|
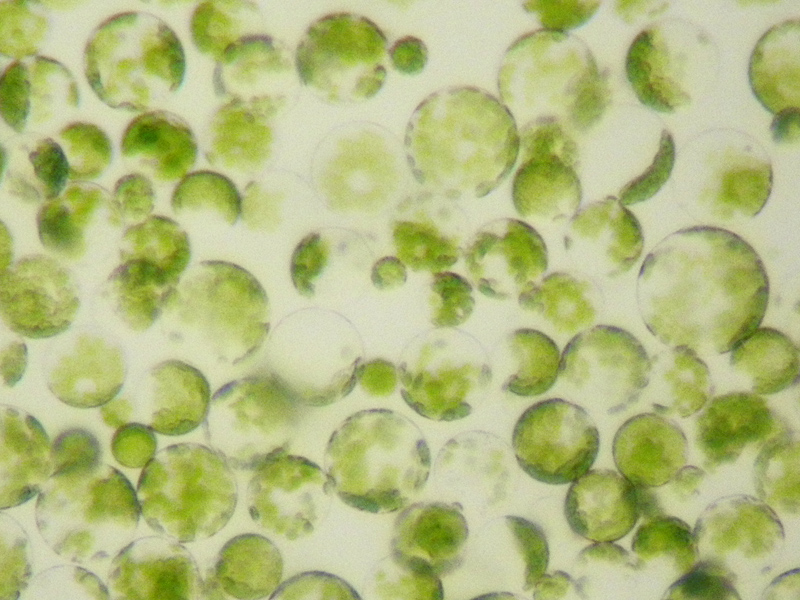
Protoplasmic
Protoplasm (; ) is the living part of a cell that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is a mixture of small molecules such as ions, monosaccharides, amino acid, and macromolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, etc. In some definitions, it is a general term for the cytoplasm (e.g., Mohl, 1846), but for others, it also includes the nucleoplasm (e.g., Strasburger, 1882). For Sharp (1921), "According to the older usage the extra-nuclear portion of the protoplast 'the entire cell, excluding the cell wall''was called "protoplasm," but the nucleus also is composed of protoplasm, or living substance in its broader sense. The current consensus is to avoid this ambiguity by employing Strasburger's '(1882)''terms cytoplasm Kölliker (1863), originally as synonym for protoplasm''and nucleoplasm ( 'term coined by van Beneden (1875), or''karyoplasm, [''used by''">Edouard Van Beneden">van Beneden (1875), or''">'term coined by Edouard Van Beneden">van Beneden (1875), or''karyopla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexico
Lexico was a dictionary website that provided a collection of English and Spanish dictionaries produced by Oxford University Press (OUP), the publishing house of the University of Oxford. While the dictionary content on Lexico came from OUP, this website was operated by Dictionary.com, whose eponymous website hosts dictionaries by other publishers such as Random House. The website was closed and redirected to Dictionary.com on 26 August 2022. Before the Lexico site was launched, the ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' and ''New Oxford American Dictionary'' were hosted by OUP's own website Oxford Dictionaries Online (ODO), later known as Oxford Living Dictionaries. The dictionaries' definitions have also appeared in Google Dictionary, Google definition search and the Dictionary (software), Dictionary application on macOS, among others, licensed through the Oxford Dictionaries application programming interface, API. History In the 2000s, OUP allowed access to content of the ''Compac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Félix Dujardin
Félix Dujardin (5 April 1801 – 8 April 1860) was a French biologist born in Tours. He is remembered for his research on protozoans and other invertebrates. Biography In 1840 he was appointed professor of geology and mineralogy at the University of Toulouse, and during the following year was a professor of zoology and botany at Rennes. In regard to his educational background, Dujardin was largely self-taught, the son of a watchmaker. Dujardin worked with microscopic animal life, and in 1834 proposed that a new group of one-celled organisms be called Rhizopoda. He denied naturalist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg's theory that microscopic organisms were "complete organisms" similar to higher animals, specifically noting that they had specialized structures unique to single-celled organisms, which meant that foraminifera he was studying was not, as his contemporaries believed it to be, a mollusk. In addition to his studies of microscopic life, he did extensive research on in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Bütschli
Johann Adam Otto Bütschli (3 May 1848 – 2 February 1920) was a German zoologist and professor at the University of Heidelberg. He specialized in invertebrates and insect development. Many of the groups of protists were first recognized by him. Life Bütschli was born Frankfurt am Main. He studied mineralogy, chemistry, and paleontology in Karlsruhe and became assistant of Karl Alfred von Zittel (geology and paleontology). He moved to Heidelberg in 1866 and worked with Robert Bunsen (chemistry). He received his PhD from the University of Heidelberg in 1868, after passing examinations in geology, paleontology, and zoology. He joined Rudolf Leuckart at the University of Leipzig in 1869. After leaving his studies to serve as an officer in the Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871), Bütschli worked in his private laboratory and then for two years (1873–1874) with Karl Möbius at the University of Kiel. After that, he worked privately. In 1876, he made Habilitation. He became profes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsomes
In cell biology, microsomes are heterogeneous vesicle-like artifacts (~20-200 nm diameter) re-formed from pieces of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) when eukaryotic cells are broken-up in the laboratory; microsomes are not present in healthy, living cells. Rough (containing ribosomes) and smooth (without ribosomes) microsomes are made from the endoplasmic reticulum through cell disruption. These microsomes have an inside that is exactly the same as the endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Both forms of microsomes can be purified by a process known as equilibrium density centrifugation. Rough and smooth microsomes do differ in their proteins and rough microsomes have shown occurrence of translation and translocation at the same time besides certain exceptions from proteins in yeast. Signal Hypothesis Microsomes play a role in the signal hypothesis. This hypothesis explores in vitro protein translation for a mRNA encoding secretory protein. When microsomes are present, the proteins s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplast
Protoplast (), is a biological term coined by Hanstein in 1880 to refer to the entire cell, excluding the cell wall. Protoplasts can be generated by stripping the cell wall from plant, bacterial, or fungal cells by mechanical, chemical or enzymatic means. Protoplasts differ from spheroplasts in that their cell wall has been completely removed. Spheroplasts retain part of their cell wall. In the case of Gram-negative bacterial spheroplasts, for example, the peptidoglycan component of the cell wall has been removed but the outer membrane component has not. Enzymes for the preparation of protoplasts Cell walls are made of a variety of polysaccharides. Protoplasts can be made by degrading cell walls with a mixture of the appropriate polysaccharide-degrading enzymes: During and subsequent to digestion of the cell wall, the protoplast becomes very sensitive to osmotic stress. This means cell wall digestion and protoplast storage must be done in an isotonic solution to preve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaloplasm
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutoplasm
The deutoplasm comprises the food particles stored in the cytoplasm of an ovum or a cell, as distinguished from protoplasm, the yolk substance. Generally, the deutoplasm accumulates about the nucleus and is heavier than the surrounding cytoplasm. In chicken egg Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...s, the cytoplasm and deutoplasm are separate. References Cell biology {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaplasm
A metaplasm is generic term for almost any kind of alteration, whether intentional or unintentional, in the pronunciation or the orthography of a word. The change may be phonetic only, such as pronouncing ''Mississippi'' as ''Missippi'' in English, or acceptance of a new word structure, such as the transformation from ''calidus'' in Latin to ''caldo'' (hot) in Italian. Orthographic metaplasms have been used in philosophy to advance humanity's conceptual terrain, such as when Derrida adapted Heidegger's Destruktion into deconstruction or the French term ''différence'' into différance. Changes at either level may or may not be recognized in standard spelling, depending on the orthographic traditions of the language in question. Originally the term referred to techniques used in Ancient Greek and Latin poetry, or processes in those languages' grammar. Sound change Many phonological changes found frequently in the natural development of languages are metaplasms: * Epenthesis, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cienkowski
Lev Semyonovich Tsenkovsky (Leon Cienkowski, russian: Лев Семенович Ценковский) (October 1 ( N.S. October 13), 1822 in Warsaw – September 25 (N.S. October 7), 1887 in Leipzig) was a Polish botanist, protozoologist, bacteriologist, who was mostly active in Ukraine, then part of the Russian Empire. He was a corresponding member of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1881). Lev Tsenkovsky graduated from Saint Petersburg University in 1844. As a professor, he taught at the Demidov Lyceum in Yaroslavl (1850-1854), Saint Petersburg University, Novorossiysk University in Odessa (1865-1871), and Kharkov University (1872-1887). Lev Tsenkovsky was one of the pioneers of the ontogenetic method of studying lower plants and lower animals. Also, he was developing a concept on genetic unity of flora and fauna. Tsenkovsky was one of the advocates of the teachings of Charles Darwin. He is known to have suggested methods of developing an effective anthrax vaccine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |