|
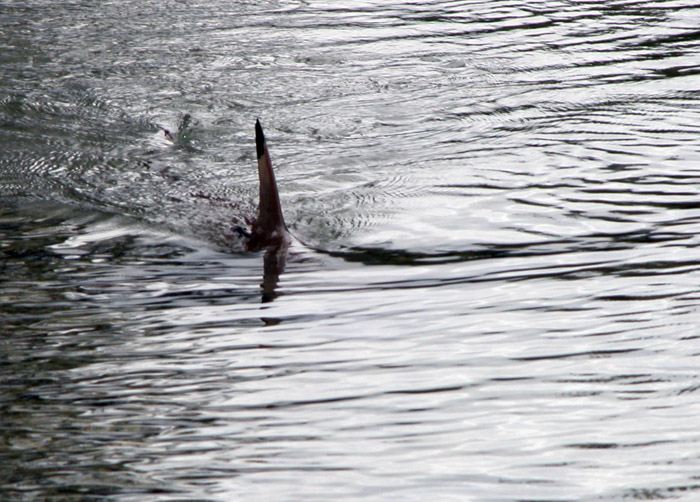
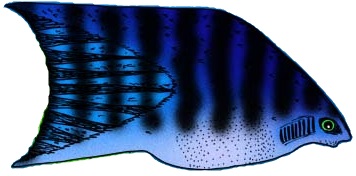
Pterosturisoma
''Pterosturisoma microps'' is the only species of the monotypic genus ''Pterosturisoma'', a genus of the family (biology), family Loricariidae of catfish (order (biology), order Siluriformes). This species is endemism, endemic to Peru where it is found in the upper Amazon basin. ''P. microps'' is a rheophile, which means it likes fast-moving water. ''Pterosturisoma microps'' reaches a length of fish measurement, SL. ''Pterosturisoma'' appears morphologically very similar to ''Lamontichthys''; however, ''Pterosturisoma'' has 6 pectoral fin rays while ''Lamontichthys'' has 7. These two genera share features with ''Sturisoma'' such as similar body depth at the dorsal fin origin, the presence of filamentous extensions on caudal fin spines, and complete abdominal plate cover that extends to the lower lip margin. The sexes of ''P. microps'' can be distinguished by the width of a naked trapezoidal area framed by four bony plates in the genital region; this area appeared broader in fema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamontichthys
''Lamontichthys'' is a genus of Loricariidae, armored catfishes native to South America. Taxonomy The phylogenetics, phylogenetic position of ''Lamontichthys'' remains uncertain. It has been considered to be cladistics, sister to ''Harttia'', whereas ''Lamontichthys'' shows much more similarities with ''Pterosturisoma microps'' of the monotypic genus ''Pterosturisoma'', which only differs from ''Lamontichthys'' by the number of pectoral fin rays. Species There are currently six recognized species in this genus: * ''Lamontichthys avacanoeiro'' Andrea de Carvalho Paixão, de Carvalho Paixão & Mônica de Toledo-Piza Ragazzo, Toledo-Piza, 2009 * ''Lamontichthys filamentosus'' (Francesca Raimonde La Monte, La Monte, 1935) * ''Lamontichthys llanero'' Donald Charles Taphorn Baechle, Taphorn & Craig Gustav Lilyestrom, Lilyestrom, 1984 * ''Lamontichthys maracaibero'' Donald Charles Taphorn Baechle, Taphorn & Craig Gustav Lilyestrom, Lilyestrom, 1984 * ''Lamontichthys parakana'' Andrea de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harttiini
Loricariinae is a subfamily of the family Loricariidae of catfish (order Siluriformes). This subfamily is divided into two tribes and about 30 genera. They are mainly native to freshwater habitats in South America, but there are also several species (in genera '' Crossoloricaria'', '' Dasyloricaria'', '' Fonchiiichthys'', ''Rineloricaria'', '' Spatuloricaria'', '' Sturisoma'' and '' Sturisomatichthys'') in Panama and a single (''Fonchiiichthys'') in Costa Rica.Angulo; Garita-Alvarado; Bussing; and López (2013). Annotated checklist of the freshwater fishes of continental and insular Costa Rica: additions and nomenclatural revisions.'' Check List 9(5): 987–1019. Taxonomy Loricariinae was first described in 1831. Later, in 1979, many genera were described and Loricariinae was divided into four subfamilies: Loricariini, Harttiini, Farlowellini, and Acestridiini. Eventually, the genera of Acestridiini was included under Hypoptopomatinae and genera of Farlowellini was reclassified in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheophile
A rheophile is an animal that prefers to live in fast-moving water. Examples of rheophilic animals Insects *Many aquatic insects living in riffles require current to survive. *'' Epeorus sylvicola'', a rheophilic mayfly species ( Ephemeroptera) *Some African (''Elattoneura'') and Asian threadtail (''Prodasineura'') species Birds *Dippers (''Cinclus'') * Grey wagtail (''Motacilla cinerea'') and mountain wagtail (''Motacilla clara'') *A few swifts often nest behind waterfalls, including American black swift (''Cypseloides niger''), giant swiftlet (''Hydrochous gigas''), great dusky swift (''Cypseloides senex'') and white-collared swift (''Streptoprocne zonaris'') *Some waterfowl, including African black duck (''Anas sparsa''), blue duck (''Hymenolaimus malacorhynchos''), Brazilian merganser (''Mergus octosetaceus''), bronze-winged duck (''Speculanas specularis''), harlequin duck (''Histrionicus histrionicus''), Salvadori's teal (''Salvadorina waigiuensis'') and torren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catfish Genera
Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Catfish are named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, though not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers", with some seemingly not having them. Siluriformes as a whole are scale-less, with neither the armour-plated nor the naked species having scales. This order of fish are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivorous and scavenging bottom feeders, down to tiny ectoparasitic species known as the candirus. In the Southern United States, catfish species may be known by a variety of slang names, such as "mud cat", "polliwogs", or "chuckleheads". These nicknames are not standardized, so one area may call a bullhead catfish by the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Ray-finned Fish Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Amazon Basin
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Fish Of Peru
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mineral-rich waters, such as chalybeate springs. Fresh water may encompass frozen and meltwater in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, snowfields and icebergs, natural precipitations such as rainfall, snowfall, hail/ sleet and graupel, and surface runoffs that form inland bodies of water such as wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, as well as groundwater contained in aquifers, subterranean rivers and lakes. Water is critical to the survival of all living organisms. Many organisms can thrive on salt water, but the great majority of vascular plants and most insects, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds need fresh water to survive. Fresh water is the water resource that is of the most and immediate use to humans. Fresh water is not always pot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of South America
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal (phylogenetics), basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all extant taxon, living cartilaginous fish, cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single Class (biology), class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are ectotherm, cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large nekton, active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communication in aquatic animals#Acoustic, communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish (Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are predominan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found in most fish, in mammals such as whales, and in extinct ancient marine reptiles such as ichthyosaurs. Most have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of whales to identify individuals in the field. The bones or cartilages that support the dorsal fin in fish are called pterygiophores. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is usually to stabilize the animal against rolling and to assist in sudden turns. Some species have further adapted their dorsal fins to other uses. The sunfish uses the dorsal fin (and the anal fin Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sturisoma
''Sturisoma'' is a genus of armored catfishes native to Central and South America. Taxonomy ''Sturisoma'' has been shown to be sister to ''Farlowella''. Species There are currently 12 recognized species in this genus: * '' Sturisoma barbatum'' ( Kner, 1853) * '' Sturisoma brevirostre'' ( C. H. Eigenmann & R. S. Eigenmann, 1889) * '' Sturisoma caquetae'' (Henry Weed Fowler, 1945) * '' Sturisoma graffini'' Londoño-Burbano, 2018 * '' Sturisoma guentheri'' ( Regan, 1904) * '' Sturisoma lyra'' ( Regan, 1904) * '' Sturisoma monopelte'' Fowler, 1914 * '' Sturisoma nigrirostrum'' Fowler, 1940 * '' Sturisoma reisi'' Londoño-Burbano and Britto, 2022Londoño-Burbano, Alejandro & Britto, Marcelo. (2022). A new species of Sturisoma Swainson, 1838 (Loricariidae: Loricariinae) from the Madeira River basin, with a discussion of historical biogeography of western Amazonas and Paraguay River basins. Journal of fish biology. 102. 10.1111/jfb.15251. * '' Sturisoma robustum'' ( Regan, 1904 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |