|
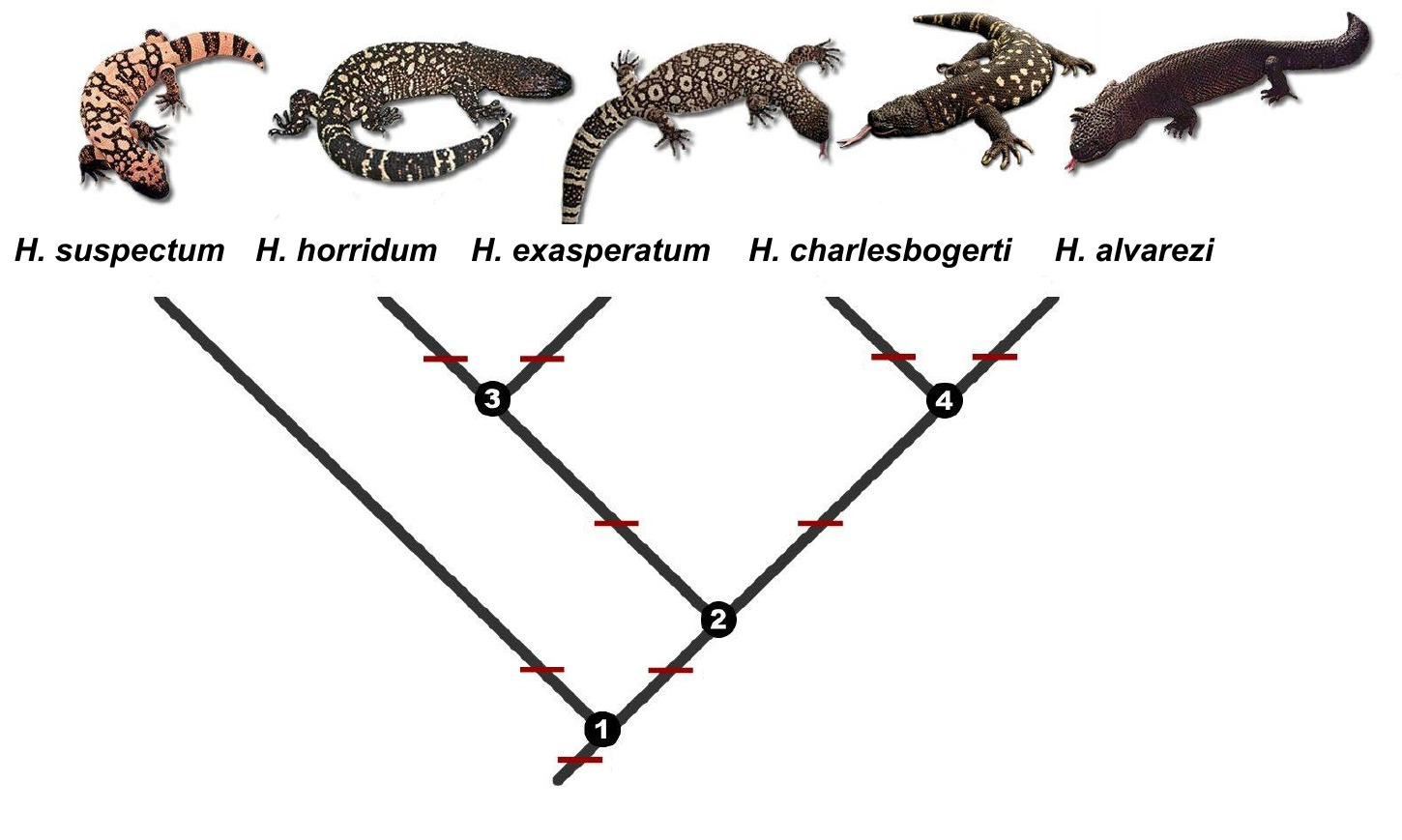
Pseudomonas Reptilivora
''Pseudomonas reptilivora'' is a fluorescent, yellow-green, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming, multiple polar flagellated, motile bacterium that is pathogenic to reptiles. It was originally isolated in Gila monsters (''Heloderma suspectum''), horned lizard ''Phrynosoma'', whose members are known as the horned lizards, horny toads, or horntoads, is a genus of North American lizards and the type genus of the Family (biology), family Phrynosomatidae. Their common names refer directly to their horns or ...s (''Phrynosoma solare''), and chuckawallas (''Sauromalus ater''). The type strain is ATCC 14836. Gluconic Acid Production by ''Pseudomonas reptilivora'' ''P. reptilivora'' has demonstrated a remarkable ability to convert glucose into gluconic acid, a valuable organic acid widely used in the food, pharmaceutical, and eco-friendly cleaning industries. This bioconversion occurs through an oxidative process catalyzed by membrane-bound dehydrogenases, particularly pyrrol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescent
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colored visible light. The color of the light emitted depends on the chemical composition of the substance. Fluorescent materials generally cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops. This distinguishes them from the other type of light emission, phosphorescence. Phosphorescent materials continue to emit light for some time after the radiation stops. This difference in duration is a result of quantum spin effects. Fluorescence occurs when a photon from incoming radiation is absorbed by a molecule, exciting it to a higher energy level, followed by the emission of light as the molecule returns to a lower energy state. The emitted light may have a longer wavelength and, therefore, a lower photon energy than the absorbed rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner ( cytoplasmic) membrane and an outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth. Within this category, notable species include the model organism '' Escherichia coli'', along with various pathogenic bacteria, such as '' Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', '' Chlamydia trachomatis'', and '' Yersinia pestis''. They pose significant challenges in the medical field due to their outer membrane, which acts as a protective barrier against numerous antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and the antimicrobial enzyme lysozyme produced by animals as part of their innate immune system. Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporulation
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. They were thought to have appeared as early as the mid-late Ordovician period as an adaptation of early land plants. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. In some rare cases, a diploid spore is also produced in some algae, or fungi. Under favourable conditions, the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium '' Helicobacter pylori'', for example, uses its flagella to propel itself through the stomach to reach the mucous lining where it may colonise the epithelium and potentially cause gastritis, and ulcers – a risk factor for stomach cancer. In some swarming bacteria, the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota, the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motile
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently using metabolic energy. This biological concept encompasses movement at various levels, from whole organisms to cells and subcellular components. Motility is observed in animals, microorganisms, and even some plant structures, playing crucial roles in activities such as foraging, reproduction, and cellular functions. It is genetically determined but can be influenced by environmental factors. In multicellular organisms, motility is facilitated by systems like the nervous and musculoskeletal systems, while at the cellular level, it involves mechanisms such as amoeboid movement and flagellar propulsion. These cellular movements can be directed by external stimuli, a phenomenon known as taxis. Examples include chemotaxis (movement along chemical gradients) and phototaxis (movement in response to light). Motility also includes physiological processes like gastrointestinal movements and peristalsis. Understanding moti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in mutualistic, commensal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gila Monster
The Gila monster (''Heloderma suspectum'', ) is a species of venomous lizard native to the Southwestern United States and the northwestern Mexico, Mexican state of Sonora. It is a heavy, slow-moving reptile, up to long, and it is the only venomous lizard native to the United States. Its venomous close relatives, the four Mexican beaded lizard, beaded lizards (all former subspecies of ''Heloderma horridum'') inhabit Mexico and Guatemala. The Gila monster is sluggish in nature, so it is not generally dangerous and very rarely poses a real threat to humans. However, it has a fearsome reputation and is sometimes killed despite the species being protected by state law in Arizona. History The name "Gila" refers to the Gila River Basin in the U.S. states of Arizona and New Mexico, where the Gila monster was once plentiful. ''Heloderma'' means "studded skin", from the Ancient Greek words (), "the head of a nail or stud", and (), "skin". The species epithet ''suspectum'' comes fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horned Lizard
''Phrynosoma'', whose members are known as the horned lizards, horny toads, or horntoads, is a genus of North American lizards and the type genus of the Family (biology), family Phrynosomatidae. Their common names refer directly to their horns or to their flattened, rounded bodies (squat bodied), and blunt snouts. The Genus, generic name ''Phrynosoma'' means "toad-bodied". In common with true toads (amphibians of the family Bufonidae), horned lizards tend to move sluggishly, often remain motionless, and rely on their remarkable camouflage to avoid detection by predators. They are adapted to arid or semiarid areas. The spines on the lizard's back and sides are modified reptile scales, which prevent water loss through the skin, whereas the horns on the head are true horns (i.e., they have a bony core). A Bladder#Reptiles, urinary bladder is absent. Of the 21 species of horned lizards, 15 are native to the USA. The largest-bodied and most widely distributed of the American species i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuckwalla
Chuckwallas are lizards found primarily in arid regions of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. Some are found on coastal islands. The five species of chuckwallas are all placed within the genus ''Sauromalus''; they are part of the iguanid family (biology), family, Iguanidae. Taxonomy and etymology The genera, generic name, ''Sauromalus'', is said to be a combination of two ancient Greek words: ''sauros'' meaning "lizard" and ''homalos'' (ὁμαλός) meaning "flat". The common name "chuckwalla" derives from the Shoshoni_language, Shoshone word ''tcaxxwal'' or Cahuilla language, Cahuilla ''čaxwal'', transcribed by Spain, Spaniards as ''chacahuala''. Extant species Description Chuckwallas are stocky, wide-bodied lizards with flattened midsections and prominent bellies. Their tails are thick, tapering to a blunt tip. Loose folds of skin characterize the neck and sides of their bodies, which are covered in small, coarsely granular scales. The Sauromalus ater, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadales
The Pseudomonadales are an order of Pseudomonadota. A few members are pathogens, such as species of ''Pseudomonas'', ''Moraxella'', and '' Acinetobacter'', which may cause disease in humans, animals and plants. ''Pseudomonas'' The bacterial genus ''Pseudomonas'' includes the opportunistic human pathogen '' P. aeruginosa'', plant pathogenic bacteria, plant beneficial bacteria, ubiquitous soil bacteria with bioremediation capabilities and other species that cause spoilage of milk and dairy products. ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' can cause chronic opportunistic infections that have become increasingly apparent in immunocompromised patients and the ageing population of industrialised societies. The genome sequences of several pseudomonads have become available in recent years and researchers are beginning to use the data to make new discoveries about this bacterium. ''Acinetobacter'' The genus '' Acinetobacter'' is a group of Gram-negative, nonmotile and nonfermentative bacteria belongi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |