Reino de Chile'', written by Andrés Febrés in Lima in 1765, the word ''Cuyo'' comes from Araucanian ''cuyum puulli'', meaning "sandy land" or "desert country". History Huarpe people settled in permanent villages beginning in the 5th century CE. About 50 to 100 people lived in a village, making them smaller than Diaguita settlements. They were agrarian people who grew corn (''Zea mays''), beans, squash, and quinoa ('' Chenopodium quinoa'').Lewis 18 Towards the 15th century, Huarpe territory expanded into the current Argentinian provinces of San Luis, Mendoza and San Juan and even on the north of the Neuquen Province. They inhabited between the Jáchal River at north, to the Diamante River at south and between the Andes and Conlara Valle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carob
The carob ( ; ''Ceratonia siliqua'') is a flowering evergreen tree or shrub in the Caesalpinioideae sub-family of the legume family, Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated for its edible fruit, which takes the form of seed pods, and as an ornamental tree in gardens and landscapes. The carob tree is native to the Mediterranean region and the Middle East. Portugal is the largest producer of carob, followed by Italy and Morocco. In the Mediterranean Basin, extended to the southern Atlantic coast of Portugal (i.e., the Algarve region) and the Atlantic northwestern Moroccan coast, carob pods were often used as animal feed and in times of famine, as "the last source of umanfood in hard times". The ripe, dried and sometimes toasted pod is often ground into carob powder, which is used as a substitute for cocoa powder; this often occurred in the 1970s natural food movement. The powder and chips can be used as a chocolate alternative in most recipes. The plant's seeds are used to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lonko
A lonko or lonco (from Mapudungun ''longko'', literally "head"), is a chief of several Mapuche communities. These were often Ulmen (Mapuche), ulmen, the wealthier men in the lof. In wartime, lonkos of the various local rehue or the larger aillarehue would gather in a koyag or parliament and would elect a toqui to lead the warriors in battle. ''Lonco'' sometimes forms part of geographical names such as the city of Loncoche (English: "head of an important person"). References Mapuche Lonkos, Social history of Chile Indigenous leaders in South America, * Titles of national or ethnic leadership Mapuche words and phrases {{Chile-culture-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carob Tree
The carob ( ; ''Ceratonia siliqua'') is a flowering evergreen tree or shrub in the Caesalpinioideae sub-family of the legume family, Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated for its edible fruit, which takes the form of seed pods, and as an ornamental tree in gardens and landscapes. The carob tree is native to the Mediterranean region and the Middle East. Portugal is the largest producer of carob, followed by Italy and Morocco. In the Mediterranean Basin, extended to the southern Atlantic coast of Portugal (i.e., the Algarve region) and the Atlantic northwestern Moroccan coast, carob pods were often used as animal feed and in times of famine, as "the last source of umanfood in hard times". The ripe, dried and sometimes toasted pod is often ground into carob powder, which is used as a substitute for cocoa powder; this often occurred in the 1970s natural food movement. The powder and chips can be used as a chocolate alternative in most recipes. The plant's seeds are used to produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Araucaria Araucana
''Araucaria araucana'', commonly called the monkey puzzle tree, monkey tail tree, pewen, pehuen pine or piñonero, is an evergreen tree belonging to the family Araucariaceae and growing to a trunk diameter of and a height of . It is native to central and southern Chile and western Argentina. It is the hardiest species in the conifer genus ''Araucaria''. Because of the prevalence of similar species in ancient prehistory, it is sometimes called an animate living fossil, fossil. It is also the list of national trees, official tree of Chile and of the neighboring Argentine province of Neuquén. The IUCN changed its conservation status to Endangered species, Endangered in 2013 as logging, forest fires, and grazing caused its population to dwindle. Description The leaf, leaves are thick, tough, and scale-like, triangular, long, broad at the base, and with sharp edges and tips. According to the scientist Christopher Lusk, the leaves have an average lifespan of 24 years and so c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18th parallel south, 18°S and 20th parallel south, 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from south to north through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depression (geology), depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, Mérida, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano, Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuquén Province
Neuquén () is a Provinces of Argentina, province of Argentina, located in the west of the country, at the northern end of Patagonia. It borders Mendoza Province to the north, Rio Negro Province to the southeast, and Chile to the west. It also meets La Pampa Province at its northeast corner. History The Neuquén Province receives its name from the Neuquén River. The term ''"Neuquén"'' derives from the Mapudungun (a local dialect of the Mapuche language) word ''"Nehuenken"'' meaning ''drafty'', which the aborigines used for the river. The word (without the accentuation) is a palindrome. Lácar Department in Neuquén Province has the southernmost known remains of maize before it was further diffused by the Inca Empire. Maize remains were found as far south as 40°19' S in Melinquina, with it being found inside pottery dated to 730 ±80 BP and 920 ±60 BP. This maize was probably brought across the Andes from Peru during the Inca Empire that also reached Chile. Agriculture was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheas
The rhea ( ), also known as the ñandu ( ) or South American ostrich, is a South American ratite (flightless bird without a keel (bird anatomy), keel on the sternum bone) of the order Rheiformes. They are distantly related to the two African Ostrich, ostriches and Australia's emu (the largest, second-largest and third-largest living ratites, respectively), with rheas placing just behind the emu in height and overall size. Most taxonomic authorities recognize two Extant taxon, extant species: the Greater rhea, greater or American rhea (''Rhea americana''), and the Darwin's rhea, lesser or Darwin's rhea (''Rhea pennata''). The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies the puna rhea as another species instead of a subspecies of the lesser rhea. The IUCN currently rates the greater and puna rheas as near-threatened in their native ranges, while Darwin's rhea is of least concern, having recovered from past threats to its survival. In addition, the feral populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
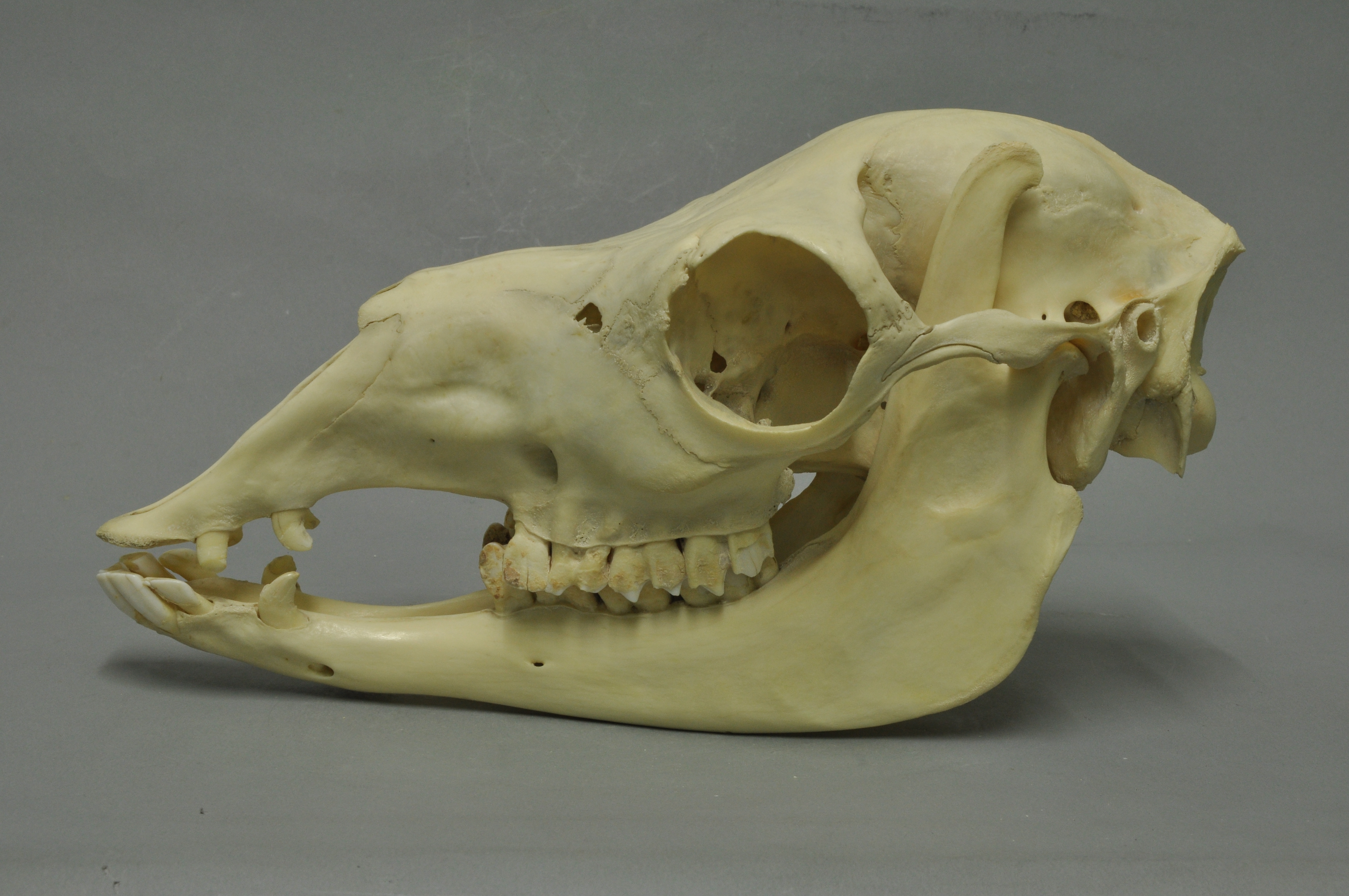
Guanaco
The guanaco ( ; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids; the other species is the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations. Etymology The guanaco gets its name from the Quechua word ''wanaku''. Young guanacos are called ''chulengos'' or "guanaquitos". Characteristics Guanacos stand between at the shoulder, body length of , and weigh . Their color varies very little (unlike the domestic llama), ranging from a light brown to dark cinnamon and shading to white underneath. Guanacos have grey faces and small, straight ears. The lifespan of a guanaco can be as long as 28 years. Guanacos are one of the largest terrestrial mammals native to South America today.San Diego Zoo's Animal Bytes Other terrestrial mammalian [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |