|
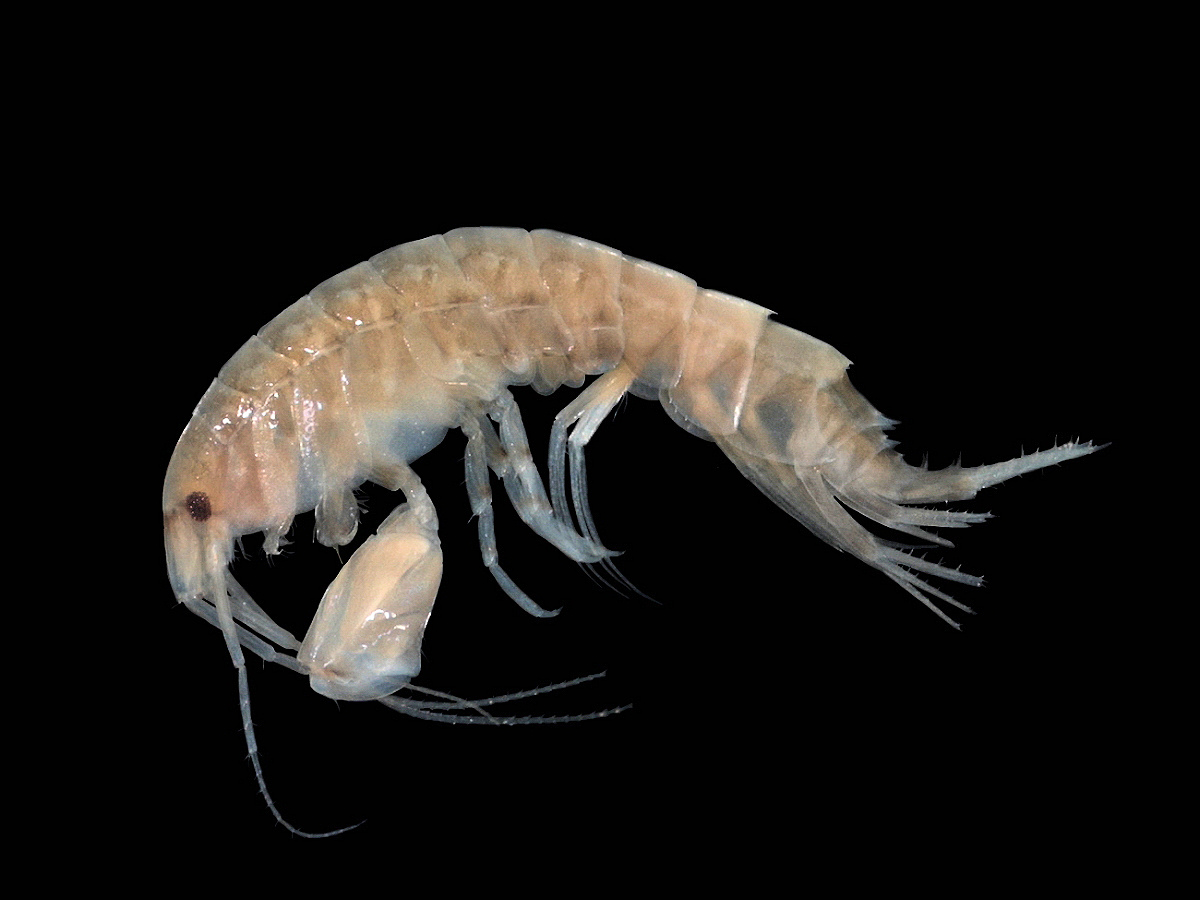
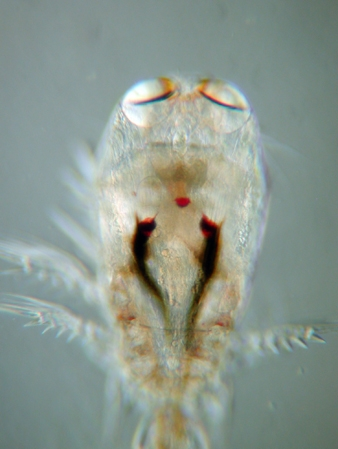
Pseudocalanus Minutus
''Pseudocalanus minutus'' is a small copepod found in the Arctic Ocean and surrounding waters. Description A small copepod, the female is generally between , and the male typically between in length. Distribution ''P. minutus'' is found primarily in the Arctic, but it is also found in the northwest Atlantic, the northern Pacific, and more temperate waters where Atlantic and Arctic waters are mixed. Ecology Life cycle and reproduction In Toyama Bay, ''P. minutus'' reproduces from February to April, producing two generations. This is during the temperature minimum (of about ) and phytoplankton maximum. All stages are found at shallower depths during the night (diel vertical migration) in Toyama Bay during this time. During the annual temperature maximum (of over ) in September, stage V copepodites migrate (possibly gradually) to deeper, colder waters to diapause (in contrast to the congeneric '' P. newmani'', which does not seem to be able to diapause). They moult to adults befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans ( Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxillopoda
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the adult and then, after more molts, achieves adult development. The nauplius form is so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calanoida
Calanoida is an order of copepods, a group of arthropods commonly found as zooplankton. The order includes around 46 families with about 1800 species of both marine and freshwater copepods between them. Description Calanoids can be distinguished from other planktonic copepods by having first antennae at least half the length of the body and biramous second antennae. However, their most distinctive anatomical trait is the presence of a joint between the fifth and sixth body segments. The largest specimens reach long, but most do not exceed long. Classification Calanoida contains the following families, as well as the genus '' Microdisseta'' (which is currently ''incertae sedis''); * Acartiidae * Aetideidae * Arctokonstantinidae * Arietellidae * Augaptilidae * Bathypontiidae * Calanidae * Calocalanidae * Candaciidae * Centropagidae * Clausocalanidae * Diaixidae * Diaptomidae * Discoidae * Epacteriscidae * Eucalanidae * Euchaetidae * Fosshageniidae * Heterorha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clausocalanidae
Clausocalanidae is a family of copepods belonging to the order Calanoida Calanoida is an order of copepods, a group of arthropods commonly found as zooplankton. The order includes around 46 families with about 1800 species of both marine and freshwater copepods between them. Description Calanoids can be distinguis .... Genera: * '' Clausocalanus'' Giesbrecht, 1888 * '' Ctenocalanus'' Giesbrecht, 1888 * '' Drepanopus'' Brady, 1883 * '' Microcalanus'' Sars, 1903 * '' Peniculoides'' Markhaseva & Renz, 2015 * '' Pseudocalanus'' Boeck, 1872 * '' Spicipes'' Grice & Hulsemann, 1965 * '' Streptocalanus'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q6551367 Copepods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning "oar-feet") are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (inhabiting sea waters), some are benthic (living on the ocean floor), a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, and puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses (phytotelmata) of plants such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the adult and then, after more molts, achieves adult development. The nauplius form is so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyama Bay
is a bay located on the northern shores of the Hokuriku region of Honshu, Japan on the Sea of Japan. The bay borders Toyama and Ishikawa prefectures. The bay is known for the mirages on the horizon during the winter months and for being a spawning ground for the firefly squid. It is also one of Japan's three largest bays. Parts of the bay are within the borders of the Noto Hantō Quasi-National Park. Geography Border communities ;Toyama Prefecture :Kurobe, Uozu, Namerikawa, Toyama, Imizu, Takaoka, Himi ;Ishikawa Prefecture : Nanao Rivers Kurobe River, Jōganji River, Jinzū River, Shō River The has its source in Mount Eboshi (烏帽子岳 ''Eboshigatake'') in the Shōkawa-chō area of Takayama, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. After flowing for through the northern part of Gifu Prefecture and the western part of Toyama Prefecture, it empt ..., etc. References {{Authority control Bays of Japan Bays of the Sea of Japan Landforms of Toyama Prefecture Landforms of Ishikaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diel Vertical Migration
Diel vertical migration (DVM), also known as diurnal vertical migration, is a pattern of movement used by some organisms, such as copepods, living in the ocean and in lakes. The word ''diel'' comes from the Latin ''dies'' day, and means a 24-hour period. The migration occurs when organisms move up to the uppermost layer of the sea at night and return to the bottom of the daylight zone of the oceans or to the dense, bottom layer of lakes during the day. It is important to the functioning of deep-sea food webs and the biologically driven sequestration of carbon. In terms of biomass, it is the largest synchronous migration in the world. It is not restricted to any one taxon as examples are known from crustaceans (copepods), molluscs ( squid), and ray-finned fishes (trout). The phenomenon may be advantageous for a number of reasons, most typically to access food and avoid predators. It is triggered by various stimuli, the most prominent being response to changes in ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudocalanus Newmani
''Pseudocalanus newmani'' is a copepod found in Arctic and northern Pacific waters. It was described by Frost in 1989. It is found in the Arctic and surrounding waters. There are multiple generations. Unlike some copepods, ''P. newmani'' undergoes reverse diel vertical migration, descending during the night, and ascending during the day, although it may undergo normal or no migration at all depending on predation. This copepod is primarily herbivorous. Taxonomy ''P. newmani'' was originally described by Frost in 1989 from multiple samples caught in the main basin of Puget Sound. Its specific name references Bill H. Newman. Description Female ''P. newmani'' usually range in length from about , and the male is generally between about . The female is distinguished from other species by its rounded cephalosome, which is barely anterior to the rostrum. It is also distinguished by its urosomal segments being the longest in its genus relative to cephalosome length. The male is distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |