|
Prothous
In Greek mythology, Prothous (Ancient Greek: Πρόθοος ''Prothoös'') may refer to: *Prothous, an Arcadian prince as one of the 50 sons of the impious King Lycaon either by the naiad Cyllene, Nonacris or by unknown woman. He and his brothers were the most nefarious and carefree of all people. To test them, Zeus visited them in the form of a peasant. These brothers mixed the entrails of a child into the god's meal, whereupon the enraged Zeus threw the meal over the table. Aegaeon was killed, along with his brothers and their father, by a lightning bolt of the god. *Prothous, son of Thestius and brother of Althaea. He was one of the Calydonian Boar Hunters. *Prothous, son of the Aetolian Agrius, killed by Diomedes. *Prothous of Argos, a warrior in the army of the Seven against Thebes. He cast lots to assign places in the chariot race at the funeral games of Opheltes. *Prothous, a defender of Thebes against the Seven, killed by Tydeus. *Prothous, son of Tenthredon and eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thestius
In Greek mythology, Thestius (; Ancient Greek: Θέστιος) was a king of Pleuronians in Aetolia. He is not to be confused with Thespius, who was sometimes referred to as "Thestius". The patronymic "Thestias" may refer to one of his daughters, Leda or Althaea, and "Thestiades" to his son Iphiclus. Family Thestius was the son either of Ares by Demonice or Pisidice,Pseudo-Plutarch, ''De fluviis'22.1/ref> or of Agenor (son of Pleuron) possibly by Epicasta. He was the brother of Evenus, Pylus and Molus or of Demonice and Porthaon instead. Thestius was the father of Iphiclus by Leucippe or Eurythemis, daughter of Cleoboea, who was the mother of his other children, Althaea,Antoninus Liberalis2as cited in Nicander's ''Metamorphoses'' Eurypylus, Evippus, Hypermnestra, Leda and Plexippus. In other sources, the mother of Iphiclus, Althaea and Leda was named either Laophonte, daughter of Pleuron or Deidameia, daughter of Perieres. Other sons of Thestius were Comet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleobule
In Greek mythology, the name Cleobule, Cleoboule, Kleobule or Kleoboule (Ancient Greek: Κλεοβούλη, ''Kleoboúlē'') or Cleobula refers to: *Cleobule, daughter of Aeolus or Aeopolus, one of the possible mothers of Myrtilus by Hermes. *Cleobule, wife of Aleus of Tegea, mother of Cepheus and Amphidamas. *Cleobula, mother by Ares of Cycnus who was killed by Heracles. *Cleobule, mother of Amphimachus by Cteatus instead of Theronice. *Cleobule, mother of Leonteus by Coronus. *Cleobule, daughter of Eurytus and by Tenthredon, possibly the mother of Prothous, leader of the Magnesians during the Trojan War. Otherwise, Eurymache was called the mother of the Prothous. *Cleobule, mother of Phoenix by Amyntor. Otherwise, Hippodameia or Alcimede was called the mother). Cleobule had two other possible children by Amyntor, Asydameia and Crantor. *Cleobule, the Boeotian mother of Leitus by Lacritus; alternately, mother of Arcesilaus by Alector ( Alectryon). Otherwise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurymache
In Greek mythology, Eurymache (Ancient Greek: Εὐρυμάχη) was the mother by Tenthredon of Prothous, leader of the Magnesians during the Trojan War. Otherwise, Prothous's mother was called Kleoboule, daughter of Eurytos.Tzetzes, ''Allegories of the Iliad'' Prologue 635 Notes References * Apollodorus, ''The Library'' with an English Translation by Sir James George Frazer, F.B.A., F.R.S. in 2 Volumes, Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1921. Online version at the Perseus Digital Library. * , ''Fabulae from The Myths of Hyginus'' translated and edited by Mary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
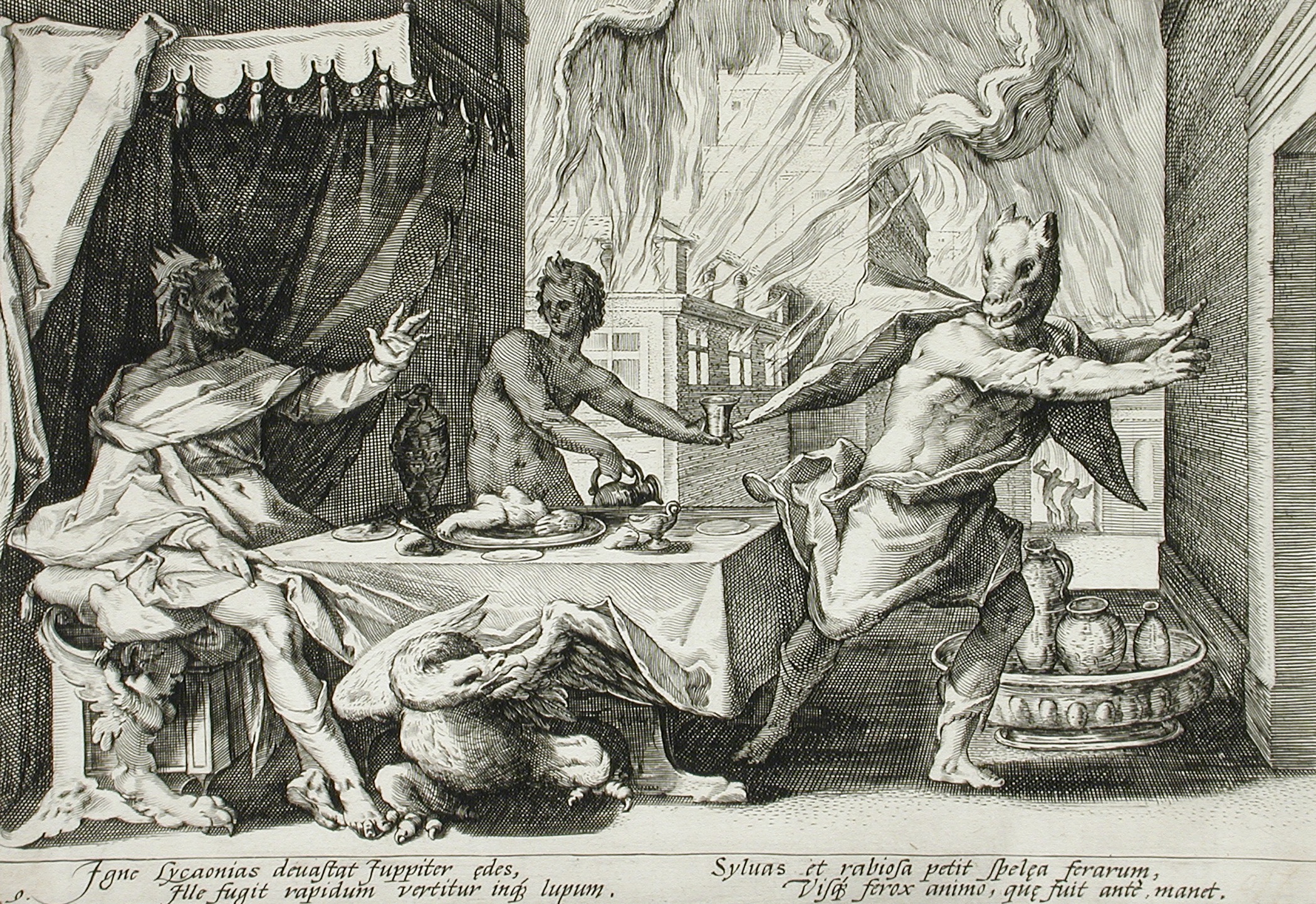
Lycaon Of Arcadia
In Greek mythology, Lycaon (/laɪˈkeɪɒn/; , ) was a king of Arcadia who, in the most popular version of the myth, killed and cooked his son Nyctimus and served him to Zeus, to see whether the god was sufficiently all-knowing to recognize human flesh. Disgusted, Zeus transformed Lycaon into a wolf, while Nyctimus was restored to life. Despite being notorious for his horrific deeds, Lycaon was also remembered as a culture hero: he was believed to have founded the city Lycosura, to have established a cult of Zeus Lycaeus and to have started the tradition of the Lycaean Games, which Pausanias thinks were older than the Panathenaic Games. According to Gaius Julius Hyginus (d. AD 17), Lycaon dedicated the first temple to Hermes of Cyllene. Hyginus, ''Fabulae'225/ref> Family Lycaon was the son of Pelasgus and either the Oceanid Meliboea or Deianira, daughter of an elder Lycaon. His wife was called Cyllene, an Oread nymph who gave her name to Mount Cyllenê though s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurytus
Eurytus, Eurytos (; Ancient Greek: Εὔρυτος) or Erytus (Ἔρυτος) is the name of several characters in Greek mythology, and of at least one historical figure. Mythological *Eurytus, one of the Giants, sons of Gaia, killed by Dionysus during the Gigantomachy, the battle of the Giants versus the Olympian gods. *Eurytus, a chieftain at the court of king Cepheus, and was killed by Perseus during the battle between the latter and Phineus. *Eurytus, king of Caria and the father of Eidothea, who was one of the possible spouses of Miletus. *Eurytus, a centaur present at the wedding of Pirithous and Hippodamia, and the one that caused the conflict between the Lapiths and the Centaurs by trying to carry the bride off. The most violent of the centaurs involved in the battle with the Lapiths, he was killed by Theseus. * Eurytus, king of Oechalia, Thessaly, and father of Iole and Iphitus. *Eurytus, father of Cleobule, mother by Tenthredon of Prothous, leader of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calydonian Boar
The Calydonian boar hunt is one of the great heroic adventures in Greek legend. It occurred in the generation prior to that of the Trojan War, and stands alongside the other great heroic adventure of that generation, the voyage of the Argonauts, which preceded it. The purpose of the hunt was to kill the Calydonian boar (also called the Aetolian boar), which had been sent by Artemis to ravage the region of Calydon in Aetolia, because its king Oeneus had failed to honour her in his rites to the gods. The hunters, led by the hero Meleager, included many of the foremost heroes of Greece. In most accounts it is also concluded that a great heroine, Atalanta, won its hide by first wounding it with an arrow. This outraged many of the men, leading to a tragic dispute. Importance in Greek mythology and art Since the Calydonian boar hunt drew together numerous heroes—among whom were many who were venerated as progenitors of their local ruling houses among tribal groups of Hellenes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenthredon
In Greek mythology, Tenthredon (Ancient Greek: Τενθρηδών) was a son of Hyperochus, son of Haemon, a descendant of Magnes. He was the father of Prothous, leader of the Magnesians during the Trojan War. Tenthredon's wife who bore his son was either Eurymache or Cleobule, daughter of Eurytus.Tzetzes, ''Allegories of the Iliad'' Prologue 635 Notes References * Apollodorus, ''The Library'' with an English Translation by Sir James George Frazer, F.B.A., F.R.S. in 2 Volumes, Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1921. Online version at the Perseus Digital Library. * |
Greek Mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancient Greek religion's view of the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world; the lives and activities of List of Greek deities, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures; and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of mythmaking itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statius
Publius Papinius Statius (Greek language, Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; , ; ) was a Latin poetry, Latin poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid (Latin poem), Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, the ''Silvae''; and an unfinished epic, the ''Achilleid''. He is also known for his appearance as a guide in the ''Purgatorio, Purgatory'' section of Dante Alighieri, Dante's epic poem, the ''Divine Comedy''. Life Family background The poet's father (whose name is unknown) was a native of Velia but later moved to Naples and spent time in Rome where he taught with marked success. From boyhood to adulthood, Statius's father proved himself a champion in the poetic contests at Naples in the Augustalia and in the Nemean, Pythian Games, Pythian, and Isthmian Games, Isthmian games, which served as important events to display poetic skill during the early empire. Statius declares in his lament for his fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebaid (Latin Poem)
The ''Thebaid'' (; ) is a Latin epic poem written by the Roman poet Statius. Published in the early 90s AD, it contains 9748 lines arranged in 12 books, and recounts the clash of two brothers, Eteocles and Polynices, over the throne of the Greek city of Thebes, Greece, Thebes. After Polynices is sent into exile, he forges an alliance of Seven against Thebes, seven Greek princes and embarks on a military campaign against his brother. Although its source material derives predominantly from the Ancient Greek literature, Greek literary tradition, the ''Thebaid'' has close ties with other Latin texts such as Virgil's ''Aeneid'' and Senecan tragedy, the tragedies of Seneca the Younger. The poem's central themes include the relationship between politics and the family, civil war, and the amoral acts to which it gives rise. Critics have also noted the poem's innovative depiction of Roman mythology. Following in the footsteps of Ovid, Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Statius used an episodic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tydeus
Tydeus (; Ancient Greek: Τυδεύς ''Tūdeus'') was an Aetolian hero in Greek mythology, belonging to the generation before the Trojan War. He was one of the Seven against Thebes, and the father of Diomedes, who is frequently known by the patronymic ''Tydides''. Life Tydeus was a son of Oeneus and either Periboea, Oeneus's second wife, or Gorge, Oeneus's daughter. He was the husband of Deipyle, the mother of Diomedes. Tydeus was banished from Calydon by his uncle Agrius because he had killed either his brother or a different uncle or six of his cousins. He travelled to Argos, where he married Deipyle, daughter of king Adrastus. Seven against Thebes Gathering of the Seven While housing Tydeus, King Adrastus of Argos also lodged Polynices, the exiled son of Oedipus who had shared the rule of Thebes with his brother Eteocles before he was expelled by the latter. Late one night, the two young exiles got into a fierce dispute over the guest room in Adrastus's palace. Awake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and was written in dactylic hexameter. It contains 15,693 lines in its most widely accepted version. The ''Iliad'' is often regarded as the first substantial piece of Western literature, European literature and is a central part of the Epic Cycle. Set towards the end of the Trojan War, a ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean Greek states, the poem depicts significant events in the war's final weeks. In particular, it traces the anger () of Achilles, a celebrated warrior, from a fierce quarrel between him and King Agamemnon, to the death of the Trojan prince Hector.Homer, ''Iliad, Volume I, Books 1–12'', translated by A. T. Murray, revised by William F. Wyatt, Loeb Classical Library 170, Cambridge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |