|
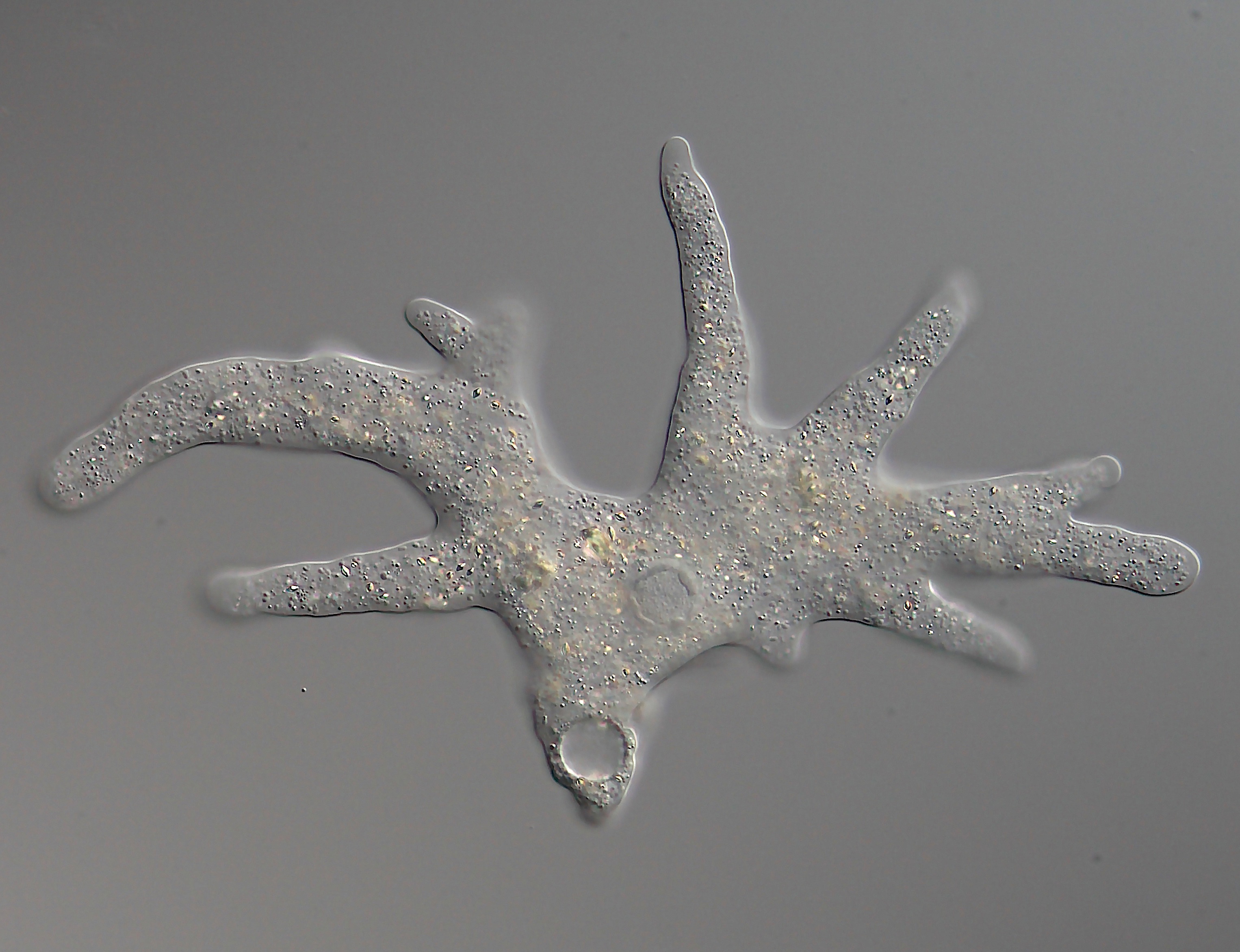
Pseudopodium
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and may also contain microtubules and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and ingestion. They are often found in amoebas. Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia are broad and thin. Filopodia are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact. Generally, several pseudopodia arise from the surface of the body, (''polypodial'', for example, ''Amoeba proteus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a Multicellular organism, multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. The two main cells that do this are the Macrophages and the Neutrophils of the immune system. Where phagocytosis is used as a means of feeding and provides the organism part or all of its nourishment, it is called phagotrophy and is distinguished from osmotrophy, which is nutrition taking place by absorption. History The history of phag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
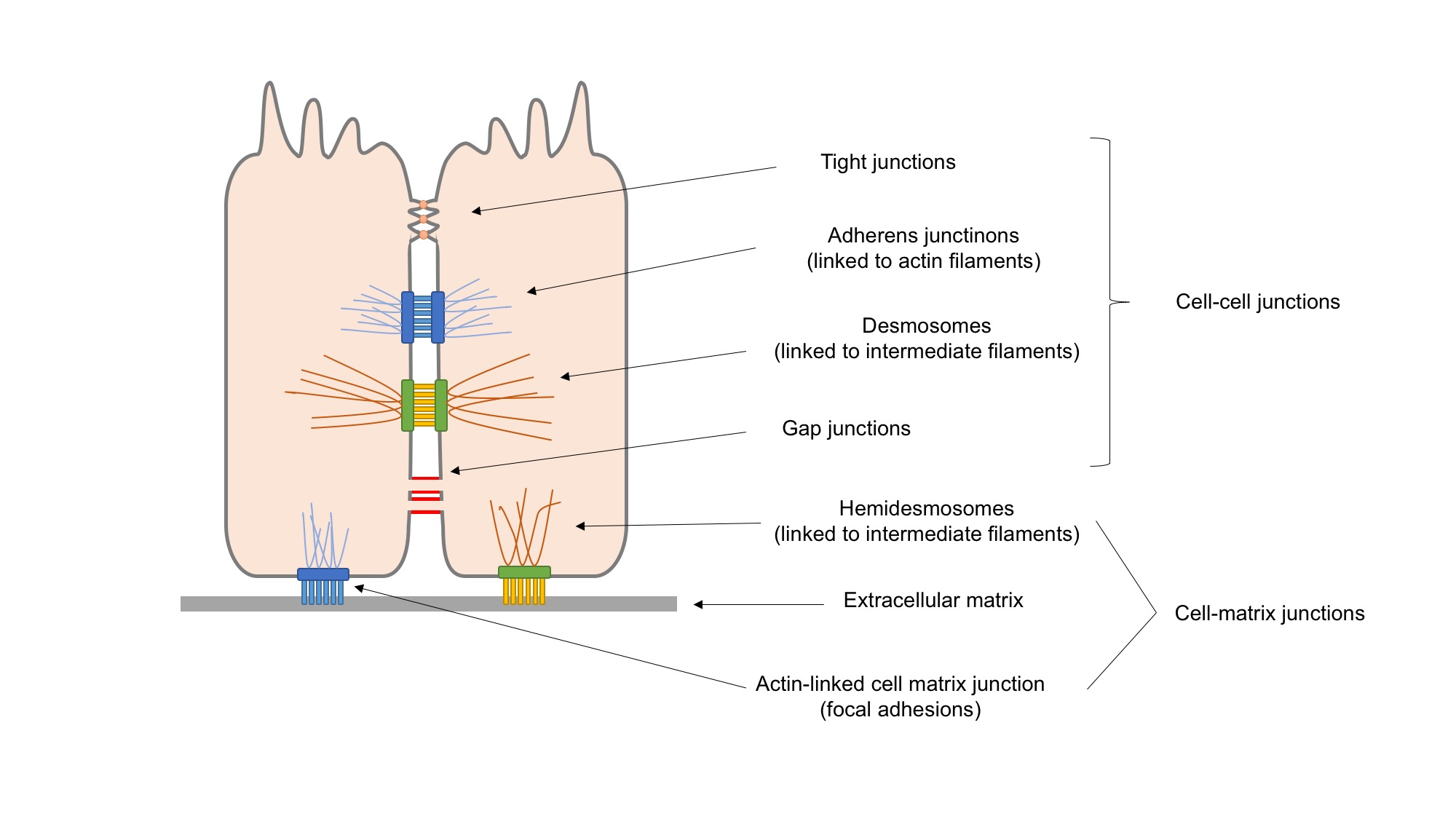
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as Cell_junction, cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM), a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell adhesion molecules, cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
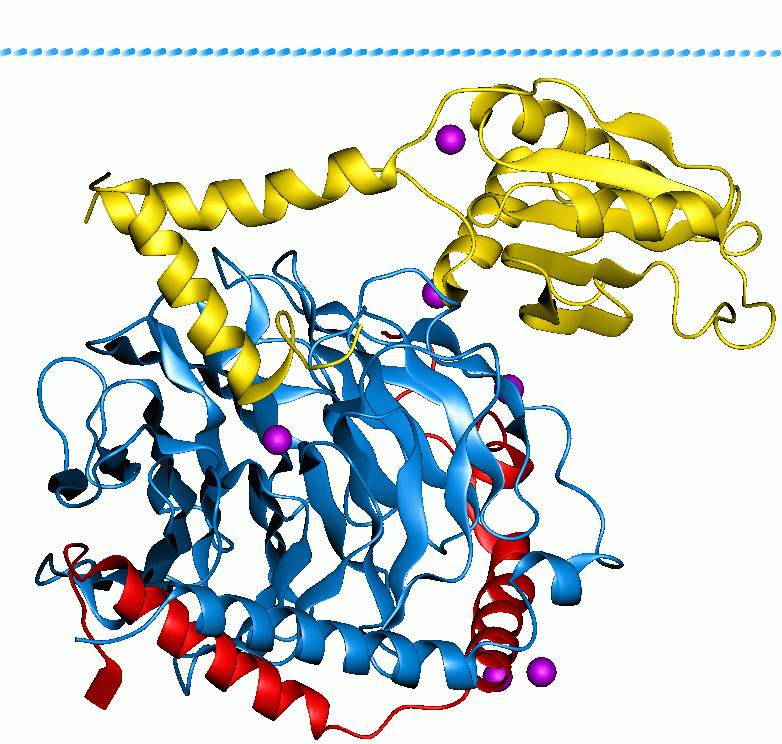
Arp2/3 Complex
Arp2/3 complex (Actin Related Protein 2/3 complex) is a seven-subunit protein complex that plays a major role in the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. It is a major component of the actin cytoskeleton and is found in most actin cytoskeleton-containing eukaryotic cells. Two of its subunits, the ''A''ctin-''R''elated ''P''roteins ARP2 and ARP3, closely resemble the structure of monomeric actin and serve as nucleation sites for new actin filaments. The complex binds to the sides of existing ("mother") filaments and initiates growth of a new ("daughter") filament at a distinctive 70-degree angle from the mother. Branched actin networks are created as a result of this nucleation of new filaments. The regulation of rearrangements of the actin cytoskeleton is important for processes like cell locomotion, phagocytosis, and intracellular motility of lipid vesicles. The Arp2/3 complex was named after it was identified in 1994 by affinity chromatography from ''Acanthamoeba castellani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiskott–Aldrich Syndrome Protein
The Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein (WASp) is a 502-amino acid protein expressed in cells of the hematopoietic system that in humans is encoded by the ''WAS'' gene. In the inactive state, WASp exists in an autoinhibited conformation with sequences near its C-terminus binding to a region near its N-terminus. Its activation is dependent upon CDC42 and PIP2 acting to disrupt this interaction, causing the WASp protein to 'open'. This exposes a domain near the WASp C-terminus that binds to and activates the Arp2/3 complex. Activated Arp2/3 nucleates new F-actin. WASp is the founding member of a gene family which also includes the broadly expressed N-WASP (neuronal Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein), SCAR/ WAVE1, WASH, WHAMM, and JMY. WAML (WASP and MIM like), WAWH (WASP without WH1 domain), and WHIMP (WAVE Homology in Membrane Protrusions) have more recently been discovered. Structure and function The Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome (WAS) family of proteins share similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''alpha'' (Gα), ''beta'' (Gβ) and ''gamma'' (Gγ) subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable dimeric complex referred to as the beta-gamma complex . Heterotrimeric G proteins located within the cell are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Family Of GTPases
The Rho family of GTPases is a family of small (~21 kDa) signaling G proteins, and is a subfamily of the Ras superfamily. The members of the Rho GTPase family have been shown to regulate many aspects of intracellular actin dynamics, and are found in all eukaryotic kingdoms, including yeasts and some plants. Three members of the family have been studied in detail: Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. All G proteins are "molecular switches", and Rho proteins play a role in organelle development, cytoskeletal dynamics, cell movement, and other common cellular functions. History Identification of the Rho family of GTPases began in the mid-1980s. The first identified Rho member was RhoA, isolated serendipitously in 1985 from a low stringency cDNA screening. Rac1 and Rac2 were identified next, in 1989 followed by Cdc42 in 1990. Eight additional mammalian Rho members were identified from biological screenings until the late 1990s, a turning point in biology where availability of complete genome sequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictyostelium
''Dictyostelium'' is a genus of single- and multi-celled eukaryotic, phagotrophic bacterivores. Though they are Protista and in no way fungal, they traditionally are known as "slime molds". They are present in most terrestrial ecosystems as a normal and often abundant component of the soil microflora, and play an important role in the maintenance of balanced bacterial populations in soils. The genus ''Dictyostelium'' is in the order Dictyosteliida, the so-called cellular slime molds or social amoebae. In turn the order is in the infraphylum Mycetozoa. Members of the order are of great theoretical interest in biology because they have aspects of both unicellularity and multicellularity. The individual cells in their independent phase are common on organic detritus or in damp soils and caves. In this phase they are amoebae. Typically, the amoebal cells grow separately and wander independently, feeding mainly on bacteria. However, they interact to form multi-cellular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from ''chemical substance, chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell organism, single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function and health (e.g., migration of White blood cell, leukocytes during injury or infection). In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis, and the aberrant change of the overall property of these networks, which contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alphabetical order, alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionary, dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on Linguistics, linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammar, grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |