|
Prāṇāyāma
Pranayama (Sanskrit: प्राणायाम, "Prāṇāyāma") is the yogic practice of focusing on breath. In classical yoga, the breath is associated with ''prana'', thus, pranayama is a means to elevate the ''prana-shakti'', or life energies. Pranayama is described in Hindu texts such as the ''Bhagavad Gita'' and the ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali''. Later, in Hatha yoga texts, it meant the complete suspension of breathing. The pranayama practices in modern yoga as exercise differ from those of the Hatha yoga tradition, often using the breath in synchrony with movements. Etymology ''Prāṇāyāma'' (Devanagari: ') is a Sanskrit compound. It is defined variously by different authors. Macdonell gives the etymology as prana ('), breath, + ''āyāma'' and defines it as the suspension of breath. Monier-Williams defines the compound ' as "of the three 'breath-exercises' performed during (''See'' ', ', '".Monier-Williams, p706, left column./ref> This technical definition r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashtanga (eight Limbs Of Yoga)
Ashtanga yoga (, "eight limbs of yoga") is Patanjali, Pātañjali's classification of classical yoga, as set out in his ''Yoga Sutras of Patanjali, Yoga Sūtras''. He defined the eight limbs as ''Yamas, yama'' (abstinences), ''niyama'' (observances), ''Asana, āsana'' (postures), ''Pranayama, prāṇāyāma'' (breath control), ''Pratyahara, pratyāhāra'' (withdrawal of the senses), ''dhāraṇā'' (concentration), ''Dhyana in Hinduism, dhyāna'' (meditation), and ''Samadhi, samādhi'' (absorption). The eight limbs form a sequence from the outer to the inner. The posture, asana, must be steady and comfortable for a long time, in order for the yogi to practice the limbs from ''Pranayama, prāṇāyāma'' until ''Samadhi, samādhi''. The main aim is ''kaivalya'', discernment of ''Purusha, Puruṣa'', the witness-conscious, as separate from ''Prakṛti'', the cognitive apparatus, and disentanglement of ''Puruṣa'' from its muddled defilements. Definition of yoga Patanjali, Pā ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Sutras Of Patanjali
The ''Yoga Sutras of Patañjali'' (IAST: Patañjali yoga-sūtra) is a compilation "from a variety of sources" of Sanskrit sutras (aphorisms) on the practice of yoga – 195 sutras (according to Vyasa, Vyāsa and Krishnamacharya) and 196 sutras (according to others, including BKS Iyengar). The ''Yoga Sutras'' were compiled in India in the early centuries CE by the sage Patanjali, who collected and organized knowledge about yoga from Samkhya, Buddhism, and older Yoga traditions, and possibly another compiler who may have added the fourth chapter. He may also be the author of the ''Yogabhashya'', a commentary on the ''Yoga Sutras'', traditionally attributed to the legendary Vedic sage Vyasa, but possibly forming a joint work of Patanjali called the ''Pātañjalayogaśāstra''. The ''Yoga Sutras'' draw from three distinct traditions from the 2nd century BCE to the 1st century CE, namely Samkhya, Buddhism traditions, and "various older ascetic and religious strands of speculatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatha Yoga
Hatha yoga (; Sanskrit हठयोग, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''haṭhayoga'') is a branch of yoga that uses physical techniques to try to preserve and channel vital force or energy. The Sanskrit word हठ ''haṭha'' literally means "force", alluding to a system of physical techniques. Some hatha yoga style techniques can be traced back at least to the 1st-century CE, in texts such as the Hindu Itihasa, Sanskrit epics and Buddhism's Pali canon. The oldest dated text so far found to describe hatha yoga, the 11th-century ''Amritasiddhi, Amṛtasiddhi'', comes from a Tantra, tantric Buddhist milieu. The oldest texts to use the terminology of ''hatha'' are also Vajrayana Buddhist. Hindu hatha yoga texts appear from the 11th century onward. Some of the early hatha yoga texts (11th-13th c.) describe methods to raise and conserve bindu (vital force, that is, semen, and in women ''rajas –'' menstrual fluid). This was seen as the physical esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
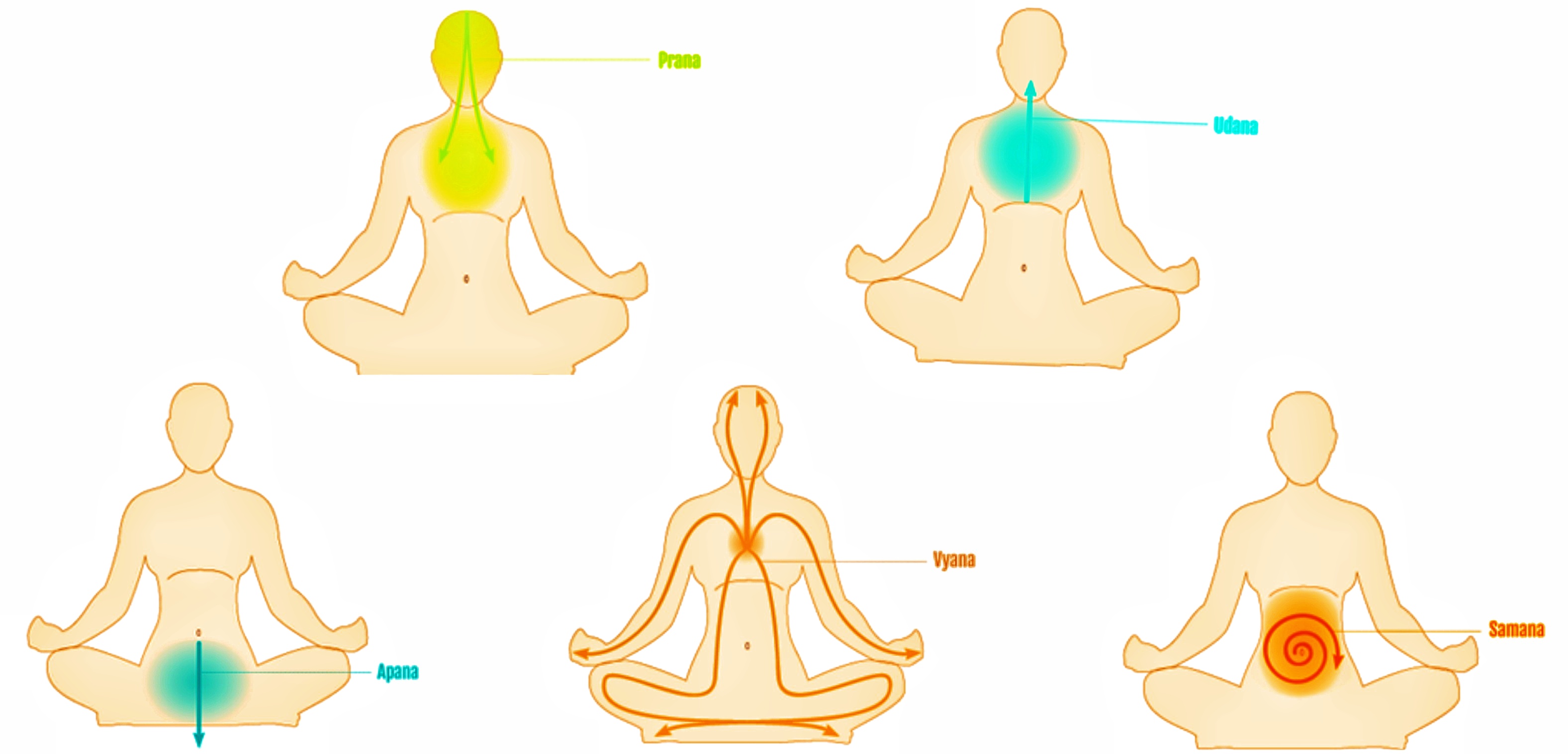
Prana
In yoga, Ayurveda, and Indian martial arts, prana (, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five '' vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand conscious awareness of prana. Etymology V.S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashtanga (vinyasa) Yoga
Ashtanga yoga (not to be confused with Patanjali's ''Ashtanga (eight limbs of yoga), aṣṭāṅgayoga'', the eight limbs of yoga) is a style of yoga as exercise popularised by K. Pattabhi Jois during the twentieth century, often promoted as a dynamic form of medieval hatha yoga. Jois claimed to have learnt the system from his teacher Tirumalai Krishnamacharya. The style is energetic, synchronising breath with movements. The individual poses (asanas) are linked by flowing movements called vinyasas. Jois established his Ashtanga Yoga Research Institute in 1948. The current style of teaching is called "Mysore style", after the city in India where the practice was originally taught. Ashtanga yoga has given rise to various spinoff styles of Power Yoga, power yoga. Approach Traditionally, Ashtanga yoga students memorised a sequence of asanas and practised it together without being led by a teacher. Teacher-led classes were introduced in K. Pattabhi Jois's later years. Such classes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ujjayi Breath
Ujjayi (, IAST ujjāyī, "victorious" or "conquering" ) is a pranayama ( breathing technique) practised simultaneously with asanas in modern yoga as exercise. It is practised especially in Pattabhi Jois's Ashtanga (vinyasa) yoga, where it accompanies vigorous asana flow exercise. It is described as a seated practice in B. K. S. Iyengar's 1966 book '' Light on Yoga''. Etymology and origins "Ujjayi ranayama () means "victorious or conquering reath in Sanskrit. According to B. K. S. Iyengar, the prefix "ut" denotes superiority, while the word "jaya" means victory or conquest. While ujjayi is described as pranayama, the classical yoga practice is stated by the yoga scholar Andrea Jain to have been "marginal to the most widely cited sources" before the 20th century, and "dramatically" unlike the modern ones. She writes that while modern pranayama in yoga as exercise consists of synchronising the breath with movements (between asanas), in classical texts like the ''Bhagavad Gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gheranda Samhita
''Gheranda Samhita'' (IAST: gheraṇḍasaṁhitā, घेरंडसंहिता, meaning “Gheranda's collection”) is a Sanskrit text of Yoga in Hinduism. It is one of the three classic texts of hatha yoga (the other two being the '' Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' and the '' Shiva Samhita''), and one of the most encyclopedic treatises in yoga.B. Heimann (1937)Review: The Ǧheraṇda Saṁhitā. A Treatise on Haṭha Yoga by Śrīś Chandra Vasu The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, Cambridge University Press, No. 2 (Apr., 1937), pp. 355-357 Fourteen manuscripts of the text are known, which were discovered in a region stretching from Bengal to Rajasthan. The first critical edition was published in 1933 by Adyar Library, and the second critical edition was published in 1978 by Digambarji and Ghote. Some of the Sanskrit manuscripts contain ungrammatical and incoherent verses, and some cite older Sanskrit texts. It is likely a late 17th-century te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurst Publishers
Hurst Publishers (C. Hurst & Co Publishers Ltd) is an independent non-fiction publisher based in the Bloomsbury area of London. Hurst specializes in books on global affairs and has lists in Islamic Studies Islamic studies is the academic study of Islam, which is analogous to related fields such as Jewish studies and Quranic studies. Islamic studies seeks to understand the past and the potential future of the Islamic world. In this multidiscipli ..., European History, War & Conflict, African Studies and International Relations. Christopher Hurst founded the company in 1969. Michael Dwyer, who joined Hurst in 1986, took over its running after the death of Christopher Hurst in April 2007.Hurst Publishers"About" Hurst Publishers website. Hurst authors include the French intellectual Olivier Roy, the British cultural critic Ziauddin Sardar, the Australian counterinsurgency expert David Kilcullen, and the historians Faisal Devji and Christopher Davidson, among others. The H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rishi
In Indian religions, a ''rishi'' ( ) is an accomplished and enlightened person. They find mention in various Vedic texts. Rishis are believed to have composed hymns of the Vedas. The Post-Vedic tradition of Hinduism regards the rishis as "great yogis" or "sages" who after intense meditation (Tapas (Sanskrit), tapas) realized the supreme truth and eternal knowledge, which they composed into hymns.Hartmut Scharfe (2002), Handbook of Oriental Studies, BRILL Academic, , pp. 13–15. The term appears in Pali literature as Ishi; in Buddhism they can be either Buddhas, Pratyekabuddha, Paccekabuddhas, Arhat, Arahats or a Buddhist monasticism, monk of high rank. Etymology According to Indian tradition, the word may be derived from two different meanings of the root 'rsh' (). Sanskrit grammarians derive this word from the second meaning: "to go, to move". V. S. Apte gives this particular meaning and derivation, and Monier-Williams also gives the same, with some qualification. Another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Journal
''Yoga Journal'' is a website and digital journal, formerly a print magazine, on yoga as exercise founded in California in 1975 with the goal of combining the essence of traditional yoga with scientific understanding. It has produced live events and materials such as DVDs on yoga and related subjects. The magazine grew from the California Yoga Teachers Association's newsletter, which was called ''The Word''. ''Yoga Journal'' has repeatedly won Western Publications Association's Maggie Awards for "Best Health and Fitness Magazine". It has however been criticized for representing yoga as being intended for affluent white women; in 2019 it attempted to remedy this by choosing a wider variety of yoga models. The magazine was acquired by Outside in 2020. Beginnings ''Yoga Journal'' was started in May 1975 by the California Yoga Teachers Association (CYTA), with Rama Jyoti Vernon as President, William Staniger as the founding editor, and Judith Lasater on the board and serving as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nadi Shodhana
''Anuloma Pranayama'' () is one of several Pranayama or breath exercises used in the Hindu practice of hatha yoga. Similar to the practice of ''Nadi Shodhana'' (commonly called alternate nostril breathing and known in some circles as ''Anuloma Viloma'') is the practice of inhaling through both nostrils together and exhaling each breath alternately between the left and right nostrils. The thumb of the right hand is used to manipulate the right nostril, while the pinky and ring finger are used to control the left nostril. Inverted Anuloma breath is called ''Pratiloma'' and involves inhaling through alternating nostrils and exhaling through both together. The practice of a ''kumbhaka'' or retention is encouraged as students advance at the practice; first at the end of the inhale and eventually the end of the exhale. When practiced as ''Saṃa Vṛtti'' the inhalation, retention and exhalation are all of equal duration. More advanced students may employ ''Viṣaṃa Vṛtti'' or unev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Mallinson (author)
Sir James Mallinson, 5th Baronet, of Walthamstow (born 22 April 1970) is a British Indologist, writer and translator. He is Boden Professor of Sanskrit at the University of Oxford, and recognised as one of the world's leading experts on the history of medieval Hatha yoga. Early life Mallinson became interested in India by reading Rudyard Kipling's novel ''Kim (novel), Kim'' as a teenager; the book describes an English boy travelling India with a holy man. He was educated at Eton College and the University of Oxford, where he read Sanskrit and Old Iranian for his bachelor's degree, and studied the ethnography of South Asia for his master's degree at SOAS University of London. Mallinson is described as "perhaps the only baronet to wear dreadlocks"; he let his hair grow out from 1988 on his first visit to India during his gap year. He cut his hair in 2019 after the death of his guru, Mahant Balyogi Sri Ram Balak Das, who had initiated him into the Ramanandi Sampradaya at the Ujjai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |