|
Prozostrodontidae
Prozostrodontia is a clade of cynodonts including mammaliaforms and their closest relatives such as Tritheledontidae and Tritylodontidae. It was erected as a node-based taxon by Liu and Olsen (2010) and defined as the least inclusive clade containing ''Prozostrodon brasiliensis'', '' Tritylodon langaevus'', ''Pachygenelus monus'', and ''Mus musculus'' (the house mouse). Prozostrodontia is diagnosed by several characters, including: * Reduced prefrontal and postorbital bones, with the disappearance of a strut of bone called the postorbital bar separating the eye socket from the temporal region * Unfused symphysis between the dentary bones in the lower jaw * The presence of a small hole within the eye socket called the sphenopalatine foramen * A long sagittal crest extending to the rearmost part of the lambdoidal crest at the back of the skull * Neural spines of the dorsal vertebrae angled backward * A convex-shaped iliac crest and a reduced posterior iliac spine on the hip * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudotherium
''Pseudotherium'' ("false beast") is an extinct genus of prozostrodontian cynodonts from the Late Triassic of Argentina. It contains one species, ''P. argentinus'', which was first described in 2019 from remains found in the La Peña Member of the Ischigualasto Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin. Discovery and naming The holotype and only known specimen, PVSJ 882, was discovered in 2006 by Argentine palaeontologist Ricardo N. Martínez during an expedition to the Ischigualasto Formation. It consists of a partial skull lacking the lower jaw, quadrate bones and most of the zygomatic arches and premaxillae. The generic name ''Pseudotherium'' is derived from the Greek words , meaning "false", and , meaning "beast". The specific name ''argentinus'' references the country of Argentina where it was found. Description ''Pseudotherium'' would have been a relatively large cynodont; excluding its missing premaxillae, the holotype skull is in length. Running along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
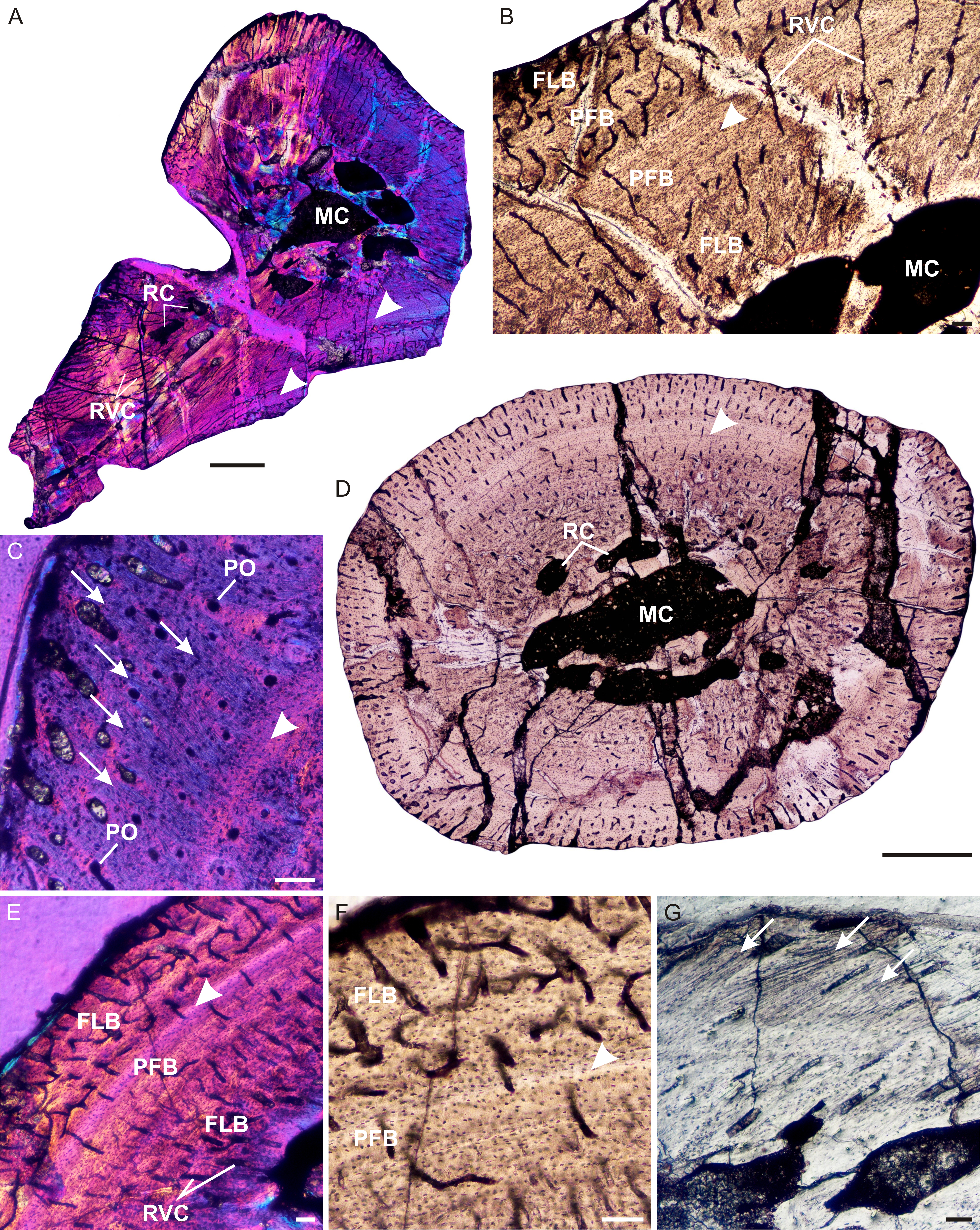
Prozostrodon
''Prozostrodon'' is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts that was closely related to mammals. The remains were found in Brazil and are dated to the Carnian age of the Late Triassic. The holotype has an estimated skull length of , indicating that the whole animal may have been the size of a cat. The teeth were typical of advanced cynodonts, and the animal was probably a carnivore hunting reptiles and other small prey. Discovery and naming ''Prozostrodon brasiliensis'' was originally described as a species of ''Thrinaxodon'' in a 1987 paper by Mário Costa Barberena, Mário C. Barberena, José F. Bonaparte and A. M. Sá Teixeira. The holotype (UFRGS-PV-0248-T) includes a well-preserved skull preserving the front half of the cranium, a mostly complete lower jaw and all of the teeth, but missing most of the braincase, sagittal crest and zygomatic arches. It also preserves multiple postcranial elements, including parts of the vertebral column, ribs, interclavicle, humeri, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prozostrodon Brasiliensis
''Prozostrodon'' is an extinct genus of probainognathian cynodonts that was closely related to mammals. The remains were found in Brazil and are dated to the Carnian age of the Late Triassic. The holotype has an estimated skull length of , indicating that the whole animal may have been the size of a cat. The teeth were typical of advanced cynodonts, and the animal was probably a carnivore hunting reptiles and other small prey. Discovery and naming ''Prozostrodon brasiliensis'' was originally described as a species of '' Thrinaxodon'' in a 1987 paper by Mário C. Barberena, José F. Bonaparte and A. M. Sá Teixeira. The holotype (UFRGS-PV-0248-T) includes a well-preserved skull preserving the front half of the cranium, a mostly complete lower jaw and all of the teeth, but missing most of the braincase, sagittal crest and zygomatic arches. It also preserves multiple postcranial elements, including parts of the vertebral column, ribs, interclavicle, humeri, right ilium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachygenelus Monus
''Pachygenelus'' is a genus of extinct cynodont. Fossils have been found from the Karoo basin in South Africa and date back to the Early Jurassic. The genus was named in 1913 on the basis of a partial lower jaw found from South Africa, with the type species being named ''P. monus''. A new species, ''P. milleri'', was named in 1983 and distinguished from the type species in possessing an accessory posterior cusp on the lower postcanines. Description ''Pachygenelus'' had both an articular- quadrate and dentary- squamosal jaw joint characteristic of ictidosaurs. Only mammals possess the dentary-squamosal articulation, while all other tetrapods possess the typical arcticular-quadrate articulation. Thus the jaw of ''Pachygenelus'' can be seen as transitional between non-mammalian synapsids and true mammals. Another feature of ''Pachygenelus'' that is shared with mammals is plesiomorphic prismatic enamel, or enamel arranged into strengthened prisms. The upper and lower tooth rows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', ''Herrerasaurus'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Node-based Taxon
Phylogenetic nomenclature is a method of nomenclature for taxon, taxa in biology that uses phylogenetics, phylogenetic definitions for taxon names as explained below. This contrasts with Biological classification, the traditional method, by which taxon names are defined by a ''Type (biology), type'', which can be a specimen or a taxon of lower Taxonomic rank, rank, and a description in words. Phylogenetic nomenclature is regulated currently by the ''PhyloCode, International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature'' (''PhyloCode''). Definitions Phylogenetic nomenclature associates names with clades, groups consisting of an ancestor and all its descendants. Such groups are said to be Monophyly, monophyletic. There are slightly different methods of specifying the ancestor, which are discussed below. Once the ancestor is specified, the meaning of the name is fixed: the ancestor and all organisms which are its descendants are included in the taxon named. Listing all these organisms (i.e. prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Socket
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is about , of which the eye occupies . The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves. Structure The orbits are conical or four-sided pyramidal cavities, which open into the midline of the face and point back into the head. Each consists of a base, an apex and four walls."eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2009 Openings There are two important foramina, or windows, two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentary Bone
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). The jawbone is the skull's only movable, posable bone, sharing joints with the cranium's temporal bones. The mandible hosts the lower teeth (their depth delineated by the alveolar process). Many muscles attach to the bone, which also hosts nerves (some connecting to the teeth) and blood vessels. Amongst other functions, the jawbone is essential for chewing food. Owing to the Neolithic advent of agriculture (), human jaws evolved to be smaller. Although it is the strongest bone of the facial skeleton, the mandible tends to deform in old age; it is also subject to fracturing. Surgery allows for the removal of jawbone fragments (or its entirety) as well as regenerative methods. Additionally, the bone is of great forensic significance. Structure In hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibular Symphysis
In human anatomy, the facial skeleton of the skull the external surface of the mandible is marked in the median line by a faint ridge, indicating the mandibular symphysis (Latin: ''symphysis menti'') or line of junction where the two lateral halves of the mandible typically fuse in the first year of life (6–9 months after birth). It is not a true symphysis as there is no cartilage between the two sides of the mandible. This ridge divides below and encloses a triangular eminence, the mental protuberance, the base of which is depressed in the center but raised on either side to form the mental tubercle. The lowest (most inferior) end of the mandibular symphysis — the point of the chin — is called the "menton". It serves as the origin for the geniohyoid and the genioglossus muscles. Other animals Solitary mammalian carnivores that rely on a powerful canine bite to subdue their prey have a strong mandibular symphysis, while pack hunters delivering shallow bites have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Fenestra
Temporal fenestrae are openings in the temporal region of the skull of some amniotes, behind the orbit (eye socket). These openings have historically been used to track the evolution and affinities of reptiles. Temporal fenestrae are commonly (although not universally) seen in the fossilized skulls of dinosaurs and other sauropsids (the total group of reptiles, including birds). The major reptile group Diapsida, for example, is defined by the presence of two temporal fenestrae on each side of the skull. The infratemporal fenestra, also called the lateral temporal fenestra or lower temporal fenestra, is the lower of the two and is exposed primarily in lateral (side) view.The supratemporal fenestra, also called the upper temporal fenestra, is positioned above the other fenestra and is exposed primarily in dorsal (top) view. In some reptiles, particularly dinosaurs, the parts of the skull roof lying between the supratemporal fenestrae are thinned out by excavations from the adjacent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbit (anatomy)
In anatomy Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old scien ..., the orbit is the Body cavity, cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and Accessory visual structures, its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is about , of which the eye occupies . The orbital contents comprise the eye, the Orbital fascia, orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves optic nerve, II, oculomotor nerve, III, trochlear nerve, IV, trigeminal nerve, V, and abducens nerve, VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its Lacrimal sac, sac and nasolacrimal duct, duct, the eyelids, Medial palpebral ligament, medial and Lateral palpebral raphe, lateral palpebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postorbital Bar
The postorbital bar (or postorbital bone) is a bony arched structure that connects the frontal bone of the skull to the zygomatic arch, which runs laterally around the eye socket. It is a trait that only occurs in mammalian taxa, such as most strepsirrhine primates and the hyrax, while haplorhine primates have evolved fully enclosed sockets. One theory for this evolutionary difference is the relative importance of vision to both orders. As haplorrhines (tarsiers and simians) tend to be diurnal, and rely heavily on visual input, many strepsirrhines are nocturnal and have a decreased reliance on visual input. Postorbital bars evolved several times independently during mammalian evolution and the evolutionary histories of several other clades. Some species, such as tarsiers, have a postorbital septum. This septum can be considered as joined processes with a small articulation between the frontal bone, the zygomatic bone and the alisphenoid bone and is therefore different from the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |