|
Protozoan Infection
Protozoan infections are parasitic diseases caused by organisms formerly classified in the kingdom Protozoa. These organisms are now classified in the supergroups Excavata, Amoebozoa, Harosa (SAR supergroup), and Archaeplastida. They are usually contracted by either an insect vector or by contact with an infected substance or surface. Protozoan infections are responsible for diseases that affect many different types of organisms, including plants, animals, and some marine life. Many of the most prevalent and deadly human diseases are caused by a protozoan infection, including African sleeping sickness, amoebic dysentery, and malaria. The species originally termed "protozoa" are not closely related to each other and only have superficial similarities (eukaryotic, unicellular, motile, though with exceptions). The terms "protozoa" and "protist" are usually discouraged in modern biosciences. However, this terminology is still encountered in medicine. This is partially because of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
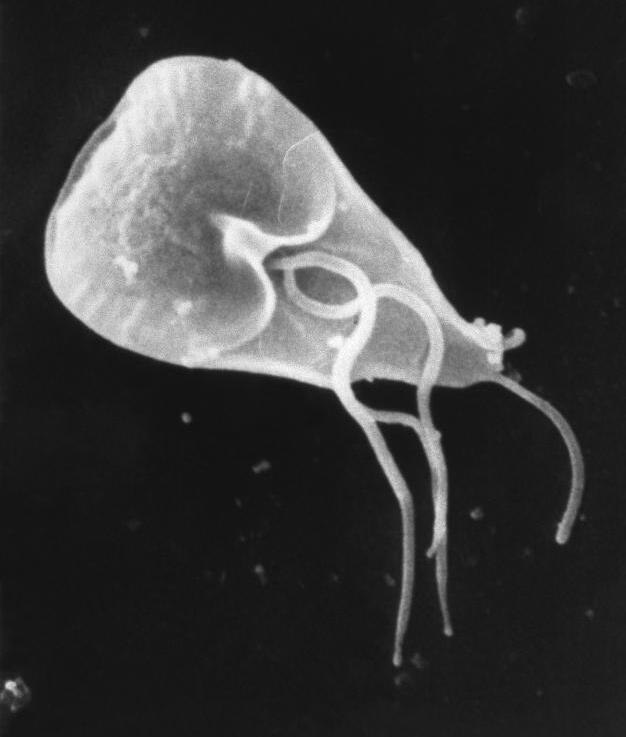
Giardia Lamblia SEM 8698 Lores
''Giardia'' ( or ) is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing the disease giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates between a binucleated motile trophozoite and an infective, metabolically inert, environmentally resistant tetranucleate cyst. Cysts are transmitted between hosts through the fecal-oral route, contaminated water and/or food. ''Giardia'' were first seen by the Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1681 under the light microscope. The genus is named after French zoologist Alfred Mathieu Giard. Characteristics ''Giardia'' trophozoites are 12–15 μm long and 5–9 μm wide and have a shape of a pear bisected lengthwise. Like other diplomonads, ''Giardia'' has two transcriptionally operational nuclei that contain an equal number of well-defined chromosomes and replicate synchronously with the cell division. The cytoskeleton of ''Giarida'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have been proposed to define what an organism is. Among the most common is that an organism has autonomous reproduction, Cell growth, growth, and metabolism. This would exclude viruses, despite the fact that they evolution, evolve like organisms. Other problematic cases include colonial organisms; a colony of eusocial insects is organised adaptively, and has Germ-Soma Differentiation, germ-soma specialisation, with some insects reproducing, others not, like cells in an animal's body. The body of a siphonophore, a jelly-like marine animal, is composed of organism-like zooids, but the whole structure looks and functions much like an animal such as a jellyfish, the parts collaborating to provide the functions of the colonial organism. The evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
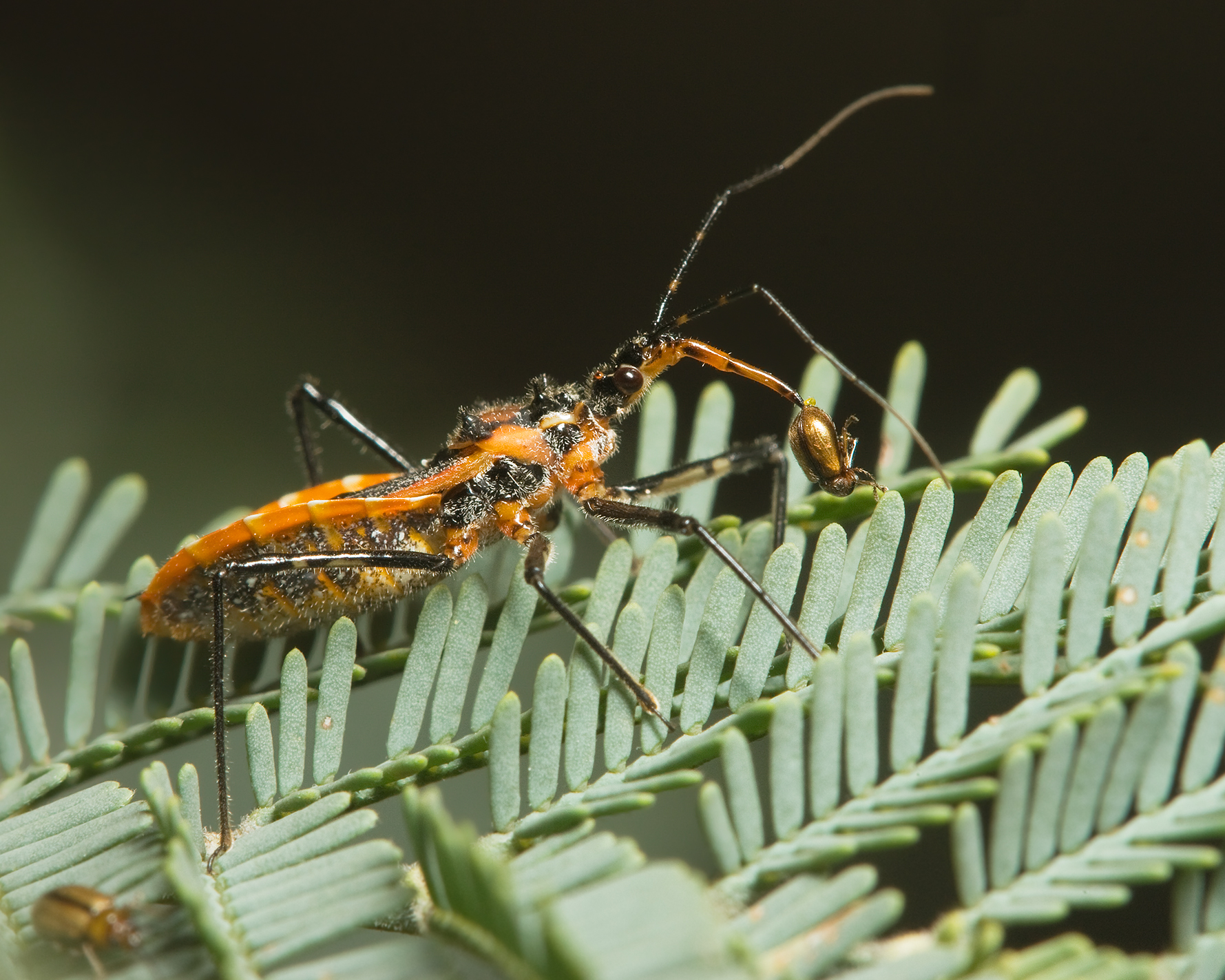
Reduviid Bug, Vohimana Reserve, Madagascar (13950547197)
The Reduviidae is a large cosmopolitan family of the suborder Heteroptera of the order Hemiptera (true bugs). Among the Hemiptera and together with the Nabidae almost all species are terrestrial ambush predators; most other predatory Hemiptera are aquatic. The main examples of non-predatory Reduviidae are some blood-sucking ectoparasites in the subfamily Triatominae, with a few species from South America noted for their ability to transmit Chagas disease. Though spectacular exceptions are known, most members of the family are fairly easily recognizable: they have a relatively narrow neck, sturdy build, and formidable curved proboscis (sometimes called a rostrum). Large specimens should be handled with caution, if at all, because they sometimes defend themselves with a very painful stab from the proboscis. Taxonomy The family members are almost all predatory, except for a few blood-sucking species, some of which are important as disease vectors. About 7000 species have been describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leishmania Braziliensis Peru
''Leishmania'' () is a genus of parasitic protozoans, single-celled eukaryotic organisms of the trypanosomatid group that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. The parasites are transmitted by sandflies of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' in the Old World, and of the genus ''Lutzomyia'' in the New World. There are 53 species and about 20 of them are responsible for human infections. They are transmitted by around 100 species of sandflies. The primary hosts are vertebrates. They commonly infect hyraxes, canids, rodents, and humans. History Members of an ancient genus of ''Leishmania''-like parasites, ''Paleoleishmania'', have been detected in fossilized sand flies dating back to the early Cretaceous period. The first written reference to the conspicuous symptoms of cutaneous leishmaniasis surfaced in the Paleotropics within oriental texts dating back to the 7th century BC (allegedly transcribed from sources several hundred years older, between 1500 and 2000 BC). Due to its br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pellicle (biology)
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals". When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss, in 1818, the taxon Protozoa was erected as a class within the Animalia, with the word 'protozoa' meaning "first animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. This classification remained widespread in the 19th and early 20th century, and even became elevated to a variety of higher ranks, including phylum, subkingdom, kingdom, and then sometimes included within the paraphyletic Protoctista or Protista. By the 1970s, it became usual to require that all taxa be monophyletic (derived from a common ancestor that would also be regarded as protozo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemoorganotroph
Primary nutritional groups are groups of organisms, divided in relation to the nutrition mode according to the sources of energy and carbon, needed for living, growth and reproduction. The sources of energy can be light or chemical compounds; the sources of carbon can be of organic or inorganic origin. The terms ''aerobic respiration'', '' anaerobic respiration'' and ''fermentation'' (''substrate-level phosphorylation'') do not refer to primary nutritional groups, but simply reflect the different use of possible electron acceptors in particular organisms, such as in aerobic respiration, or nitrate (), sulfate () or fumarate in anaerobic respiration, or various metabolic intermediates in fermentation. Primary sources of energy ''Phototrophs'' absorb light in photoreceptors and transform it into chemical energy. ''Chemotrophs'' release chemical energy. The freed energy is stored as potential energy in ATP, carbohydrates, or proteins. Eventually, the energy is used for life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototroph
Phototrophs () are organisms that carry out photon capture to produce complex organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates) and acquire energy. They use the energy from light to carry out various cellular metabolic processes. It is a list of common misconceptions, common misconception that phototrophs are obligatorily photosynthetic. Many, but not all, phototrophs often photosynthesize: they anabolism, anabolically convert carbon dioxide into organic material to be utilized structurally, functionally, or as a source for later catabolism, catabolic processes (e.g. in the form of starches, sugars and fats). All phototrophs either use electron transport chains or direct proton pumping to establish an electrochemical gradient which is utilized by ATP synthase, to provide the molecular energy currency for the cell. Phototrophs can be either autotrophs or heterotrophs. If their electron and hydrogen donors are inorganic compounds (e.g., , as in some purple sulfur bacteria, or , as in some gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichomonas Vaginalis
''Trichomonas vaginalis'' is an Anaerobic organism, anaerobic, flagellated protozoan parasite and the causative agent of a Sexually transmitted infection, sexually transmitted disease called trichomoniasis. It is the most common pathogenic protozoan that infects humans in industrialized countries. Infection rates in men and women are similar but women are usually symptomatic, while infections in men are usually asymptomatic. Transmission usually occurs via direct, skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual, most often through vaginal intercourse. It is estimated that 160 million cases of infection are acquired annually worldwide. The estimates for North America alone are between 5 and 8 million new infections each year, with an estimated rate of asymptomatic cases as high as 50%. Usually treatment consists of either metronidazole or tinidazole. More recent studies on Trichomonas vaginalis have shed light on the parasite’s evolution, genomic complexity, and pathogenesis proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritrichomonas Foetus (259 26) Cultured
''Tritrichomonas'' is a genus of single celled flagellated parasitic excavates, some of whose species are known to be pathogens of the bovine reproductive tract as well as the intestinal tract of felines. Species Example species within the genus ''Tritrichomonas'' are '' T. augusta'' and '' T. foetus'', the latter of which characteristically interacts with bacteria that reside in the intestinal tract by adhering to the intestinal epithelium of the host. ''T. augusta'' have been observed in the rough-skinned newt, ''Taricha granulosa'', in certain northern California Northern California (commonly shortened to NorCal) is a geocultural region that comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California, spanning the northernmost 48 of the state's List of counties in California, 58 counties. Northern Ca ... coastal counties in the United States.C.M. Hogan, 2008 References * K. Hausmann, N. Hülsmann and R. Radek (2003) ''Protistology'' 3rd completely revised edition, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabasalid
The parabasalids are a group of flagellated protists within the supergroup Excavata. Most of these eukaryotic organisms form a symbiosis, symbiotic relationship in animals. These include a variety of forms found in the intestines of termites and cockroaches, many of which have symbiotic bacteria that help them digest cellulose in woody plants. Other species within this supergroup are known parasites, and include human pathogens. Characteristics The flagella are arranged in one or more clusters near the anterior of the cell. Their basal bodies are linked to parabasal fibers that are associated with a prominent Golgi apparatus, Golgi complex, together forming a parabasal apparatus distinctive to the group. Attachment of a parabasal fiber to the first Golgi cisterna by thin filaments has been reported in ''Tritrichomonas foetus''. Usually they also give rise to a sheet of cross-like microtubules that runs down the center of the cell and in some cases projects past the end. This i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophozoite
A trophozoite (G. ''trope'', nourishment + ''zoon'', animal) is the activated, feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoa such as malaria-causing ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and those of the ''Giardia'' group. The complementary form of the trophozoite state is the thick-walled microbial cyst, cyst form. They are often different from the cyst stage, which is a protective, dormant form of the protozoa. Trophozoites are often found in the host's body fluids and tissues and in many cases, they are the form of the protozoan that causes disease in the host. In the protozoan, ''Entamoeba histolytica'' it invades the intestinal mucosa of its host, causing dysentery, which aid in the trophozoites traveling to the liver and leading to the production of hepatic abscesses. Life cycle stages ''Plasmodium falciparium'' The causative organism of malaria is a protozoan, ''Plasmodium falciparium'', that is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito, ''Anopheles'' mosquito. Malaria is reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giardia Intestinalis
''Giardia duodenalis'', also known as ''Giardia intestinalis'' and ''Giardia lamblia'', is a flagellated parasitic protozoan microorganism of the genus ''Giardia'' that colonizes the small intestine, causing a diarrheal condition known as giardiasis. The parasite attaches to the intestinal epithelium by a ventral disc (''syn''. adhesive disc or sucker), and reproduces via binary fission. ''G. duodenalis'' is a non-invasive parasite, that does not spread to other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, but remains confined to the lumen of the small intestine. The parasite exists in two forms; trophozoites and cysts. The microorganism can undergo encystation, transforming into a dormant cyst that enables it to survive outside of its host. ''Giardia'' trophozoites are anaerobic, and absorb their nutrients from the intestinal lumen. If the organism is stained, its characteristic pattern resembles the familiar " smiley face" symbol. Chief pathways of human infection include ingestio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |