|
Pseudophryne Corroboree
The southern corroboree frog (''Pseudophryne corroboree'') is a species of Australian ground frog native to southeastern Australia. The species was described in 1953 by Fulbright research scholar John A. Moore from a specimen collected at Towong Hill Station at Corryong, Victoria, and sent to the Australian Museum. The curator, Roy Kinghorn, recognised it as a new species and allowed Moore to describe it. Description Adult female southern corroboree frogs are long, while males measure ; both bear vivid yellow and black stripes across the head, back, and limbs. The body and head are short and wide, the snout has a slight point, and the fingers and toes lack webbing. The iris is black. The northern corroboree frog has narrower and more greenish-yellow striping. Habitat and conservation The southern corroboree frog is native to Kosciuszko National Park in the northern Snowy Mountains, where it found at locales between the Maragle Range and Smiggin Holes. Reported as abundant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Alexander Moore
John Alexander Moore (June 27, 1915 – May 26, 2002) was an American zoology professor emeritus. Early life and education Moore was born to Louise Hammond Blume and George Douglas Moore, a lawyer, in Charles Town, West Virginia in 1915. Four years later his parents divorced and Moore traveled with his mother first to Carson City, Nevada and Oakland, California until she remarried and moved the family to Markham, Virginia two years after her divorce. Although the schools he attended at the time were not the best, Moore's location in the Blue Ridge Mountains kindled his interest in birds from a young age; Moore published his first academic article in ''The Auk'' at age 15. In the early 1930s Moore's mother divorced again and took the family to Washington D.C. and then to New York City. Moore finished his last two years of high school at Haaren High School. He also volunteered at the American Museum of Natural History. Despite his humble background he was accepted to Columbia Coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Broadcasting Corporation
The Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC) is the national broadcaster of Australia. It is principally funded by direct grants from the Australian Government and is administered by a government-appointed board. The ABC is a publicly-owned body that is politically independent and fully accountable, with its charter enshrined in legislation, the ''Australian Broadcasting Corporation Act 1983''. ABC Commercial, a profit-making division of the corporation, also helps to generate funding for content provision. The ABC was established as the Australian Broadcasting Commission on 1 July 1932 by an act of federal parliament. It effectively replaced the Australian Broadcasting Company, a private company established in 1924 to provide programming for A-class radio stations. The ABC was given statutory powers that reinforced its independence from the government and enhanced its news-gathering role. Modelled after the British Broadcasting Corporation ( BBC), which is funded by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Of New South Wales
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has been a dramati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frogs Of Australia
Amphibians of Australia are limited to members of the order Anura, commonly known as frogs. All Australian frogs are in the suborder Neobatrachia, also known as the modern frogs, which make up the largest proportion of extant frog species. About 230 of the 5,280 species of frog are native to Australia with 93% of them endemic. Compared with other continents, species diversity is low, and may be related to the climate of most of the Australian continent. There are two known invasive amphibians, the cane toad and the smooth newt. Origins The Australian continent once formed part of the supercontinent Pangaea, which split into Gondwana and Laurasia approximately 180 million years ago. The earliest true frog fossil, '' Vieraella herbsti'', is dated between 188 and 213 million years old. This predates the splitting of Gondwana, and has resulted in frogs present on all continents. The first two continents to split from Australia were South America and Africa. The amphibian fauna of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudophryne
''Pseudophryne'' is a genus of small myobatrachid frogs. All of these frogs are small terrestrial frogs, and as such, most species are commonly called toadlets (''pseudo-'' meaning deceptive, ''phryne'' meaning toad). The genus comprises thirteen species, ten from eastern Australia, and three from Western Australia Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to .... Species within the genus ''Pseudophryne'' lay their eggs on moist ground. The tadpoles develop within the eggs, and once they reach hatching size, will become dormant. Once sufficient rain occurs to flush the eggs into a creek or river, the eggs will hatch and release tadpoles into the water. Many of the species within this genus have the ability to form hybrids. Species The following species are recognised in the genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019–20 Australian Bushfire Season
The 201920 Australian bushfire season (Black Summer), was a period of bushfires in many parts of Australia, which, due to its unusual intensity, size, duration, and uncontrollable dimension, is considered a megafire. The Australian National University reported that the area burned in 2019/2020 was "well below average" due to low fuel levels and fire activity in unpopulated parts of Northern Australia, but that "Despite low fire activity overall, vast forest fires occurred in southeast Australia from southeast Queensland to Kangaroo Island." In June 2019 the Queensland Fire and Emergency Service acting director warned of the potential for an early start to the bushfire season which normally starts in August. The warning was based on the Northern Australia bushfire seasonal outlook noting exceptional dry conditions and a lack of soil moisture, combined with early fires in central Queensland. Throughout the summer, hundreds of fires burnt, mainly in the southeast of the country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Healesville Sanctuary
Healesville Sanctuary, formally known as the Sir Colin MacKenzie Sanctuary, is a zoo specialising in native Australian animals. It is located at Healesville in rural Victoria, Australia, and has a history of breeding native animals. It is one of only two places to have successfully bred a platypus, the other being Sydney's Taronga Zoo. It also assists with a breeding population of the endangered helmeted honeyeater. The zoo is set in a natural bushland environment where paths wind through different habitat areas showcasing wallabies, wombats, dingoes, kangaroos, and over 200 native bird varieties. Guided tours, bird shows and information areas are available to visitors. History Dr Colin MacKenzie (knighted in 1929) set up the Institute of Anatomical Research in 1920 on of land which had formerly been part of the Aboriginal reserve known as Coranderrk. The Reserve passed to the Healesville Council in 1927 and became the ''Sir Colin MacKenzie Sanctuary'' in 1934. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taronga Zoo
Taronga Zoo is a zoo located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, in the suburb of Mosman, on the shores of Sydney Harbour. The opening hours are between 9:30 a.m. to 5 p.m. Taronga is an Aboriginal word meaning 'beautiful water view'. It was officially opened on 7 October 1916. Taronga Zoo Sydney is managed by the Zoological Parks Board of New South Wales, under the trading name Taronga Conservation Society, along with its sister zoo, the Taronga Western Plains Zoo in Dubbo. Divided into various zoogeographic regions, the Taronga Zoo Sydney is home to more than 2,600 animals of approximately 250 different species. It has a zoo shop, a cafe, and an information centre. History The Royal Zoological Society of New South Wales opened the first public zoo in New South Wales in 1884 at Billy Goat Swamp in Moore Park, on a site now occupied by Sydney Boys High School and Sydney Girls High School. Inspired by a 1908 visit to the Hamburg Zoo, the secretary of the zoo, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melbourne Zoo
Melbourne Zoo is a zoo in Melbourne, Australia. It is located within Royal Park in Parkville, approximately north of the centre of Melbourne. It is the primary zoo serving Melbourne. The zoo contains more than 320 animal species from Australia and around the world, and is accessible via Royal Park station on the Upfield railway line, and is also accessible via tram routes 58 and 19, as well as by bicycle on the Capital City Trail. Bicycles are not allowed inside the zoo itself. The Royal Melbourne Zoological Gardens is a full institutional member of the Zoo and Aquarium Association and the World Association of Zoos and Aquariums. The zoo is set among flower gardens and picnic areas. Many of the animals are now organised in bioclimatic zones: African rainforest ('Gorilla Rainforest') that include gorillas and lemurs; Asian rainforest ('Trail of the 'Elephants') that includes elephants, orangutans, tigers and otters; and the Australian bush with kangaroos, koalas, wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian Research Centre
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial animal, terrestrial, fossorial, arboreal or freshwater aquatic ecosystems. Thus amphibians typically start out as larvae living in water, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. The young generally undergo metamorphosis from larva with gills to an adult air-breathing form with lungs. Amphibians use their skin as a secondary respiratory surface and some small terrestrial salamanders and frogs lack lungs and rely entirely on their skin. They are superficially similar to reptiles like lizards but, along with mammals and birds, reptiles are amniotes and do not require water bodies in which to breed. With their complex reproductive needs and permeable skins, amphibians are often ecological indicators; in recent decades there has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
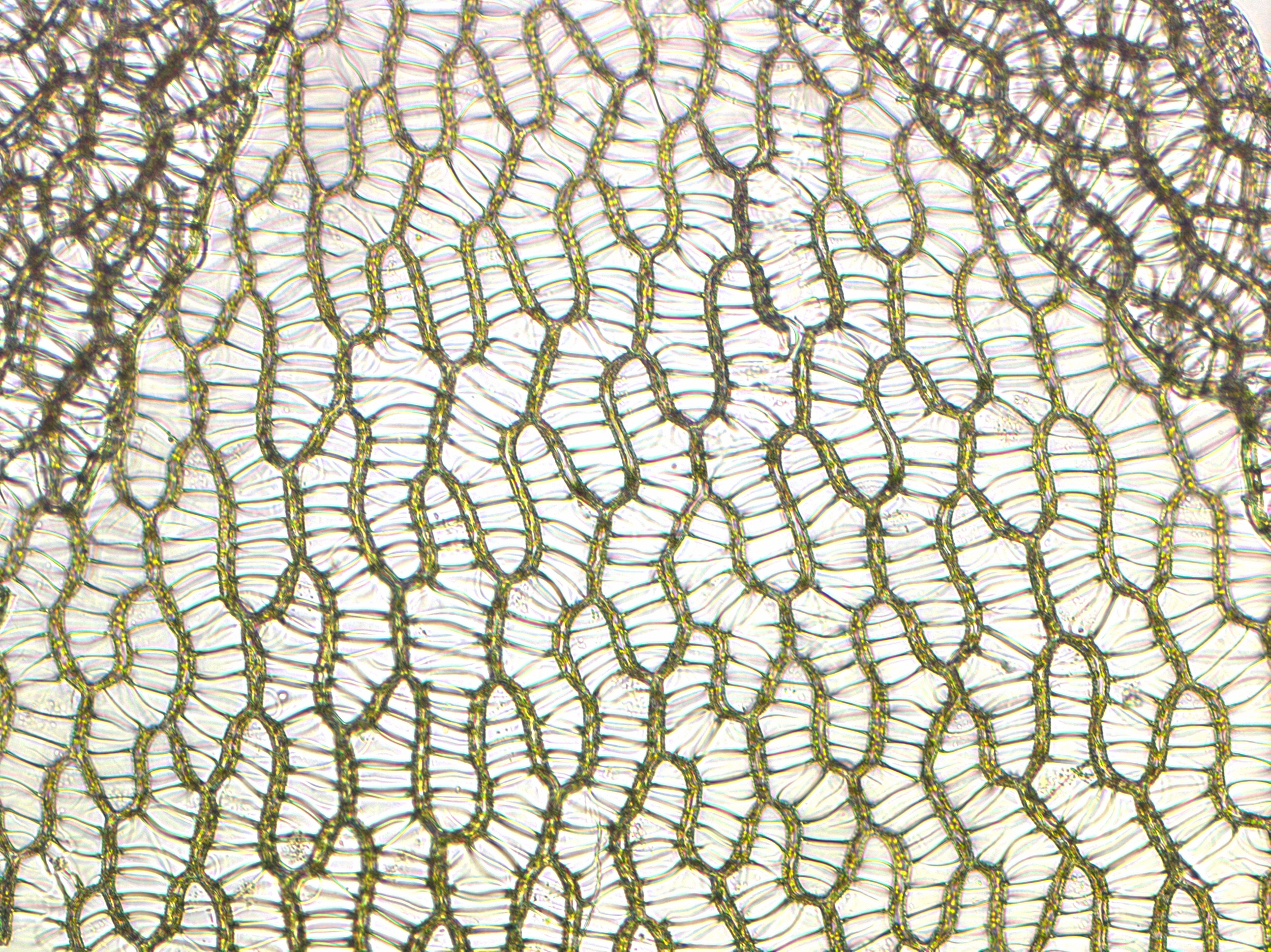
Sphagnum
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225-229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As sphagnum moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, sphagnum can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing sphagnum as 'habitat manipulators'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and ericaceous shrubs, as well as orchids and carnivorous plants.Keddy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)