|
Pseudohynobius Kuankuoshuiensis
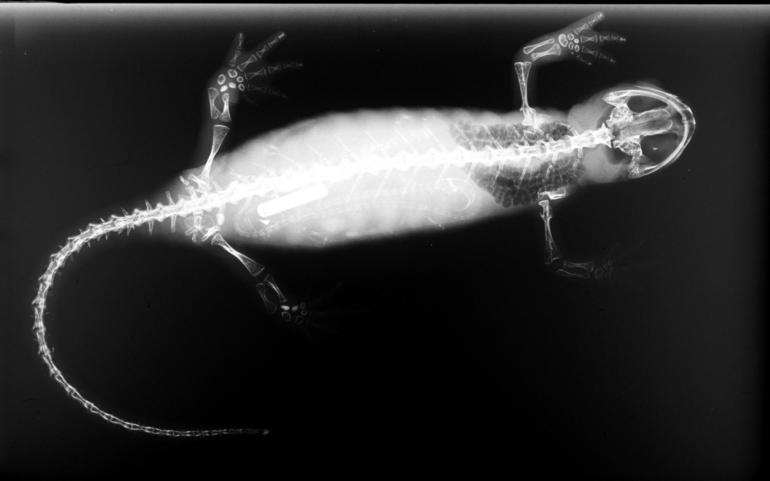
The Kuankuoshui salamander (''Pseudohynobius kuankuoshuiensis'') is a species of salamander in the family Hynobiidae endemic to China and only know from its type locality, Puchang-Kuankuoshui Nature Reserve (蒲昌宽阔水) in Suiyang County, Guizhou Province. Its natural habitats are temperate forests, stream A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream ...s, and pools. It is threatened by habitat loss. The Kuankuoshui salamander is a relative large salamander, about in total length. References Pseudohynobius Amphibians of China Endemic fauna of China Amphibians described in 2007 {{salamander-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela. Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders rarely have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. Some salamander species are fully aquatic throughout their lives, some take to the water intermittently, and others are entirely terrestrial as adults. This group of amphibians is capable of regenerating lost l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hynobiidae
The Asiatic salamanders (family Hynobiidae) are primitive salamanders found all over Asia, and in European Russia. They are closely related to the giant salamanders (family Cryptobranchidae), with which they form the suborder Cryptobranchoidea. About half of hynobiids currently described are endemic to Japan. Hynobiid salamanders practice external fertilization, or spawning. And, unlike other salamander families which reproduce internally, male hynobiids focus on egg sacs rather than females during breeding. The female lays two egg sacs at a time, each containing up to 70 eggs. Parental care is common. A few species have very reduced lungs, or no lungs at all. Larvae can sometimes have reduced external gills if they live in cold and very oxygen-rich water. Fossils of hynobiids are known from the Miocene to the present in Asia and Eastern Europe, though fossils of Cryptobranchoids more closely related to hynobiids than to giant salamanders extend back to the Middle Jurassic. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example ''Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. ''Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suiyang County
Suiyang County () is a county in Guizhou Province, China. It is under the jurisdiction of the prefecture-level city of Zunyi Zunyi () is a prefecture-level city in northern Guizhou province, People's Republic of China, situated between the provincial capital Guiyang to the south and Chongqing to the north, also bordering Sichuan to the northwest. Along with Guiyang an .... It has an area of 2,566 square kilometers and a population of 560,000 as of 2017. Suiyang leaf-litter toad, '' Leptobrachella suiyangensis'', is only known from the Huoqiuba Nature Reserve in Suiyang County. Climate References External linksOfficial website of Suiyang County government County-level divisions of Guizhou Zunyi {{Guizhou-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guizhou Province
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to the south, Yunnan to the west, Sichuan to the northwest, the municipality of Chongqing to the north, and Hunan to the east. The population of Guizhou stands at 38.5 million, ranking 18th among the provinces in China. The Dian Kingdom, which inhabited the present-day area of Guizhou, was annexed by the Han dynasty in 106 BC. Guizhou was formally made a province in 1413 during the Ming dynasty. After the overthrow of the Qing in 1911 and following the Chinese Civil War, the Chinese Communist Party took refuge in Guizhou during the Long March between 1934 and 1935. After the establishment of the People's Republic of China, Mao Zedong promoted the relocation of heavy industry into inland provinces such as Guizhou, to better protect them fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors will include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, with habitat generalist species able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species requiring a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' (FRA 2020) found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the predominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are found around the globe. More than half of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, Canada, China, Russia, and the United States). The largest share of forests (45 percent) are in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream
A stream is a continuous body of surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long large streams are usually called rivers, while smaller, less voluminous and more intermittent streams are known as streamlets, brooks or creeks. The flow of a stream is controlled by three inputs – surface runoff (from precipitation or meltwater), daylighting (streams), daylighted subterranean river, subterranean water, and surfaced groundwater (Spring (hydrology), spring water). The surface and subterranean water are highly variable between periods of rainfall. Groundwater, on the other hand, has a relatively constant input and is controlled more by long-term patterns of precipitation. The stream encompasses surface, subsurface and groundwater fluxes that respond to geological, geomorphological, hydrological and biotic controls. Streams are importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream Pool
A stream pool, in hydrology, is a stretch of a river or stream in which the water depth is above average and the water velocity is below average. Formation A stream pool may be bedded with sediment or armoured with gravel, and in some cases the pool formations may have been formed as basins in exposed bedrock formations. Plunge pools, or plunge basins, are stream pools formed by the action of waterfalls. Pools are often formed on the outside of a bend in a meandering river. Dynamics The depth and lack of water velocity often leads to stratification in stream pools, especially in warmer regions. In warm arid regions of the Western United States, surface waters were found to be 3-9 °C higher than those at the bottom Habitat This portion of a stream often provides a specialized aquatic ecosystem habitat for organisms that have difficulty feeding or navigating in swifter reaches of the stream or in seasonally warmer water. Such pools can be important for fish habitat, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat Loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby reducing biodiversity and species abundance. Habitat destruction is the leading cause of biodiversity loss. Fragmentation and loss of habitat have become one of the most important topics of research in ecology as they are major threats to the survival of endangered species. Activities such as harvesting natural resources, industrial production and urbanization are human contributions to habitat destruction. Pressure from agriculture is the principal human cause. Some others include mining, logging, trawling, and urban sprawl. Habitat destruction is currently considered the primary cause of species extinction worldwide. Environmental factors can contribute to habitat destruction more indirectly. Geological processes, climate change, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudohynobius
''Pseudohynobius'' is a genus of salamanders in the family Hynobiidae and is endemic to China. It contains these species: *''Pseudohynobius flavomaculatus'' (Hu and Fei, 1978) (yellow-spotted salamander) *''Pseudohynobius guizhouensis'' Li, Tian, and Gu, 2010 (Guizhou salamander) *''Pseudohynobius jinfo'' Wei, Xiong, and Zeng, 2009 (Jinfo Mountain salamander) *''Pseudohynobius kuankuoshuiensis'' Xu and Zeng, 2007 (Kuankuoshui salamander) *''Pseudohynobius puxiongensis'' (Fei and Ye, 2000) (Puxiong salamander) *''Pseudohynobius shuichengensis The Shuicheng salamander (''Pseudohynobius shuichengensis'') is a species of salamander in the family Hynobiidae, endemic to China. Its type locality is Shuicheng in Guizhou Province, and it is not yet known from elsewhere; it is not likely t ...'' Tian, Gu, Li, Sun, and Li, 1998 (Shuicheng salamander) References Amphibians of Asia Amphibian genera {{Salamander-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)

_nahe_dem_Weiherdamm_in_Wildbergerhütte.jpg)
