|
Pseudoganglion
A ganglion (: ganglia) is a group of neuron cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. In the somatic nervous system, this includes dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal ganglia among a few others. In the autonomic nervous system, there are both sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia which contain the cell bodies of postganglionic sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons respectively. A pseudoganglion looks like a ganglion, but only has nerve fibers and has no nerve cell bodies. Structure Ganglia are primarily made up of somata and dendritic structures, which are bundled or connected. Ganglia often interconnect with other ganglia to form a complex system of ganglia known as a plexus. Ganglia provide relay points and intermediary connections between different neurological structures in the body, such as the peripheral and central nervous systems. Among vertebrates there are three major groups of ganglia: * Dorsal root ganglia (also known as the spinal ganglia) contain the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
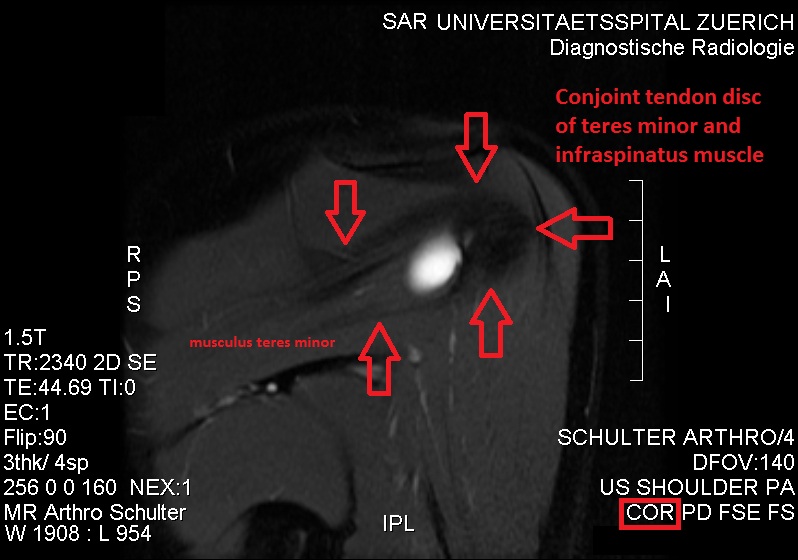
Teres Minor Muscle
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule. The primary function of the teres minor is to modulate the action of the deltoid, preventing the humeral head from sliding upward as the arm is abducted. It also functions to rotate the humerus laterally. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve. Structure It arises from the dorsal surface of the axillary border of the scapula for the upper two-thirds of its extent, and from two aponeurotic laminae, one of which separates it from the infraspinatus muscle, the other from the teres major muscle. Its fibers run obliquely upwards and laterally; the upper ones end in a tendon which is inserted into the lowest of the three impressions on the great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
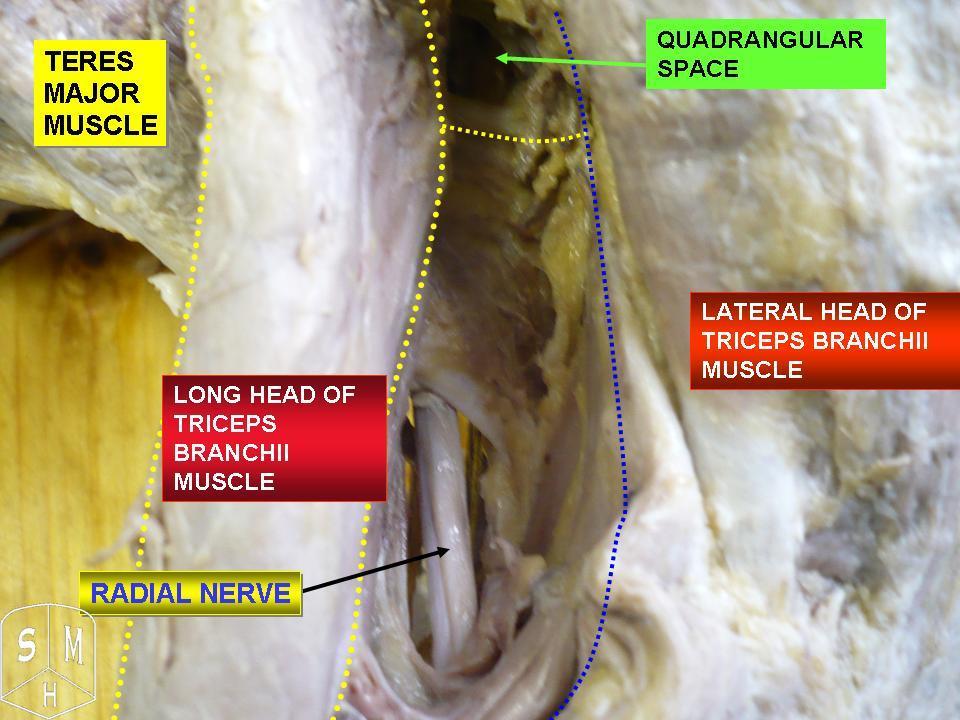
Radial Nerve
The radial nerve is a nerve in the human body that supplies the posterior portion of the upper limb. It innervates the medial and lateral heads of the triceps brachii muscle of the arm, as well as all 12 muscles in the Posterior compartment of the forearm, posterior osteofascial compartment of the forearm and the associated joints and overlying skin. It originates from the brachial plexus, carrying fibers from the posterior roots of spinal nerves C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1. The radial nerve and its branches provide Motor neuron, motor innervation to the dorsal arm muscles (the triceps brachii and the anconeus) and the extrinsic extensors of the wrists and hands; it also provides cutaneous Nerve supply to the skin, sensory innervation to most of the back of the hand, except for the back of the little finger and adjacent half of the ring finger (which are innervated by the ulnar nerve). The radial nerve divides into a deep branch, which becomes the posterior interosseous nerve, and a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A photographic micrograph is a photomicrograph, and one taken with an electron microscope is an electron micrograph. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurons
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Free Dictionary
''The Free Dictionary'' is an American online dictionary and encyclopedia that aggregates information from various sources. It is accessible in fourteen languages. History The Free Dictionary was launched in 2005 by Farlex. In the same year, it was included in '' PCMag'' Make Your Browser Better list. Content The site cross-references the contents of dictionaries such as ''The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language'', the ''Collins English Dictionary''; encyclopedias such as the '' Columbia Encyclopedia'', the ''Computer Desktop Encyclopedia'', the '' Hutchinson Encyclopedia'' (subscription), and Wikipedia; book publishers such as McGraw-Hill, Houghton Mifflin, HarperCollins, as well as the Acronym Finder database, several financial dictionaries, legal dictionaries, and other content. It has a feature that allows a user to preview an article while positioning the mouse cursor over a link. One can also click on any word to look it up in the dictionary. The we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminologia Anatomica
''Terminologia Anatomica'' (commonly abbreviated TA) is the international standard for human anatomy, human anatomical terminology. It is developed by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminology (FIPAT) a program of the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA). History The sixth edition of the previous standard, ''Nomina Anatomica'', was released in 1989. The first edition of ''Terminologia Anatomica'', superseding Nomina Anatomica, was developed by the Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT) and the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA) and released in 1998. In April 2011, this edition was published online by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminologies (FIPAT), the successor of FCAT. The first edition contained 7635 Latin items. The second edition was released online by FIPAT in 2019 and approved and adopted by the IFAA General Assembly in 2020. The latest errata is dated Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating heart and respiratory system, respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, known as the thalamocortical radiations, allowing hub (network science), hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory neuron, sensory and motor neuron, motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, the thalami are paramedian symmetrical structures (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalami ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The six-layered neocortex makes up approximately 90% of the Cortex (anatomy), cortex, with the allocortex making up the remainder. The cortex is divided into left and right parts by the longitudinal fissure, which separates the two cerebral hemispheres that are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum and other commissural fibers. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the neurocranium, cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, gyrification, cortical folding is crucial for the Neural circuit, brain circuitry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a nucleus (: nuclei) is a cluster of neurons in the central nervous system, located deep within the cerebral hemispheres and brainstem. The neurons in one nucleus usually have roughly similar connections and functions. Nuclei are connected to other nuclei by tracts, the bundles (fascicles) of axons (nerve fibers) extending from the cell bodies. A nucleus is one of the two most common forms of nerve cell organization, the other being layered structures such as the cerebral cortex or cerebellar cortex. In anatomical sections, a nucleus shows up as a region of gray matter, often bordered by white matter. The vertebrate brain contains hundreds of distinguishable nuclei, varying widely in shape and size. A nucleus may itself have a complex internal structure, with multiple types of neurons arranged in clumps (subnuclei) or layers. The term "nucleus" is in some cases used rather loosely, to mean simply an identifiably distinct group of neurons, even if they are sprea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into external and internal regions, and in the division of the striatum. Positioned at the base of the forebrain and the top of the midbrain, they have strong connections with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, brainstem and other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including regulating voluntary motor control, motor movements, procedural memory, procedural learning, habituation, habit formation, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion. The main functional components of the basal ganglia include the striatum, consisting of both the dorsal striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) and the ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), the globus pallidus, the ventral pallidum, the substa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postganglionic Fiber
In the autonomic nervous system, nerve fibers from the ganglion to the effector organ are called postganglionic nerve fibers. Neurotransmitters The neurotransmitters of postganglionic fibers differ: * In the parasympathetic division, neurons are ''cholinergic''. That is to say acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter responsible for the communication between neurons on the parasympathetic pathway. * In the sympathetic division, neurons are mostly ''adrenergic'' (that is, epinephrine and norepinephrine function as the primary neurotransmitters). Notable exceptions to this rule include the sympathetic innervation of sweat glands and arrectores pilorum muscles where the neurotransmitter at both pre and post ganglionic synapses is acetylcholine. Another notable structure is the medulla of the adrenal gland, where chromaffin cells function as modified post-ganglionic nerves. Instead of releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine into a synaptic cleft, these cells of the adrenal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |