|
Providence Island Sign Language
Providence Island Sign Language (PISL; ), also known as Provisle, is a village sign language of the small island community of Providence Island in the Western Caribbean, off the coast of Nicaragua but belonging to Colombia Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel .... The island is about and the total population is about 5000, of which an unusual proportion are deaf (5 in 1,000). It is believed that the sign language emerged in the late 19th or early 20th century. Brief sociological studies have suggested that deaf people on the island are regarded as inferior in mental ability; hearing people do not discuss complex ideas with them, and they hold a marginalized social position. Perhaps consequently, PISL is rather simplistic in comparison to other sign languages. Another po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Peru and Ecuador to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 Departments of Colombia, departments. The Capital District of Bogotá is also the List of cities in Colombia by population, country's largest city hosting the main financial and cultural hub. Other major urban areas include Medellín, Cali, Barranquilla, Cartagena, Colombia, Cartagena, Santa Marta, Cúcuta, Ibagué, Villavicencio and Bucaramanga. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi) and has a population of around 52 million. Its rich cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Sign Language
A village sign language, or village sign, also known as a shared sign language, is a local indigenous sign language used by both deaf and hearing in an area with a high incidence of congenital deafness. Meir ''et al.'' define a village sign language as one which "arise in an existing, relatively insular community into which a number of deaf children are born." The term "rural sign language" refers to almost the same concept. In many cases, the sign language is known throughout the community by a large portion of the hearing population. These languages generally include signs derived from gestures used by the hearing population, so that neighboring village sign languages may be lexically similar without being actually related, due to local similarities in cultural gestures which preceded the sign languages. Most village sign languages are endangered due to the spread of formal education for the deaf, which use or generate deaf-community sign languages, such as a national or foreign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Providencia–Cayman Sign Language Family
The Providencia–Cayman Sign Language family is a possible language family of two related sign language Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with #Non-manual elements, no ...s: Providencia Sign and Old Cayman Sign. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Providencia-Cayman Sign Language family Sign languages Sign language families Languages of the Caribbean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottolog
''Glottolog'' is an open-access online bibliographic database of the world's languages. In addition to listing linguistic materials ( grammars, articles, dictionaries) describing individual languages, the database also contains the most up-to-date language affiliations based on the work of expert linguists. Glottolog was first developed and maintained at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, and between 2015 and 2020 at the Max Planck Institute of Geoanthropology in Jena, Germany. Its main curators include Harald Hammarström and Martin Haspelmath. Overview Sebastian Nordhoff and Harald Hammarström established the Glottolog/Langdoc project in 2011. The creation of ''Glottolog'' was partly motivated by the lack of a comprehensive language bibliography, especially in ''Ethnologue''. Glottolog provides a catalogue of the world's languages and language families and a bibliography on individual languages. It differs from ''Ethnologue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtle Island
Turtle Island is a name for Earth or North America, used by some Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indigenous peoples, as well as by some Indigenous rights, Indigenous rights activists. The name is based on a creation myth common to several indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of North America. A number of contemporary works continue to use and/or tell the Turtle Island creation story. Lenape The Lenape story of the "Great Turtle" was first recorded by Europeans between 1678 and 1680 by Jasper Danckaerts. Iroquois mythology, The story is shared by other Northeastern Woodlands tribes, notably the Iroquois, Iroquois peoples. The Lenape believe that before creation there was nothing, an empty dark space. However, in this emptiness, there existed a spirit of their creator, Kishelamàkânk. Eventually in that emptiness, he fell asleep. While he slept, he dreamt of the world as we know it today, the Earth with mountains, forests, and animals. He also dreamt up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
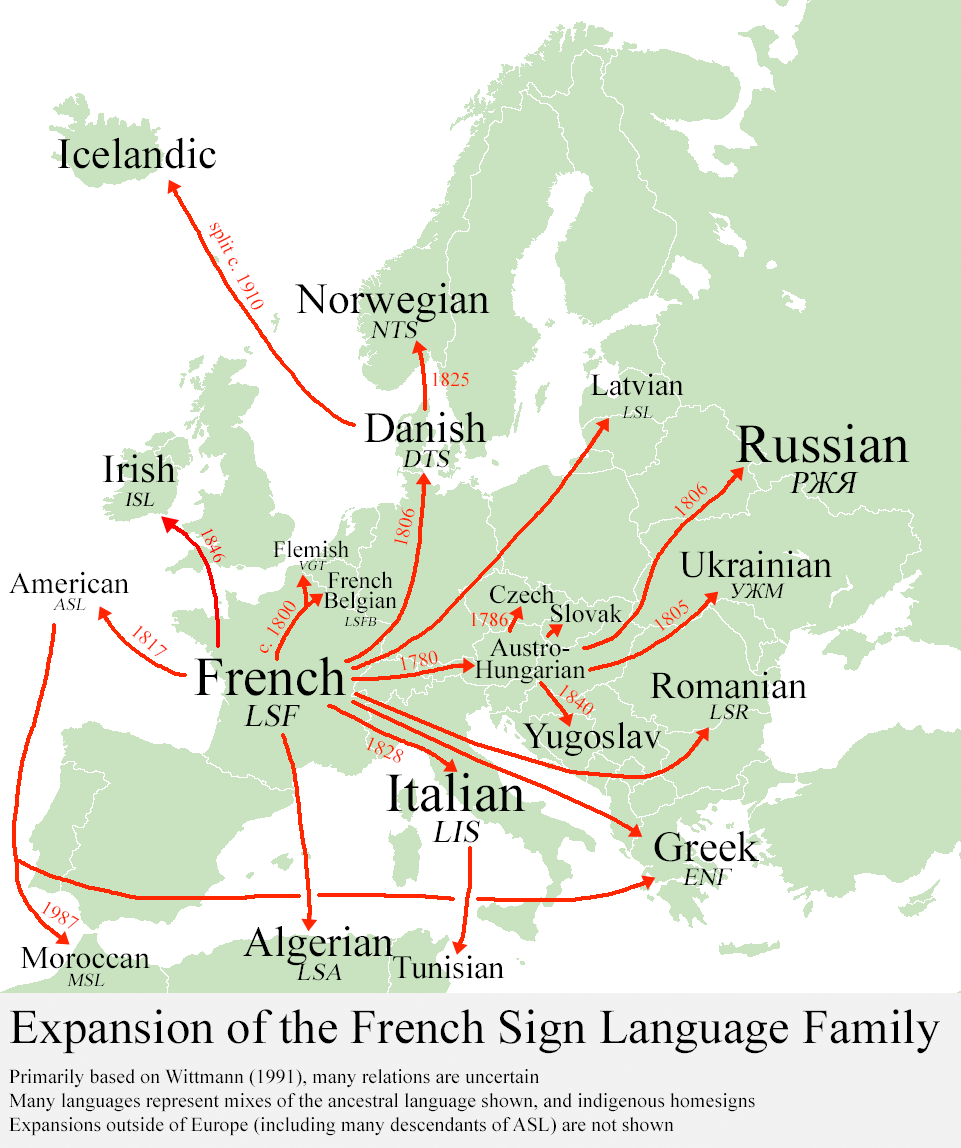
Francosign Languages
The French Sign Language (LSF, from ) or Francosign family is a language family of sign languages which includes French Sign Language and American Sign Language. The LSF family descends from Old French Sign Language (VLSF), which developed among the deaf community in Paris. The earliest mention of Old French Sign Language is by the abbé Charles-Michel de l'Épée in the late 18th century, but it could have existed for centuries prior. Several European sign languages, such as Russian Sign Language, derive from it, as does American Sign Language, established when French educator Laurent Clerc taught his language at the American School for the Deaf. Others, such as Spanish Sign Language, are thought to be related to French Sign Language even if they are not directly descendent from it. Language family tree Anderson (1979) Anderson (1979) postulated the following classification of LSF and its relatives, with derivation from Medieval monks' sign systems, though some lineages are ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, and South America to the south, it comprises numerous List of Caribbean islands, islands, cays, islets, reefs, and banks. It includes the Lucayan Archipelago, Greater Antilles, and Lesser Antilles of the West Indies; the Quintana Roo Municipalities of Quintana Roo#Municipalities, islands and Districts of Belize#List, Belizean List of islands of Belize, islands of the Yucatán Peninsula; and the Bay Islands Department#Islands, Bay Islands, Miskito Cays, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina, Corn Islands, and San Blas Islands of Central America. It also includes the coastal areas on the Mainland, continental mainland of the Americas bordering the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America after Guatemala and Honduras. Nicaragua is bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean and shares maritime borders with El Salvador to the west and Colombia to the east. The country's largest city and national capital is Managua, the List of largest cities in Central America#Largest cities proper, fourth-largest city in Central America, with a population of 1,055,247 as of 2020. Nicaragua is known as "the breadbasket of Central America" due to having the most fertile soil and arable land in all of Central America. Nicaragua's multiethnic population includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European, and African heritage. The country's most spoken language is Spanish language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Washabaugh
William Washabaugh (born January 14, 1945) is professor emeritus of anthropology at the University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee. He has pursued studies of Creole languages, Sign languages of the Deaf, flamenco artistry, sport fishing, and cinema. Research interests William Washabaugh has produced works of critical scholarship in linguistics and popular culture. His studies of the Creole language of Providence islanders and of the Sign language of Deaf islanders raised doubts about prevailing views of linguistic variation. Whereas the dominant opinion in studies of Creole variation had emphasized universal constraints, the Providence case, as published in the flagship journal ''Language'' (1977), demonstrated that other forces, external to language, bear on that variation. In ''Five Fingers for Survival: A Deaf Sign Language in the Caribbean'' (1986), Washabaugh found reasons to question the dominant assumption that the vernacular signing of the Deaf is guided by universal acquisiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Languages Of Colombia
A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or medical symptoms a sign of disease. A conventional sign signifies by agreement, as a full stop signifies the end of a sentence; similarly the words and expressions of a language, as well as bodily gestures, can be regarded as signs, expressing particular meanings. The physical objects most commonly referred to as signs (notices, road signs, etc., collectively known as signage) generally inform or instruct using written text, symbols, pictures or a combination of these. The philosophical study of signs and symbols is called semiotics; this includes the study of semiosis, which is the way in which signs (in the semiotic sense) operate. Nature Semiotics, epistemology, logic, and philosophy of language are concerned about the nature of sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |