|
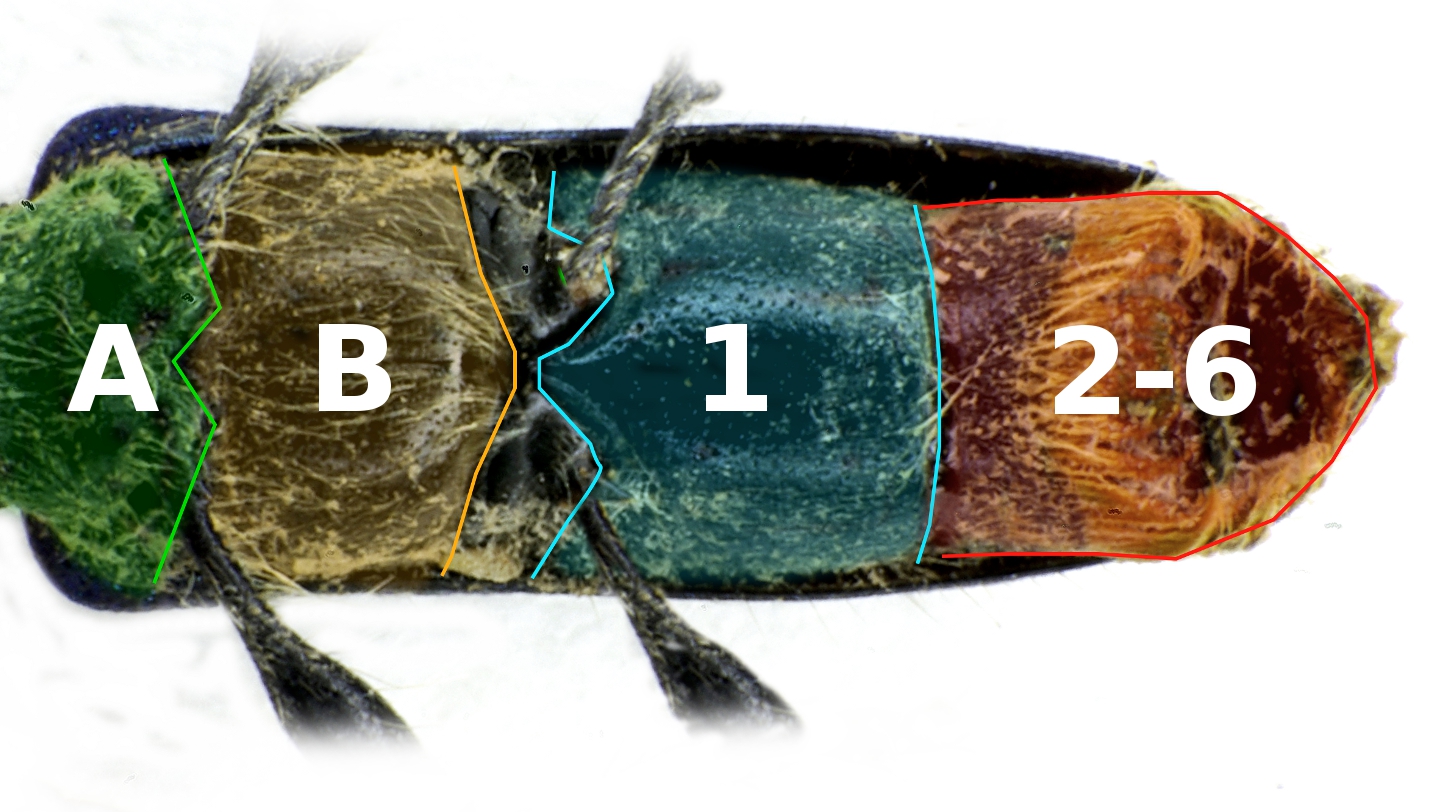
Pseudicius Africanus
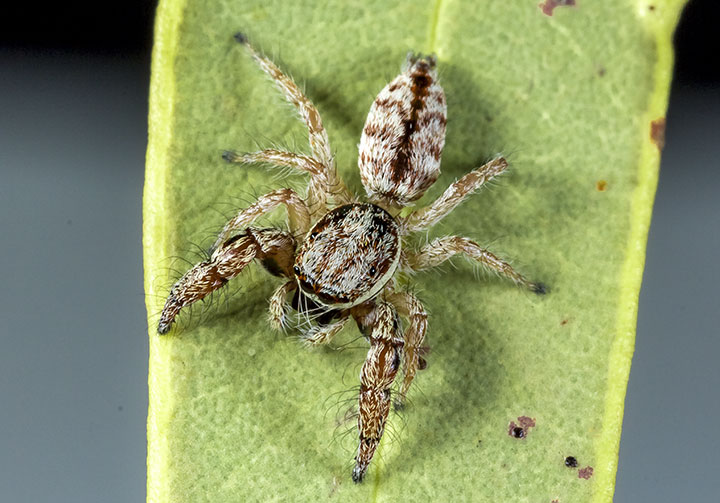
''Pseudicius africanus'' is a species of jumping spider in the genus '' Pseudicius'' that lives in Lesotho and South Africa. The spider was first defined in 1903 by George and Elizabeth Peckham. It is small, with an oval cephalothorax measuring between in length and an ovoid abdomen that is between in length. The female is smaller than the male. Otherwise, they are similar, generally dark brown but with white stripes, made of hairs, down the middle and the along the sides of the top of both the carapace and abdomen. The underside of the abdomen differs in being grey and marked by two lighter lines. The female's legs are also lighter, and the front legs on the male are stouter than all the others. The pattern on the abdomen helps distinguish the spider from the related '' Pseudicius maculatus''. It also has distinctive copulatory organs. The male has a shorter curved embolus and a characteristic tooth near the base of the tibial apophysis, or spike on the palpal tibia. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can reproduction, produce Fertility, fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugène Simon
Eugène Louis Simon (; 30 April 1848 – 17 November 1924) was a French naturalist who worked particularly on insects and spiders, but also on birds and plants. He is by far the most prolific spider taxonomist in history, describing over 4,000 species. Work on spiders His most significant work was ''Histoire Naturelle des Araignées'' (1892–1903), an encyclopedic treatment of the spider genera of the world. It was published in two volumes of more than 1000 pages each, and the same number of drawings by Simon. Working at the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle in Paris, it took Simon 11 years to complete, while working at the same time on devising a taxonomic scheme that embraced the known taxa. Simon described a total of 4,650 species, and as of 2013 about 3,790 species are still considered valid. The International Society of Arachnology offers a Simon Award recognising lifetime achievement. The Eocene fossil spider species '' Cenotextricella simoni'' was named in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider Vision
The eyes of spiders vary significantly in their structure, arrangement, and function. They usually have eight, each being a simple eye with a single lens (optics), lens rather than multiple units as in the compound eyes of insects. The specific arrangement and structure of the eyes is one of the features used in the identification and classification of different species, genera, and families. Most Haplogynae, haplogynes have six eyes, although some have eight (Plectreuridae), four (e.g., ''Tetrablemma'') or even two (most Caponiidae). In some cave species, there are no eyes at all (e.g. Stalita taenaria). Sometimes one pair of eyes is better developed than the rest. Several families of hunting spiders, such as jumping spiders and wolf spiders, have fair to excellent vision. The main pair of eyes in jumping spiders even sees in colour. Structure and anatomy Spiders' eyes are Simple eye in invertebrates, simple eyes, or ''ocelli'' (singular ''ocellus''), meaning their eyes have a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum (arthropod Anatomy)
The sternum (pl. "sterna") is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that vertrite numbers do not correspond to sternid numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustacea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salticoida
Salticoida is an unranked clade of the jumping spider family Salticidae. It is the larger and more widespread of the two subdivisions of the "typical" jumping spiders (subfamily Salticinae), occurring effectively world-wide. Its sister clade is Amycoida, which is also very diverse ecologically but has a mostly South American distribution. Systematics and evolution Salticoida includes the bulk of extant jumping spider diversity, with over 400 genera organized phylogenetically into 18 tribes according to Wayne Maddison's 2015 proposal. The age and origin of the Salticoida are not well determined. Certainly, by the late Paleogene the major lineages were recognizably distinct as indicated by the fossil evidence and molecular phylogeny. Thus, the salticoids presumably originated during or around the PETM or a bit earlier, but no corresponding fossils have been found yet. Their sister lineage, the Amycoida, probably originated by dispersal across the ocean to South America, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily ( Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end subfamily botanical names with "-oideae", and zoological names with "-inae". See also * International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants The ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN) is the set of rules and recommendations dealing with the formal botanical names that are given to plants, fungi and a few other groups of organisms, all those "trad ... * International Code of Zoological Nomenclature * Rank (botany) * Rank (zoology) Sources {{biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysillini
Chrysillini is a tribe of jumping spider in the family Salticidae. In Maddison's 2015 revision of the family, the subfamily Heliophaninae was reclassified as a junior synonym of Chrysillini. Genera * '' Afraflacilla'' * '' Augustaea'' * '' Chrysilla'' * '' Cosmophasis'' * '' Echinussa'' * '' Epocilla'' * ''Festucula'' * ''Hakka'' * ''Helicius'' * '' Heliophanillus'' * ''Heliophanus'' * '' Helvetia'' * '' Icius'' * '' Kupiuka'' * ''Marchena'' * '' Matagaia'' * ''Menemerus'' * ''Mexcala'' * ''Natta'' * '' Ogdenia'' * '' Orsima'' * '' Paraheliophanus'' * '' Phintella'' * '' Plesiopiuka'' * '' Siler'' * '' Tasa'' * '' Theriella'' * ''Wesolowskana'' * ''Yepoella ''Yepoella'' is a monotypic taxon, monotypic genus of Argentinian Salticidae, jumping spiders containing the single species, ''Yepoella crassistyli''. It was first described by María Elena Galiano in 1970, and is found in Argentina. A second spec ...'' References Salticidae Spider tribes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marchena
''Marchena'' is a genus of jumping spiders only found in the United States. Its only described species, ''M. minuta'', dwells on the barks of conifers along the west coast, especially California, Washington and Nevada.Maddison, Wayne. 1995. Marchena. Marchena minuta. Version 1 January 1995 (under construction). http://tolweb.org/Marchena_minuta/2986/1995.01.01 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/ It forms a monophyletic group with the genera '' Afraflacilla'', '' Pseudicius'' and ''Festucula''.Zabka & Grey 2002 Description This species can easily be distinguished from others in its range by the tubercles on the first femur of its first legs. ''M. minuta'' has a body length of about 4 mm. Name The genus name is probably derived from the Spanish city of Marchena, Seville. As witnessed by other generic names, the describers had a habit of naming taxa after places unrelated to the species' distribution. The species name is Latin for "small, minute". No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afraflacilla
''Afraflacilla'' is a genus of the spider family Salticidae (jumping spiders). Most species are distributed in Eastern to Northern Africa (including the Middle East) and Australia, with two species (''A. epiblemoides and A. tarajalis'') found in Europe. This genus was for a time included in the genus '' Pseudicius'', and the boundaries between both genera are disputed. In 2016 Jerzy Prószyński erected the genus ''Psenuc'' for some borderline species. The name ''Afraflacilla'' is combined from Africa, where most earlier described species were found, and ''Flacilla'' Simon, 1901, an obsolete salticid genus now called ''Flacillula'' Strand, 1932. This genus name is in turn derived from Aelia Flaccilla, wife of Roman Emperor Theodosius I. ''Afraflacilla'', '' Pseudicius'', ''Festucula'' and ''Marchena'' are close relatives and form a monophyletic group. Afraflacilla species have tubercles and bristles (on the sides of the carapace near the eyes and on their legs) which they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliophaninae
Chrysillini is a tribe of jumping spider in the family Salticidae. In Maddison's 2015 revision of the family, the subfamily Heliophaninae was reclassified as a junior synonym of Chrysillini. Genera * '' Afraflacilla'' * '' Augustaea'' * '' Chrysilla'' * '' Cosmophasis'' * '' Echinussa'' * '' Epocilla'' * ''Festucula'' * ''Hakka'' * ''Helicius'' * '' Heliophanillus'' * ''Heliophanus'' * '' Helvetia'' * '' Icius'' * '' Kupiuka'' * ''Marchena'' * '' Matagaia'' * ''Menemerus'' * ''Mexcala'' * ''Natta'' * '' Ogdenia'' * '' Orsima'' * '' Paraheliophanus'' * '' Phintella'' * '' Plesiopiuka'' * '' Siler'' * '' Tasa'' * '' Theriella'' * ''Wesolowskana'' * ''Yepoella ''Yepoella'' is a monotypic taxon, monotypic genus of Argentinian Salticidae, jumping spiders containing the single species, ''Yepoella crassistyli''. It was first described by María Elena Galiano in 1970, and is found in Argentina. A second spec ...'' References Salticidae Spider tribes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe (biology)
In biology, a tribe is a taxonomic rank above genus, but below family (biology), family and subfamily. It is sometimes subdivided into subtribes. By convention, all taxonomic ranks from genus upwards are capitalized, including both tribe and subtribe. In zoology, the standard ending for the name of a zoological tribe is "-ini". Examples include the tribes Goat-antelope#Tribe Caprini, Caprini (goat-antelopes), Hominini (hominins), Bombini (bumblebees), and Thunnini (tunas). The tribe Hominini is divided into subtribes by some scientists; subtribe Hominina then comprises "humans". The standard ending for the name of a zoological subtribe is "-ina". In botany, the standard ending for the name of a botanical tribe is "-eae". Examples include the tribes Acalypheae and Scilloideae#Hyacintheae, Hyacintheae. The tribe Hyacintheae is divided into subtribes, including the subtribe Massoniinae. The standard ending for the name of a botanical subtribe is "-inae". In bacteriology, the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |