|
Psyco
Psyco is an unmaintained specializing just-in-time compiler for pre-2.7 Python originally developed by Armin Rigo and further maintained and developed by Christian Tismer. Development ceased in December, 2011. Psyco ran on BSD-derived operating systems, Linux, Mac OS X and Microsoft Windows using 32-bit Intel-compatible processors. Psyco was written in C and generated only 32-bit x86-based code. Although Tismer announced on 17 July 2009 that work was being done on a second version of Psyco, a further announcement declared the project "unmaintained and dead" on 12 March 2012 and pointed visitors to PyPy instead. Unlike Psyco, PyPy incorporates an interpreter and a compiler that can generate C, improving its cross-platform compatibility over Psyco. Speed enhancement Psyco can noticeably speed up CPU-bound applications. The actual performance depends greatly on the application and varies from a slight slowdown to a 100x speedup. The average speed improvement is typically in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Run-time Algorithm Specialisation
In computer science, run-time algorithm specialization is a methodology for creating efficient algorithms for costly computation tasks of certain kinds. The methodology originates in the field of automated theorem proving and, more specifically, in the Vampire theorem prover project. The idea is inspired by the use of partial evaluation in optimising program translation. Many core operations in theorem provers exhibit the following pattern. Suppose that we need to execute some algorithm \mathit(A,B) in a situation where a value of A ''is fixed for potentially many different values of'' B. In order to do this efficiently, we can try to find a specialization of \mathit for every fixed A, i.e., such an algorithm \mathit_A, that executing \mathit_A(B) is equivalent to executing \mathit(A,B). The specialized algorithm may be more efficient than the generic one, since it can ''exploit some particular properties'' of the fixed value A. Typically, \mathit_A(B) can avoid some operations th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language) Implementations
Python may refer to: Snakes * Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia ** Python (genus), ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia * Python (mythology), a mythical serpent Computing * Python (programming language), a widely used high-level programming language * Python, a native code compiler for CMU Common Lisp * Python, the internal project name for the PERQ#PERQ 3, PERQ 3 computer workstation People * Python of Aenus (4th-century BCE), student of Plato * Python (painter) (ca. 360–320 BCE), vase painter in Poseidonia * Python of Byzantium (4th-century BCE), orator, diplomat of Philip II of Macedon * Python of Catana, poet who accompanied Alexander the Great * Python Anghelo (1954–2014), Romanian graphic artist Roller coasters * Python (Efteling), a roller coaster in the Netherlands * Python (Busch Gardens Tampa Bay), a defunct roller coaster * Python (Coney Island, Cincinnati, Ohio), a steel roller coaster Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software Programmed In Python
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, the ability to act or change without constraint or restriction * Emancipate, attaining civil and political rights or equality * Free (gratis), Free (''gratis''), free of charge * Gratis versus libre, the difference between the two common meanings of the adjective "free". Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment *, an emoji in the Enclosed Alphanumeric Supplement block. Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media personality * Free, a pseudonym for the activist and writer Abbie Hoffman * Free (active 2003–), American musician in the band FreeSol Arts and media Film and television * Free (film), ''Free'' (film), a 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YARV
YARV (Yet another Ruby VM) is a bytecode interpreter that was developed for the Ruby programming language by Koichi Sasada. The goal of the project was to greatly reduce the execution time of Ruby programs. Since YARV has become the official Ruby interpreter for Ruby 1.9, it is also named KRI (Koichi's Ruby Interpreter), in the same vein as the original Ruby MRI, named in honor of Ruby's creator Yukihiro Matsumoto. Performance Benchmarks by rubychan.de showed significant increases in performance. Benchmarks by Antonio Cangiano showed speed improvements over other Ruby VMs, with 1.9 on average four times faster than the original interpreter. All evaluations comprised a mix of mostly synthetic benchmarks. History YARV was merged into the Ruby Subversion repository on January 1, 2007. It was released as part of Ruby 1.9.0 on December 26, 2007, replacing Ruby MRI. See also * Parrot virtual machine Parrot is a discontinued register-based process virtual machine designed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
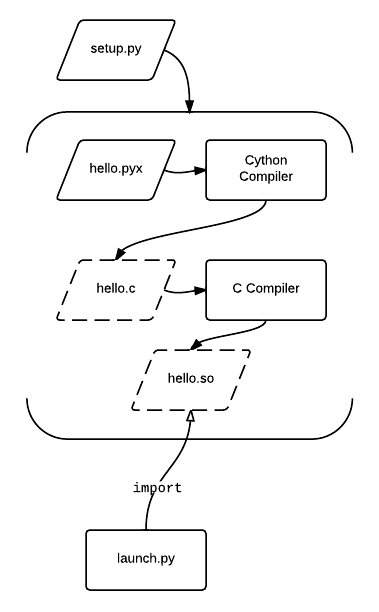
Cython
Cython () is a superset of the programming language Python, which allows developers to write Python code (with optional, C-inspired syntax extensions) that yields performance comparable to that of C. Cython is a compiled language that is typically used to generate CPython extension modules. Annotated Python-like code is compiled to C and then automatically wrapped in interface code, producing extension modules that can be loaded and used by regular Python code using the import statement, but with significantly less computational overhead at run time. Cython also facilitates wrapping independent C or C++ code into python-importable modules. Cython is written in Python and C and works on Windows, macOS, and Linux, producing C source files compatible with CPython 2.6, 2.7, and 3.3 and later versions. The Cython source code that Cython compiles (to C) can use both Python 2 and Python 3 syntax, defaulting to Python 2 syntax in Cython 0.x and Python 3 syntax in Cython 3.x. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unladen Swallow
Unladen Swallow was an optimization branch of CPython, the reference implementation of the Python programming language, which incorporated a just-in-time compiler built using LLVM into CPython's virtual machine. Like many things regarding Python (and the name "Python" itself), "Unladen Swallow" is a Monty Python reference, specifically to the joke about the airspeed velocity of unladen swallows in ''Monty Python and the Holy Grail''. The project's stated goals were to provide full compatibility with CPython specific code while quintupling its performance, and for the project to eventually be merged into CPython. Although it fell short of all its published goals, some Unladen Swallow code was added into the main Python implementation, such as improvements to the cPickle module. Unladen Swallow was sponsored by Google, and the project owners, Thomas Wouters, Jeffrey Yasskin, and Collin Winter, were Google employees, though most project contributors were not. Unladen Swallow was hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a High-level programming language, high-level, General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, Memory safety, memory-safe, object-oriented programming, object-oriented programming language. It is intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' (Write once, run anywhere, WORA), meaning that compiler, compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to Java bytecode, bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax (programming languages), syntax of Java is similar to C (programming language), C and C++, but has fewer low-level programming language, low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as Reflective programming, reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. Java gained popularity sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C Sharp (programming Language)
C# ( pronounced: C-sharp) ( ) is a general-purpose high-level programming language supporting multiple paradigms. C# encompasses static typing, strong typing, lexically scoped, imperative, declarative, functional, generic, object-oriented (class-based), and component-oriented programming disciplines. The principal inventors of the C# programming language were Anders Hejlsberg, Scott Wiltamuth, and Peter Golde from Microsoft. It was first widely distributed in July 2000 and was later approved as an international standard by Ecma (ECMA-334) in 2002 and ISO/ IEC (ISO/IEC 23270 and 20619) in 2003. Microsoft introduced C# along with .NET Framework and Microsoft Visual Studio, both of which are technically speaking, closed-source. At the time, Microsoft had no open-source products. Four years later, in 2004, a free and open-source project called Microsoft Mono began, providing a cross-platform compiler and runtime environment for the C# programming language. A decad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |