|
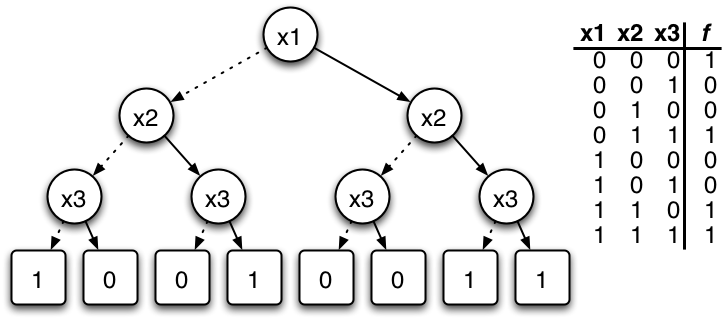
Propositional Directed Acyclic Graph
A propositional directed acyclic graph (PDAG) is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. A Boolean function can be represented as a rooted, directed acyclic graph of the following form: * Leaves are labeled with \top (true), \bot (false), or a Boolean variable. * Non-leaves are \bigtriangleup (logical and), \bigtriangledown (logical or) and \Diamond (logical not). * \bigtriangleup- and \bigtriangledown-nodes have at least one child. * \Diamond-nodes have exactly one child. Leaves labeled with \top (\bot) represent the constant Boolean function which always evaluates to 1 (0). A leaf labeled with a Boolean variable x is interpreted as the assignment x=1, i.e. it represents the Boolean function which evaluates to 1 if and only if x=1. The Boolean function represented by a \bigtriangleup-node is the one that evaluates to 1, if and only if the Boolean function of all its children evaluate to 1. Similarly, a \bigtriangledown-node represents the Boolean function tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Structure
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization and storage format that is usually chosen for Efficiency, efficient Data access, access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the Function (computer programming), functions or Operator (computer programming), operations that can be applied to the data, i.e., it is an algebraic structure about data. Usage Data structures serve as the basis for abstract data types (ADT). The ADT defines the logical form of the data type. The data structure implements the physical form of the data type. Different types of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks. For example, Relational database, relational databases commonly use B-tree indexes for data retrieval, while compiler Implementation, implementations usually use hash tables to look up Identifier (computer languages), identifiers. Data s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Function
In mathematics, a Boolean function is a function whose arguments and result assume values from a two-element set (usually , or ). Alternative names are switching function, used especially in older computer science literature, and truth function (or logical function), used in logic. Boolean functions are the subject of Boolean algebra and switching theory. A Boolean function takes the form f:\^k \to \, where \ is known as the Boolean domain and k is a non-negative integer called the arity of the function. In the case where k=0, the function is a constant element of \. A Boolean function with multiple outputs, f:\^k \to \^m with m>1 is a vectorial or ''vector-valued'' Boolean function (an S-box in symmetric cryptography). There are 2^ different Boolean functions with k arguments; equal to the number of different truth tables with 2^k entries. Every k-ary Boolean function can be expressed as a propositional formula in k variables x_1,...,x_k, and two propositional formulas a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directed Acyclic Graph
In mathematics, particularly graph theory, and computer science, a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a directed graph with no directed cycles. That is, it consists of vertices and edges (also called ''arcs''), with each edge directed from one vertex to another, such that following those directions will never form a closed loop. A directed graph is a DAG if and only if it can be topologically ordered, by arranging the vertices as a linear ordering that is consistent with all edge directions. DAGs have numerous scientific and computational applications, ranging from biology (evolution, family trees, epidemiology) to information science (citation networks) to computation (scheduling). Directed acyclic graphs are also called acyclic directed graphs or acyclic digraphs. Definitions A graph is formed by vertices and by edges connecting pairs of vertices, where the vertices can be any kind of object that is connected in pairs by edges. In the case of a directed graph, each edg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Decision Diagram
In computer science, a binary decision diagram (BDD) or branching program is a data structure that is used to represent a Boolean function. On a more abstract level, BDDs can be considered as a compressed representation of sets or relations. Unlike other compressed representations, operations are performed directly on the compressed representation, i.e. without decompression. Similar data structures include negation normal form (NNF), Zhegalkin polynomials, and propositional directed acyclic graphs (PDAG). Definition A Boolean function can be represented as a rooted, directed, acyclic graph, which consists of several (decision) nodes and two terminal nodes. The two terminal nodes are labeled 0 (FALSE) and 1 (TRUE). Each (decision) node u is labeled by a Boolean variable x_i and has two child nodes called low child and high child. The edge from node u to a low (or high) child represents an assignment of the value FALSE (or TRUE, respectively) to variable x_i. Such a BDD i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negation Normal Form
In mathematical logic, a formula is in negation normal form (NNF) if the negation operator (\lnot, ) is only applied to variables and the only other allowed Boolean operators are conjunction (\land, ) and disjunction (\lor, ). Negation normal form is not a canonical form: for example, a \land (b\lor \lnot c) and (a \land b) \lor (a \land \lnot c) are equivalent, and are both in negation normal form. Definition The following is a context-free grammar for ''NNF'': : where ''Variable'' is any variable. Examples and counterexamples : The following formulae are all in negation normal form: :\begin &((A \lor B) \land C) \\ &(A \lor \lnot B) \\ &(A \land \lnot B) \\ &\ \end The first example is also in conjunctive normal form, the next two are in both conjunctive normal form and disjunctive normal form, but the last example is in neither. The following formulae are not in negation normal form: :\begin (A &\to B) \\ \lnot (A &\lor B) \\ \lnot (A &\land B) \\ \lnot (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Structure
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization and storage format that is usually chosen for Efficiency, efficient Data access, access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the Function (computer programming), functions or Operator (computer programming), operations that can be applied to the data, i.e., it is an algebraic structure about data. Usage Data structures serve as the basis for abstract data types (ADT). The ADT defines the logical form of the data type. The data structure implements the physical form of the data type. Different types of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks. For example, Relational database, relational databases commonly use B-tree indexes for data retrieval, while compiler Implementation, implementations usually use hash tables to look up Identifier (computer languages), identifiers. Data s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Satisfiability Problem
In logic and computer science, the Boolean satisfiability problem (sometimes called propositional satisfiability problem and abbreviated SATISFIABILITY, SAT or B-SAT) asks whether there exists an Interpretation (logic), interpretation that Satisfiability, satisfies a given Boolean logic, Boolean Formula (mathematical logic), formula. In other words, it asks whether the formula's variables can be consistently replaced by the values TRUE or FALSE to make the formula evaluate to TRUE. If this is the case, the formula is called ''satisfiable'', else ''unsatisfiable''. For example, the formula "''a'' AND NOT ''b''" is satisfiable because one can find the values ''a'' = TRUE and ''b'' = FALSE, which make (''a'' AND NOT ''b'') = TRUE. In contrast, "''a'' AND NOT ''a''" is unsatisfiable. SAT is the first problem that was proven to be NP-complete—this is the Cook–Levin theorem. This means that all problems in the complexity class NP (complexity), NP, which includes a wide range of natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proposition (mathematics)
In mathematics and formal logic, a theorem is a statement that has been proven, or can be proven. The ''proof'' of a theorem is a logical argument that uses the inference rules of a deductive system to establish that the theorem is a logical consequence of the axioms and previously proved theorems. In mainstream mathematics, the axioms and the inference rules are commonly left implicit, and, in this case, they are almost always those of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory with the axiom of choice (ZFC), or of a less powerful theory, such as Peano arithmetic. Generally, an assertion that is explicitly called a theorem is a proved result that is not an immediate consequence of other known theorems. Moreover, many authors qualify as ''theorems'' only the most important results, and use the terms ''lemma'', ''proposition'' and ''corollary'' for less important theorems. In mathematical logic, the concepts of theorems and proofs have been formalized in order to allow mathematical reas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Circuit
In computational complexity theory and circuit complexity, a Boolean circuit is a mathematical model for combinational digital logic circuits. A formal language can be decided by a family of Boolean circuits, one circuit for each possible input length. Boolean circuits are defined in terms of the logic gates they contain. For example, a circuit might contain binary AND and OR gates and unary NOT gates, or be entirely described by binary NAND gates. Each gate corresponds to some Boolean function that takes a fixed number of bits as input and outputs a single bit. Boolean circuits provide a model for many digital components used in computer engineering, including multiplexers, adders, and arithmetic logic units, but they exclude sequential logic. They are an abstraction that omits many aspects relevant to designing real digital logic circuits, such as metastability, fanout, glitches, power consumption, and propagation delay variability. Formal definition In givi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Data Structures
Graph may refer to: Mathematics *Graph (discrete mathematics), a structure made of vertices and edges **Graph theory, the study of such graphs and their properties * Graph (topology), a topological space resembling a graph in the sense of discrete mathematics *Graph of a function * Graph of a relation * Graph paper *Chart, a means of representing data (also called a graph) Computing *Graph (abstract data type), an abstract data type representing relations or connections * graph (Unix), Unix command-line utility * Conceptual graph, a model for knowledge representation and reasoning *Microsoft Graph, a Microsoft API developer platform that connects multiple services and devices Other uses * HMS ''Graph'', a submarine of the UK Royal Navy See also * Complex network *Graf *Graff (other) *Graph database *Grapheme, in linguistics *Graphemics *Graphic (other) *-graphy (suffix from the Greek for "describe," "write" or "draw") * List of information graphics software *S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directed Graphs
Direct may refer to: Mathematics * Directed set, in order theory * Direct limit of (pre), sheaves * Direct sum of modules, a construction in abstract algebra which combines several vector spaces Computing * Direct access (other), a method of accessing data in a database * Direct connect (other), various methods of telecommunications and computer networking * Direct memory access, access to memory by hardware subsystems independently of the CPU Entertainment * ''Direct'' (Tower of Power album) * ''Direct'' (Vangelis album) * ''Direct'' (EP), by The 77s Other uses * Direct (music symbol), a music symbol used in music notation that is similar to a catchword in literature * Nintendo Direct, an online presentation frequently held by Nintendo * Mars Direct, a proposal for a crewed mission to Mars * DIRECT, a proposed space shuttle-derived launch vehicle * DirectX, a proprietary dynamic media platform * Direct current, a direct flow of electricity * Dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |