|
Pucciniomycetes
Pucciniomycetes (formerly known as Urediniomycetidae) is a diverse class of fungi in the subphylum Pucciniomycotina of phylum Basidiomycota. The class contains 5 orders, 21 families, 190 genera, and approximately 8,016 species. It has been estimated that this class contains about one third of all teleomorphic basidiomycetes. Pucciniomycetes contains many economically important plant pathogenic fungal rusts; the order Pucciniales (formerly Uredinales) is the largest clade in this class, representing approximately 7,000 species. Pucciniomycetes are cosmopolitan and can be found in both terrestrial and aquatic environments, although aquatic species are poorly understood. Characteristics Species in the class Pucciniomycetes develop no basidiocarp, karyogamy occurs in a thick-walled resting spore (teliospore), and meiosis occurs upon germination of the teliospore. They have simple septal pores without membrane caps, and disc-like spindle pole bodies. Except for a few species, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septobasidiales
The Septobasidiales are an order (biology), order of rust fungi in the class Pucciniomycetes. It contains the single family (biology), family Septobasidiaceae, which itself comprises six genera: ''Aphelariopsis'' (with 1 species), ''Auriculoscypha'' (with 1 species), ''Coccidiodictyon'' (with 1 species), ''Johncouchia'' (with 1 species), ''Septobasidium'' (with about 200 species) and lastly, ''Uredinella'' (with 2 species). History The order Septobasidiales was circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribed in 1964 by Marinus Anton Donk, based on an earlier description by John Nathaniel Couch in 1938. When the order used to contain just 3 families; ''Auriculoscyphaceae'' , ''Septobasidiaceae'' and ''Uredinellaceae''. It was reduced to just ''Septobasidiaceae'' with the other families being absorbed in the one family and one order. They are generally parasitic on plants, while some species are parasitic on or symbiotic with scale insects (of the order Homoptera). They have basidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachnocybales
The ''Pachnocybe'' are a genus of fungi, within the monotypic family of Pachnocybaceae , and within the monotypic order of Pachnocybales, within the class Pucciniomycetes. They are parasitic on plants or saprobic on rotten wood. History The genus of ''Pachnocybe'' was created in 1836, when English cryptogamist Miles Joseph Berkeley moved several species from other genera into his new genus. Such as ''Sporocybe albida'' became ''Pachnocybe albida''. The genus name of ''Pachnocybe'' was derived from Greek word ''Pachne'' meaning hoar-frost and also ''cybe'' meaning head. Hughes in 1958 in his review of classical hyphomycete genera selected ''Pachnocybe ferruginea'' as type species of the genus. He also excluded ''Pachnocybe grisea'' as a synonym of ''Cephalotrichum purpureofuscum'' (in the family Microascaceae). The genus ''Pachnocybe'' was then assigned as fungi imperfecti by Ellis in 1971, then in 1980 Carmichael et al. suggested it had an ascomycetous relationship. Then Oberwi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
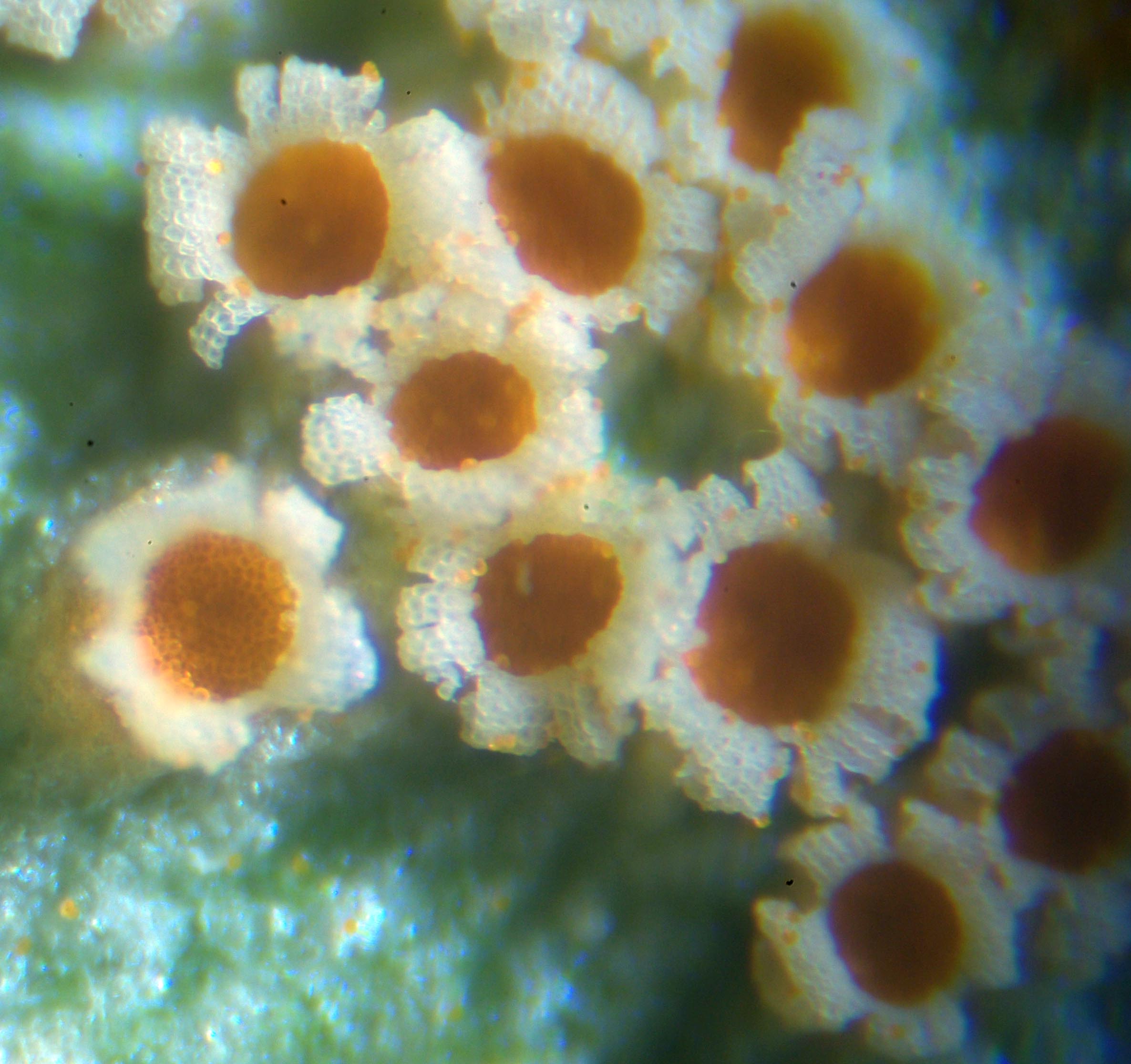
Pucciniomycotina
Pucciniomycotina is a subdivision of fungus within the division Basidiomycota. The subdivision contains 10 classes, 21 orders, and 38 families. Over 8400 species of Pucciniomycotina have been described - more than 8% of all described fungi. The subdivision is considered a sister group to Ustilaginomycotina and Agaricomycotina, which may share the basal lineage of Basidiomycota, although this is uncertain due to low support for placement between the three groups. The group was known as Urediniomycetes until 2006, when it was elevated from a class to a subdivision and named after the largest order in the group, Pucciniales. Morphology There is a high morphological diversity in the Pucciniomycontina. The sporulating forms range from macrobasidiocarp to single-celled yeasts. The presence of simple septal pores, and disc-like spindle pole bodies unites Pucciniomycotina and distinguishes it from the sister groups. The predominance of mannose in the cell walls is also a uniting f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiomycota
Basidiomycota () is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya (often referred to as the "higher fungi") within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: agarics, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and '' Cryptococcus'', the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae (except for basidiomycota-yeast) and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores (usually four). These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually (discussed below) can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platygloeales
The Platygloeales are an order of fungi in the class Pucciniomycetes. Species in the order have auricularioid basidia (tubular with lateral septa) and are typically plant parasites on mosses, ferns, and angiosperms, though '' Platygloea'' species appear to be saprotrophic. Taxonomy History The order was described in 1990 by American mycologist Royall T. Moore to accommodate fungi with auricularioid (laterally septate) basidia and simple septal pores that were formerly placed in the Auriculariaceae. The latter group was distinguished by having dolipore (not simple) septa. As such, Moore's Platygloeales included not only ''Platygloea'', but genera such as '' Helicobasidium'', '' Mycogloea'', and '' Kriegeria''. Subsequently, the order was extended to include most auricularioid fungi not included in the Auriculariaceae, including the genera '' Colacogloea'', '' Naohidea'', and '' Occultifur''. Current status Molecular research, based on cladistic analysis of DNA sequences, has rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the Biological life cycle, life cycles of many plants, algae, fungus, fungi and protozoa. They were thought to have appeared as early as the mid-late Ordovician period as an adaptation of early land plants. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. In some rare cases, a diploid spore is also p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teliospore
Teliospore (sometimes called teleutospore) is the thick-walled resting spore of some fungi (Rust (fungus), rusts and Smut (fungus), smuts), from which the basidium arises. Development They develop in ''telium, telia'' (sing. ''telium'' or ''teliosorus''). The telial host is the primary host in heteroecious rusts. The aecial host is the alternate host (look for pycnium, pycnia and Aecium, aecia). These terms apply when two hosts are required by a heteroecious rust fungus to complete its life cycle. Morphology Teliospores consist of one, two or more Dikaryon, dikaryote cells. Teliospores are often dark-coloured and thick-walled, especially in species where they overwinter (acting as chlamydospores). Two-celled teliospores formerly defined the genus ''Puccinia''. Here the wall is particularly thick at the tip of the terminal cell which extends into a beak in some species. Teliospores consist of Dikaryon, dikaryote cells. As the teliospore cells germinate, the cell nucleus, nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septal Pore
In algal anatomy, a pit connection is a hole in the septum between two algal cells, and is found only in multicellular red algae − specifically in the subphylum Eurhodophytina, except haploid Bangiales. They are often stoppered with proteinaceous "pit plugs". By contrast, many fungi (only ascomycetes and basidiomycetes, as most other groups lack septa) contain septal pores − an unrelated phenomenon. Characteristics A sieve-like membrane may cover the pit in living algae, but in the majority of algae a plug forms, they likely limit the transfer of metabolites between neighbouring cells. Formation Primary pit connections are formed between cells in the same filament, derived from the same parent cell by its division. Such connections are always single, and usually circular; this is a result of their method of formation. The septum is formed as the walls of a filament grow inwards, dividing the cell; this results in a hole in the middle of the tube where the walls don't quite mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitotic Spindle
In cell biology, the spindle apparatus is the cytoskeletal structure of eukaryotic cells that forms during cell division to separate sister chromatids between daughter cells. It is referred to as the mitotic spindle during mitosis, a process that produces genetically identical daughter cells, or the meiotic spindle during meiosis, a process that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Besides chromosomes, the spindle apparatus is composed of hundreds of proteins. Microtubules comprise the most abundant components of the machinery. Spindle structure Attachment of microtubules to chromosomes is mediated by kinetochores, which actively monitor spindle formation and prevent premature anaphase onset. Microtubule polymerization and depolymerization dynamic drive chromosome congression. Depolymerization of microtubules generates tension at kinetochores; bipolar attachment of sister kinetochores to microtubules emanating from opposite cell poles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puccinia Sessilis
''Puccinia sessilis'' is a fungal species and plant pathogen, which is also known as arum rust or ramsons rust. It commonly infects ''Arum maculatum'' and ''Allium ursinum'' causing yellow to orange circular patches on leaves. On the underside of the leaves, it produces raised orange aecia commonly covered in spores. It is common in Eurasia in the spring. It was originally found on the leaves of ''Iris versicolor'' in New York, USA. Other plant species affected by this rust include ''Convallaria majalis'', ''Dactylorhiza fuchsii'', '' Dactylorhiza incarnata'', ''Dactylorhiza majalis'', ''Gymnadenia conopsea'', ''Neottia ovata'', '' Paris quadrifolia'' and ''Phalaris arundinacea''. A specialised form, ''Puccinia sessilis'' f.sp. ''narcissi-orchidacearum'' (now called '' Aecidium narcissi'') is a cause of rust in daffodils ('' Narcissus'') and also on various wild Orchidaceae Orchids are plants that belong to the family (biology), family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and wides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |