|
Proscenium
A proscenium (, ) is the virtual vertical plane of space in a theatre, usually surrounded on the top and sides by a physical proscenium arch (whether or not truly "arched") and on the bottom by the stage floor itself, which serves as the frame into which the audience observes from a more or less unified angle the events taking place upon the stage (theatre), stage during a theatrical performance. The concept of the fourth wall of the theatre stage space that faces the audience is essentially the same. It can be considered as a Social constructionism, social construct which divides the actors and their stage-world from the audience which has come to witness it. But since the curtain usually comes down just behind the proscenium arch, it has a physical reality when the curtain is down, hiding the stage from view. The same plane also includes the drop, in traditional theatres of modern times, from the stage level to the "stalls" level of the audience, which was the original meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stage (theatre)
In theatre and performing arts, the stage (sometimes referred to as the deck in stagecraft) is a designated space for the performance of theatrical production, productions. The stage serves as a space for actors or performers and a focal point (the Projection screen, screen in movie theater, cinema theaters) for the audience. As an architectural feature, the stage may consist of a platform (often raised) or series of platforms. In some cases, these may be temporary or adjustable but in theater (structure), theaters and other buildings devoted to such productions, the stage is often a permanent feature. There are several types of stages that vary as to the usage and the relation of the audience to them. The most common form found in the West is the proscenium stage. In this type, the audience is located on one side of the stage with the remaining sides hidden and used by the performers and technicians. Thrust stages may be similar to proscenium stages but with a platform or perf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flyspace
A fly system, or theatrical rigging system, is a system of ropes, pulleys, counterweights and related devices within a theater (structure), theater that enables a stage crew to fly (hoist) quickly, quietly and safely components such as curtains, lights, theatrical scenery, scenery, stage effects and, sometimes, people. Systems are typically designed to fly components between clear view of the audience and out of view, into the large space, the fly loft, above the stage (theatre), stage. Fly systems are often used in conjunction with other theatre systems, such as scenery wagons, stage lifts and stage turntables, to physically manipulate the mise en scène. Theatrical rigging is most prevalent in proscenium theatres with stage houses designed specifically to handle the significant dead and live loads associated with fly systems. building code, Building, Occupational Safety and Health Administration, occupational safety, and Fire safety#Fire code, fire codes limit the types and qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Wall
The fourth wall is a performance dramatic convention, convention in which an invisible, imaginary wall separates actors from the audience. While the audience can see through this "wall", the convention assumes the actors act as if they cannot. From the 16th century onward, the rise of illusionism in staging practices, which culminated in the realism (theatre), realism and naturalism (theatre), naturalism of the Nineteenth-century theatre, theatre of the 19th century, led to the development of the fourth wall concept. The metaphor suggests a relationship to the mise-en-scène behind a proscenium, proscenium arch. When a scene is set indoors and three of the walls of its room are presented onstage, in what is known as a Box set (theatre), box set, the fourth of them would run along the line (technically called the proscenium) dividing the room from the auditorium. The ''fourth wall'', though, is a theatrical convention, rather than of set design. The actors ignore the audience, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre In The Round
Theatre-in-the-round, also known as arena theatre or central staging, is a theatrical stage configuration in which the audience surrounds the performance area on all sides. Historically rooted in ancient Greece and Rome performance practices, the format was reintroduced and popularized in the mid-20th century through pioneering venues like the Glenn Hughes Penthouse Theatre in Seattle, Washington. It opened on May 19, 1940, with a production of ''Spring Dance'', a comedy by playwright Philip Barry. The 160-seat theatre is located on the campus of the University of Washington and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. In 1947, Margo Jones founded America's first professional theatre-in-the-round company wit the opening of Theater '47 in Dallas. Her stage design approach was later adopted by directors for productions such as '' Fun Home'', the original stage production of '' Man of La Mancha,'' and all plays staged at the ANTA Washington Square Theatre (which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teatro Farnese
Teatro Farnese is a Renaissance Theater (structure), theatre in the Palazzo della Pilotta, Parma, Italy. It was built in 1618 by Giovanni Battista Aleotti. The idea of creating this grand theater came from the Duke of Parma and Piacenza Ranuccio I Farnese, Duke of Parma, Ranuccio I Farnese. It was part of the complex of the Ducal Palace of Parma. The theatre was almost destroyed by an Allies of World War II, Allied strategic bombing, air raid during World War II (1944). It was rebuilt and reopened in 1962. It is, along with the Teatro all'antica in Sabbioneta and the Teatro Olimpico in Vicenza, one of only three Renaissance theaters still in existence. Some claim this as the first permanent proscenium theatre (that is, a theatre in which the audience views the action through a single frame, which is known as the "proscenium arch").Kuritz, p. 167 References Notes Cited sources *King, Kimball''Western Drama Through the Ages'' Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007. *Kuritz, Paul''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Theatre
A theatrical culture flourished in ancient Greece from 700 BC. At its centre was the city-state of Athens, which became a significant cultural, political, and religious place during this period, and the theatre was institutionalised there as part of a festival called the Dionysia, which honoured the god Dionysus. Tragedy (late 500 BC), comedy (490 BC), and the satyr play were the three dramatic genres emerged there. Athens exported the festival to its numerous colonies. Modern Western theatre comes, in large measure, from the theatre of ancient Greece, from which it borrows technical terminology, classification into genres, and many of its themes, stock characters, and plot elements. Etymology The word , from which the word "tragedy" is derived, is a compound of two Greek words: or "goat" and meaning "song", from . This etymology indicates a link with the practices of the ancient Dionysian cults. It is impossible, however, to know with certainty how these fertility rituals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from the early 17th century until the 1750s. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassicism, Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran art#Baroque period, Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep color, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to the rest of Italy, France, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, Poland and Russia. By the 1730s, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballets De Cour
''Ballet de cour'' ("court ballet") is the name given to ballets performed in the 16th and 17th centuries at courts. The court ballet was a gathering of noblemen and women, as the cast and audience were largely supplied by the ruling class. The festivities, which were descendants of festivals, processions and mummeries dating back to the Middle Ages, looked more like a modern-day parade, than what people today would identify as a ballet performance. Where early court ballet differed from its predecessors, is that it was a secular, not religious happening. It was a carefully crafted mixture of art, socializing, and politics, with its primary objective being to exalt the State. Because these celebrations occurred long before the proscenium stage had been invented, and were instead executed in large halls with audience members stacked up on three sides of the performance, early court ballet's choreography was constructed as a series of patterns and geometric shapes that were intende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
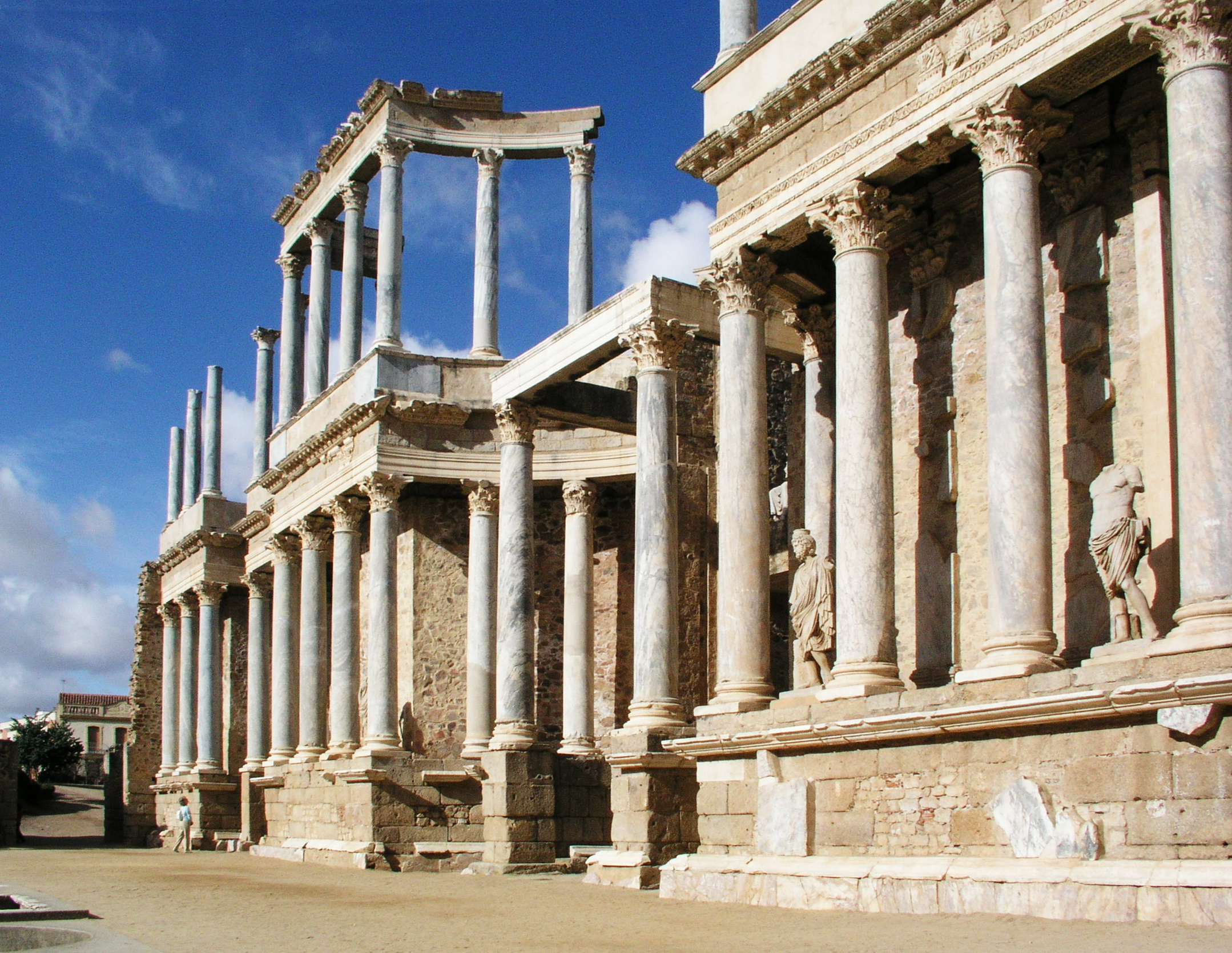
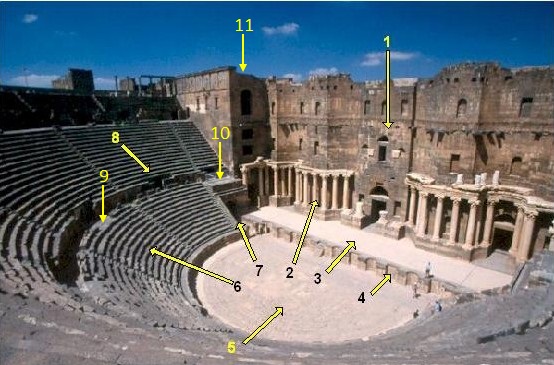
Roman Theatre (structure)
Roman theatres derive from and are part of the overall evolution of earlier Ancient Greek theatre (structure), Greek theatres. Much of the architectural influence on the Romans came from the Greeks, and theatre structural design was no different from other buildings. However, Roman theatres have specific differences, such as generally being built upon their own foundations instead of earthen works or a hillside and being completely enclosed on all sides. Architecture Roman theatres were built in all areas of the Roman Empire, Empire, from Spain to the Middle East. Because of the Romans' ability to influence local architecture, we see numerous theatres around the world with uniquely Roman attributes. Similarities exist between the theatres and Roman amphitheater, amphitheaters of ancient Rome. They were constructed out of the same material, Roman concrete, and provided a place for the public to go and see numerous events. However, they are two entirely different structures, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Stage
In theatre, a thrust stage (a platform stage or open stage) is one that extends into the audience on three sides and is connected to the backstage area by its upstage end. A thrust has the benefit of greater intimacy between performers and the audience than a proscenium, while retaining the utility of a backstage area. This is in contrast to a theatre in the round, which is exposed on all sides to the audience, is without a backstage, and relies entirely on entrances in the auditorium or from under the stage. Entrances onto a thrust are most readily made from backstage, although some theatres provide for performers to enter through the audience using vomitory entrances. As with an arena, the audience in a thrust stage theatre may view the stage from three or more sides. Because the audience can view the performance from a variety of perspectives, it is usual for the blocking, props and scenery to receive thorough consideration to ensure that no perspective is blocked from vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proskenion
In the theatre of ancient Greece, the ''skene'' was the structure at the back of a stage. The word means 'tent' or 'hut', and it is thought that the original structure for these purposes was a tent or light building of wood and was a temporary structure. It was initially a very light structure or just cloth hanging from a rope, but over the course of time the ''skene'' underwent fundamental changes. First, it became a permanent building, whose roof could sometimes be used to make speeches, and as time passed it was raised up from the level of the orchestra, creating a , or "space in front of the ". The facade of the was behind the orchestra and provided a space for supporting stage scenery. During the Roman Period, the had become a large and complex, elaborately decorated, stone building on several levels. Actors emerged from the '' parodoi'' and could use its steps and balconies to speak from. It was also where costumes were stored and to which the '' periaktoi'' (pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teatro Olimpico
The ("Olympic Theatre") is a theatre in Vicenza, northern Italy, constructed in 1580–1585. It was the final design by the Italian Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio and was not completed until after his death. The ''trompe-l'œil'' onstage scenery, designed by Vincenzo Scamozzi to give the appearance of long streets receding to a distant horizon, was installed in 1585 for the first performance held in the theatre, and is the oldest surviving theatrical scenery, stage set still in existence. The full Roman-style ''scaenae frons'' back screen across the stage is made from wood and stucco imitating marble. It was the home of the Accademia Olimpica, which was founded there in 1555. The is, along with the Teatro all'antica in Sabbioneta and the Teatro Farnese in Parma, one of only three Renaissance theatres remaining in existence. Both these theatres were based, in large measure, on the . It is still used several times a year. Since 1994 the , together with other Palladian bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |