|
Proto-Tupari
The Tuparí languages of Brazil form a branch of the Tupian language family. Internal classification The Tupari languages are:Nikulin, Andrey; Fernando O. de Carvalho. 2019Estudos diacrônicos de línguas indígenas brasileiras: um panorama ''Macabéa – Revista Eletrônica do Netlli'', v. 8, n. 2 (2019), p. 255-305.PDF * Tupari ** Makuráp ** Nuclear Tupari *** Akuntsu– Mekéns (Sakirabiá, Waratégaya) *** Tuparí, Kepkiriwát, Wayoró None are spoken by more than a few hundred people. A more recent internal classification by Nikulin & Andrade (2020) is given below:Nikulin, Andrey; Rafael Andrade. 2020The rise and fall of approximants in the Tuparian languages ''Journal of Language Relationship'' 18/4 (2020), pp. 284–319. *Tuparian **'' Makurap'' **Core Tuparian ***Wayoró–Tuparí ****'' Wayoró'' ****'' Tuparí'' ***Corumbiara ****'' Mekéns'' ****'' Akuntsú'' Varieties Below is a list of Tupari language varieties listed by Loukotka (1968), including names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Tupian
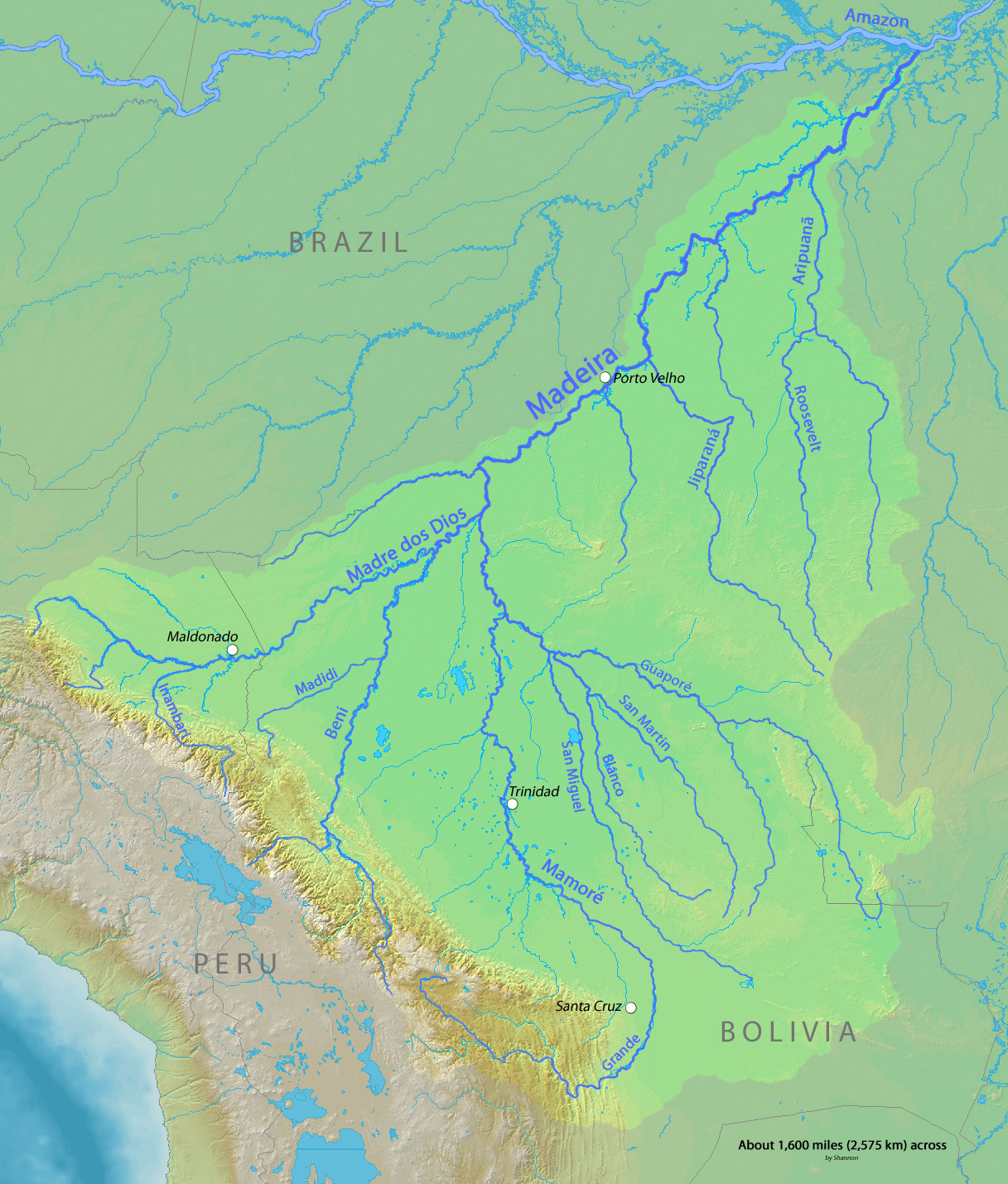
Proto-Tupian (PT) is the reconstructed common ancestor of all the Tupian languages. It consists, therefore, of a hypothetical language, reconstructed by the comparative method from data of the descendant languages. In Brazil, Tupian historical-comparative studies are being developed mainly by two scientific teams: one from the Laboratório de Línguas Indígenas (LALI) of the University of Brasília, under the coordination of Aryon Rodrigues; and the other one from the Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi, located in Belém, under the orientation of Denny Moore. These studies provide evidence about the Proto-Tupian economy and culture, suggesting, for example, that they had agriculture. The most accepted theory is that the Tupian language family originated between the Guaporé and Aripuanã rivers, in the Madeira River basin. There are currently 70 Tupian languages, including Tupi, Paraguayan Guarani, Awetï, Ayvu, etc. Linguistic homeland Rodrigues (2007) considers the Proto-T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupari Language
Tuparí is an indigenous language of Brazil. It is one of six Tupari languages of the Tupian language family. The Tuparí language, and its people, is located predominantly within the state of Rondônia, though speakers are also present in the state of Acre on the Terra Indıgena Rio Branco. There are roughly 350 speakers of this language, with the total number of members of this ethnic group being around 600. Background information Current status Regarding the vitality of the language, the number of speakers indicate that this language is critically endangered, at moribund levels, rating an (8A) on the Ethnologue scale. This has to do with many factors, including the fact that in some communities, for example those living on the Terra Indígena Rio Guaporé, intergenerational transmission has ceased entirely due to a complete shift to Portuguese. History of the language and population This Brazilian state, like many others, was once strictly belonging to indigenous pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population, seventh-largest by population, with over 212 million people. The country is a federation composed of 26 Federative units of Brazil, states and a Federal District (Brazil), Federal District, which hosts the capital, Brasília. List of cities in Brazil by population, Its most populous city is São Paulo, followed by Rio de Janeiro. Brazil has the most Portuguese-speaking countries, Portuguese speakers in the world and is the only country in the Americas where Portuguese language, Portuguese is an Portuguese-speaking world, official language. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazil, coastline of . Covering roughly half of South America's land area, it Borders of Brazil, borders all other countries and ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pimenta Bueno River
The Pimenta Bueno River is a river of Rondônia state in western Brazil. See also *List of rivers of Rondônia List of rivers in Rondônia (States of Brazil, Brazilian State). The list is arranged by drainage basin, with respective tributaries indented under each larger stream's name and ordered from downstream to upstream. Rondônia is located entirely w ... ReferencesBrazilian Ministry of Transport Rivers of Rondônia {{Rondônia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agouti
The agouti (, ) or common agouti is any of several rodent species of the genus ''Dasyprocta''. They are native to Central America, northern and central South America, and the southern Lesser Antilles. Some species have also been introduced elsewhere in the West Indies. They are related to guinea pigs and look quite similar, but they are larger and have longer legs. The species vary considerably in colour, being brown, reddish, dull orange, greyish, or blackish, but typically with lighter underparts. Their bodies are covered with coarse hair, which is raised when alarmed. They weigh and are in length, with short, hairless tails. The related pacas were formerly included in genus ''Agouti'', but these animals were reclassified in 1998 as genus ''Cuniculus''. The Spanish term is ''agutí.'' In Mexico, the agouti is called the '. In Panama, it is known as the ' and in eastern Ecuador, as the '. Etymology The name "agouti" is derived from either Guarani or Tupi, both South Ame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
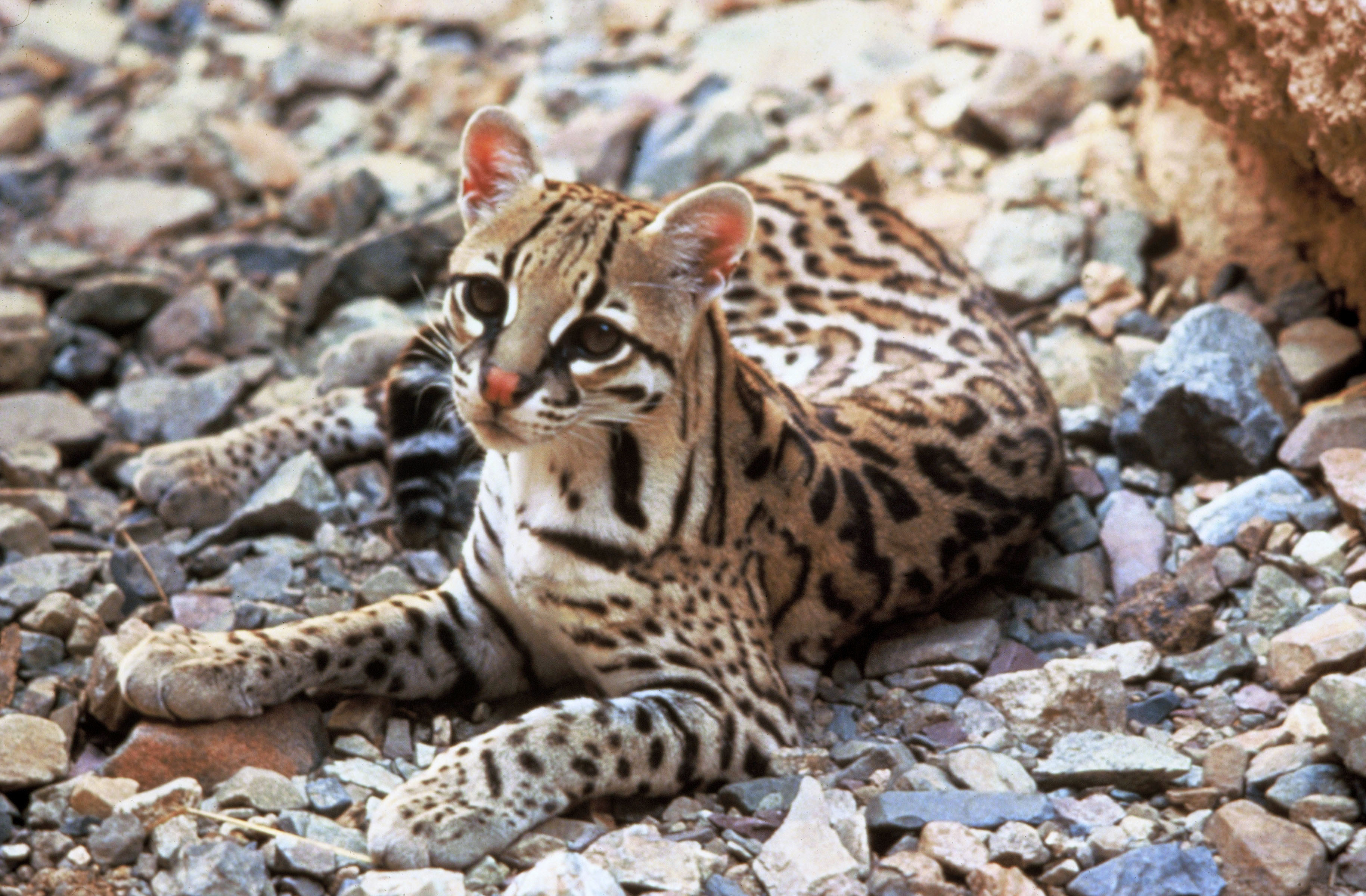
Ocelot
The ocelot (''Leopardus pardalis'') is a medium-sized spotted Felidae, wild cat that reaches at the shoulders and weighs between on average. It is native to the southwestern United States, Mexico, Central America, Central and South America, and the Caribbean islands of Trinidad and Margarita Island, Margarita. Carl Linnaeus scientific description, scientifically described it in 1758. Two subspecies are recognized. The ocelot is efficient at climbing, leaping and swimming. It prefers areas close to water sources with dense vegetation cover and high prey availability. It preys on small terrestrial mammals, such as armadillos, opossums, and lagomorphs. It is typically active during twilight and at night and tends to be solitary and Territory (animal), territorial. Both sexes become sexual maturity, sexually mature at around two years of age and can breed throughout the year; peak mating season varies geographically. After a gestation period of two to three months, the female giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achiote
''Bixa orellana'', also known as achiote, is a shrub or small tree native to Central America. ''Bixa orellana'' is grown in many countries worldwide. The plant is best known as the source of annatto, a natural orange-red condiment (also called or ) obtained from the waxy arils that cover its seeds. The ground seeds are widely used in traditional dishes in Central and South America, Mexico, and the Caribbean, such as ''cochinita pibil'', chicken in , , and . Annatto and its extracts are also used as an industrial food coloring to add yellow or orange color to many products such as butter, cheese, margarine, ice creams, meats, and condiments. Some of the indigenous peoples of North, Central, and South America originally used the seeds to make red body paint and lipstick, as well as a spice. For this reason, the ''Bixa orellana'' is sometimes called the lipstick tree. Etymology and common names The name ''Bixa orellana'' was given by Linnaeus. The botanical genus name derives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillo
Armadillos () are New World placental mammals in the order (biology), order Cingulata. They form part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of environments. Living armadillos are characterized by a leathery armour (anatomy), armor shell and long, sharp claws for digging. They have short legs, but can move quite quickly. The average length of an armadillo is about , including its tail. The giant armadillo grows up to and weighs up to , while the pink fairy armadillo has a length of only . When threatened by a predator, ''Tolypeutes'' species frequently roll up into a ball; they are the only species of armadillo capable of this. Recent genetic research has shown that the megafaunal glyptodonts (up to tall with maximum body masses of around 2 tonnes), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genipap
''Genipa americana'' () is a species of trees in the family Rubiaceae. It is native to the tropical forests of North and South America, as well as the Caribbean. Description ''Genipa americana'' trees are up to 30 m tall and up to 60 cm dbh. Their bark is smooth with little fissures. The leaves are opposite, obovate, or obovate oblong, 10–35 cm long, 6–13 cm wide, and glossy dark green, with entire margin, acute or acuminate apex, and attenuated base. The inflorescences are cymes up to 10 cm long. The flowers are white to yellowish, slightly fragrant, calyx bell-shaped, corolla at 2–4.5 cm long, trumpet-shaped, and five- or six-lobed. The five short stamens are inserted on top of the corolla tube. The fruit is a thick-skinned edible greyish berry 10–12 cm long, 5–9 cm in diameter. Distribution and habitat ''Genipa americana'' is native to the tropical forests of the Americas, from the Caribbean south to Argentina. It is present fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
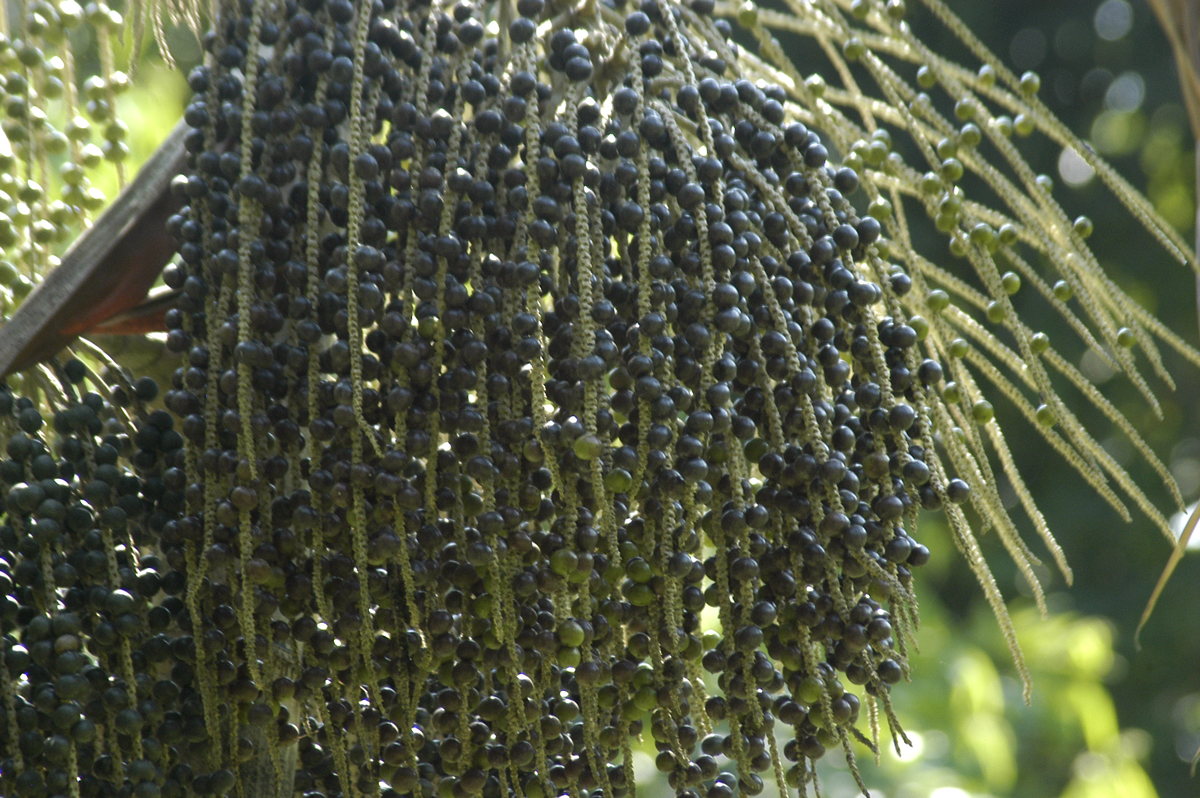
Açaí Palm
The açaí palm (, , from Nheengatu ''asai''), '' Euterpe oleracea'', is a species of palm tree (Arecaceae) cultivated for its fruit (açaí berries, or simply açaí), hearts of palm (a vegetable), leaves, and trunk wood. Global demand for the fruit has expanded rapidly in the 21st century, and the tree is cultivated for that purpose primarily. The species is native to eastern Amazonia, especially in Brazil, mainly in swamps and floodplains. Açaí palms are tall, slender trees growing to more than tall, with pinnate leaves up to long. The fruit is small, round, and black-purple in color. The fruit became a staple food in floodplain areas around the 18th century, but its consumption in urban areas and promotion as a health food only began in the mid-1990s along with the popularization of other Amazonian fruits outside the region. Name The folk etymology says that chief Itaqui ordered all newborns put to death owing to a period of famine. When his own daughter gave birth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil Nut
The Brazil nut (''Bertholletia excelsa'') is a South American tree in the family Lecythidaceae, and it is also the name of the tree's commercially harvested edible seeds. It is one of the largest and longest-lived trees in the Amazon rainforest. The fruit and its nutshell – containing the edible Brazil nut – are relatively large and weigh as much as in total. As food, Brazil nuts are notable for diverse content of micronutrients, especially a high amount of selenium. The wood of the Brazil nut tree is prized for its quality in carpentry, flooring, and heavy construction. Common names In Portuguese-speaking countries, like Brazil, they are variously called "" - Folder EmbrapaCOSTA, J. R. (et al.Uma das espécies nativas mais valiosas da floresta amazônica de terra firme é a castanha-do-brasil ou castanha-da-amazônia (''Bertholletia excelsa'') - Acta Amazônica vol. 39(4) 2009: 843 - 850 (meaning "cashew from Brazil" in Portuguese), "" (meaning "cashew from Pará" in Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |