|
Propionamide
Propanamide has the chemical formula CH3CH2C=O(NH2). It is the amide of propanoic acid. This organic compound is a mono-substituted amide. Organic compounds of the amide group can react in many different organic processes to form other useful compounds for synthesis. Preparation Propanamide can be prepared by the condensation reaction between urea and propanoic acid: : or by the dehydration of ammonium propionate: : Reactions Propanamide being an amide can participate in a Hofmann rearrangement to produce ethylamine Ethylamine, also known as ethanamine, is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula CH3CH2NH2. This colourless gas has a strong ammonia-like odor. It condenses just below room temperature to a liquid miscibility, miscible with virtual ... gas. References Propionamides {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the Polymer backbone, main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a Derivative (chemistry), derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amino group (); or, equivalently, an acyl group, acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amino group. Common amides are formamide (), acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Some uncommon examples of amides are ''N''-chloroacetamide () and chloroformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary (chemistry), primary, secondary (chemistry), secondary, and tertiary (chemistry), tertiary according to the number of acyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
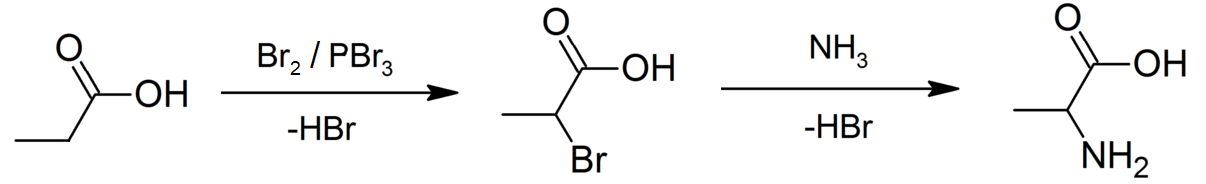
Propanoic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the cellular metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. ''Urea'' is Neo-Latin, , , itself from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂worsom''. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor base (chemistry), alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably metabolic waste#Nitrogen wastes, nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek language, Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the Carboxylate salt, salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Propionate
Ammonium propionate or ammonium propanoate is the ammonium salt of propionic acid. It has the chemical formula NH4(C2H5COO). Reaction It is formed by the reaction of propionic acid and ammonia. Uses It is used in several products, which include: fertilizers, water treatment chemicals, and plant protection products. It is also used in different areas, such as: manufacturing, forestry, agriculture, and fishing. It also serves as an antiseptic, antifungal agent, antimould agent, and preservative in feed industry or food industry. Ammonium propionate also prevents spoilage of cosmetics by preventing bacterial growth. See also * Calcium propionate * Potassium propionate * Sodium propionate Sodium propanoate or sodium propionate is the sodium salt (chemistry), salt of propionic acid which has the chemical formula Sodium, Na(Carbon, C2Hydrogen, H5Carbon, COxygen, OOxygen, O). This white crystalline solid is deliquescent in moist air. ... References {{Ammonium salts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hofmann Rearrangement
The Hofmann rearrangement (Hofmann degradation) is the organic reaction of a primary amide to a primary amine with one less carbon atom. The reaction involves oxidation of the nitrogen followed by rearrangement of the carbonyl and nitrogen to give an isocyanate intermediate. The reaction can form a wide range of products, including alkyl and aryl amines. The reaction is named after its discoverer, August Wilhelm von Hofmann, and should not be confused with the Hofmann elimination, another name reaction for which he is eponymous. Mechanism The reaction of bromine with sodium hydroxide forms sodium hypobromite ''in situ'', which transforms the primary amide into an intermediate isocyanate. The formation of an intermediate nitrene is not possible because it implies also the formation of a hydroxamic acid as a byproduct, which has never been observed. The intermediate isocyanate is hydrolyzed to a primary amine, giving off carbon dioxide. #Base abstracts an acidic N-H proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylamine
Ethylamine, also known as ethanamine, is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula CH3CH2NH2. This colourless gas has a strong ammonia-like odor. It condenses just below room temperature to a liquid miscibility, miscible with virtually all solvents. It is a nucleophilic base (chemistry), base, as is typical for amines. Ethylamine is widely used in chemical industry and organic synthesis. It is a DEA list I chemical by 21 CFR § 1310.02. Synthesis Ethylamine is produced on a large scale by two processes. Most commonly ethanol and ammonia are combined in the presence of an oxide catalyst: :CH3CH2OH + NH3 → CH3CH2NH2 + H2O In this reaction, ethylamine is coproduced together with diethylamine and triethylamine. In aggregate, approximately 80M kilograms/year of these three amines are produced industrially.Karsten Eller, Erhard Henkes, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke, "Amines, Aliphatic" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |